Dabigatran Etexilate
What is Dabigatran (Dabigatran Etexilate)?
Approved To Treat
Related Clinical Trials
Summary: After hip or knee replacement all patients receive a standardized treatment with blood thinners, this medication is called thrombosis prophylaxis. However, despite this standard treatment some individuals still develop venous thrombosis (VTE), while others experience bleeding. This indicates that not all patients have the same VTE risk following surgery. Individualizing the amount of thrombosis pr...
Summary: Atrial fibrillation (AF) is the most common sustained cardiac arrythmia encountered in clinical practice and patients suffer from this are at increased risk of ischemic stroke and systemic thromboembolism due to the formation and embolism of left atrial thrombi. Current international guidelines recommend non-vitamin K oral anticoagulants (NOACs) for stroke prevention amongst these patients with no...
Summary: This prospective, single-arm observational cohort study aims to evaluate the real-world effectiveness and safety of direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs), specifically dabigatran or rivaroxaban, in patients with cerebral venous thrombosis (CVT). The study will be conducted at Bach Mai Hospital, a national tertiary stroke referral center in Hanoi, Vietnam. A minimum of 69 adults with radiologically co...
Related Latest Advances
Brand Information
The rates of adverse reactions leading to treatment discontinuation were 21% for dabigatran etexilate capsules 150 mg and 16% for warfarin. The most frequent adverse reactions leading to discontinuation of dabigatran etexilate capsules were bleeding and gastrointestinal events (i.e., dyspepsia, nausea, upper abdominal pain, gastrointestinal hemorrhage, and diarrhea).
Bleeding [see
Table 3 shows the number of adjudicated major bleeding events during the treatment period in the RE-LY study, with the bleeding rate per 100 subject-years (%). Major bleeding is defined as bleeding accompanied by one or more of the following: a decrease in hemoglobin of ≥2 g/dL, a transfusion of ≥2 units of packed red blood cells, bleeding at a critical site or with a fatal outcome. Intracranial hemorrhage included intracerebral (hemorrhagic stroke), subarachnoid, and subdural bleeds.
Table 3 Adjudicated Major Bleeding Events in Treated Patientsa
bAnnual event rate per 100 pt-years = 100 * number of subjects with event/subject-years. Subject-years is defined as cumulative number of days from first drug intake to event date, date of last drug intake + 2, death date (whatever occurred first) across all treated subjects divided by 365.25. In case of recurrent events of the same category, the first event was considered.
c Defined as bleeding accompanied by one or more of the following: a decrease in hemoglobin of ≥ 2 g/dL, a transfusion of 2 or more units of packed red blood cells, bleeding at a critical site or with fatal outcome.
d Intracranial bleed included intracerebral (hemorrhagic stroke), subarachnoid, and subdural bleeds.
e On-treatment analysis based on the safety population, compared to ITT analysis presented in Section 14 Clinical Studies.
f Fatal bleed: Adjudicated major bleed as defined above with investigator reported fatal outcome and adjudicated death with primary cause from bleeding.
g Non-intracranial fatal bleed: Adjudicated major bleed as defined above and adjudicated death with primary cause from bleeding but without symptomatic intracranial bleed based on investigator’s clinical assessment.
There was a higher rate of any gastrointestinal bleeds in patients receiving dabigatran etexilate capsules 150 mg than in patients receiving warfarin (6.6% vs 4.2%, respectively).
The risk of major bleeds was similar with dabigatran etexilate capsules 150 mg and warfarin across major subgroups defined by baseline characteristics (see Figure 1), with the exception of age, where there was a trend toward a higher incidence of major bleeding on dabigatran etexilate capsules (hazard ratio 1.2, 95% CI: 1.0 to 1.5) for patients ≥75 years of age.
Figure 1 Adjudicated Major Bleeding by Baseline Characteristics Including Hemorrhagic Stroke Treated Patients
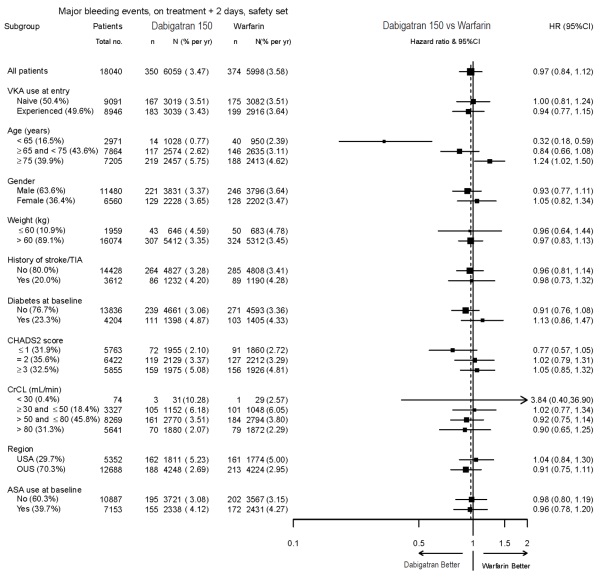
Bleeding events for the RE-NOVATE and RE-NOVATE II studies were classified as major bleeding events if at least one of the following criteria applied: fatal bleeding, symptomatic bleeding in a critical area or organ (intraocular, intracranial, intraspinal or retroperitoneal bleeding), bleeding causing a fall in hemoglobin level of 2.0 g/dL (1.24 mmol/L) or more, or leading to transfusion of 2 or more units of whole blood or red cells, requiring treatment cessation or leading to re-operation.
The RE-NOVATE study compared dabigatran etexilate capsules 75 mg taken orally 1-4 hours after surgery followed by 150 mg once daily, dabigatran etexilate capsules 110 mg taken orally 1-4 hours after surgery followed by 220 mg once daily and subcutaneous enoxaparin 40 mg once daily initiated the evening before surgery for the prophylaxis of deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism in patients who had undergone hip replacement surgery. The RE-NOVATE II study compared dabigatran etexilate capsules 110 mg taken orally 1-4 hours after surgery followed by 220 mg once daily and subcutaneous enoxaparin 40 mg once daily initiated the evening before surgery for the prophylaxis of deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism in patients who had undergone hip replacement surgery. In the RE-NOVATE and RE-NOVATE II studies, patients received 28-35 days of dabigatran etexilate capsules or enoxaparin with median exposure of 33 days. Tables 7 and 8 show the number of patients experiencing bleeding events in the analysis of RE-NOVATE and RE-NOVATE II.
Table 7 Bleeding Events in RE-NOVATE Treated Patients
Pediatric use information is approved for Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc.’s Pradaxa (dabigatran etexilate) capsules. However, due to Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc.’s marketing exclusivity rights, this drug product is not labeled with that information.
Gastrointestinal Disorders: Esophageal ulcer
Immune System Disorders: Angioedema
Renal and Urinary Disorders: Anticoagulant-related nephropathy
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders: Alopecia
Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Once opened, the product must be used within 4 months. Keep the bottle tightly closed. Store in the original package to protect from moisture.
- Tell patients to take dabigatran etexilate capsules exactly as prescribed.
- Remind patients not to discontinue dabigatran etexilate capsules without talking to the healthcare provider who prescribed it.
- Keep dabigatran etexilate capsules in the original bottle to protect from moisture. Do not put dabigatran etexilate capsules in pill boxes or pill organizers.
- When more than one bottle is dispensed to the patient, instruct them to open only one bottle at a time.
- Instruct patient to remove only one capsule from the opened bottle at the time of use. The bottle should be immediately and tightly closed.
- Advise patients not to chew or break the capsules before swallowing them and not to open the capsules and take the pellets alone.
- Advise patients that the capsule should be taken with a full glass of water.
Bleeding
Inform patients that they may bleed more easily, may bleed longer, and should call their healthcare provider for any signs or symptoms of bleeding
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Instruct patients to seek emergency care right away if they have any of the following, which may be a sign or symptom of serious bleeding:
• Unusual bruising (bruises that appear without known cause or that get bigger)
• Pink or brown urine
• Red or black, tarry stools
• Coughing up blood
• Vomiting blood, or vomit that looks like coffee grounds
Instruct patients to call their healthcare provider or to get prompt medical attention if they experience any signs or symptoms of bleeding:
• Pain, swelling or discomfort in a joint
• Headaches, dizziness, or weakness
• Reoccurring nose bleeds
• Unusual bleeding from gums
• Bleeding from a cut that takes a long time to stop
• Menstrual bleeding or vaginal bleeding that is heavier than normal
If patients have had neuraxial anesthesia or spinal puncture, and particularly, if they are taking concomitant NSAIDs or platelet inhibitors, advise patients to watch for signs and symptoms of spinal or epidural hematoma, such as back pain, tingling, numbness (especially in the lower limbs), muscle weakness, and stool or urine incontinence. If any of these symptoms occur, advise the patient to contact his or her physician immediately [see
Gastrointestinal Adverse Reactions
Instruct patients to call their healthcare provider if they experience any signs or symptoms of dyspepsia or gastritis:
- Dyspepsia (upset stomach), burning, or nausea
- Abdominal pain or discomfort
- Epigastric discomfort, GERD (gastric indigestion)
Invasive or Surgical Procedures
Instruct patients to inform their healthcare provider that they are taking dabigatran before any invasive procedure (including dental procedures) is scheduled [see
Concomitant Medications
Ask patients to list all prescription medications, over-the-counter medications, or dietary supplements they are taking or plan to take so their healthcare provider knows about other treatments that may affect bleeding risk (e.g., aspirin or NSAIDs) or dabigatran exposure (e.g., dronedarone or systemic ketoconazole) [
Prosthetic Heart Valves
Instruct patients to inform their healthcare provider if they will have or have had surgery to place a prosthetic heart valve [
Advise adult patients and caregivers that some adults taking dabigatran have developed symptoms of an allergic reaction. Advise adult patients or caregivers to inform their healthcare provider if they develop symptoms of an allergic reaction, such as hives, rash, or itching. Advise adult patients or caregivers to seek emergency medical attention if they develop chest pain or tightness, swelling of the face or tongue, trouble breathing or wheezing, or feeling dizzy or faint.
Pregnancy
Advise patients to inform their healthcare provider immediately if they become pregnant or intend to become pregnant during treatment with dabigatran [
Lactation
Advise patients not to breastfeed if they are taking dabigatran etexilate capsules [
Pediatric use information is approved for Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc.’s Pradaxa (dabigatran etexilate) capsules. However, due to Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc.’s marketing exclusivity rights, this drug product is not labeled with that information.






