Iqirvo
What is Iqirvo (Elafibranor)?
For people living with progressive liver diseases, fatigue, itching, and digestive discomfort can become part of everyday life. These symptoms often stem from underlying bile flow problems that quietly damage the liver over time. Iqirvo (elafibranor) represents a significant advancement for those affected by primary biliary cholangitis (PBC), a chronic autoimmune liver disease that can lead to scarring, cirrhosis, and ultimately liver failure if untreated.
Iqirvo is an oral medication belonging to a class of drugs called peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) agonists. Approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2024, it offers a new treatment option for adults with PBC who have not achieved adequate improvement with ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA), the standard first-line therapy. By targeting key pathways involved in bile production and inflammation, Iqirvo helps protect the liver and improve overall liver function. This medication provides hope for patients seeking better long-term management of their condition and improved quality of life.
What does Iqirvo do?
Iqirvo is prescribed to treat primary biliary cholangitis, a condition in which the body’s immune system attacks the small bile ducts in the liver. These ducts normally carry bile, a fluid that helps digest fats and remove toxins from the liver to the intestines. When they become damaged, bile builds up inside the liver, leading to inflammation, scarring, and eventually liver dysfunction.
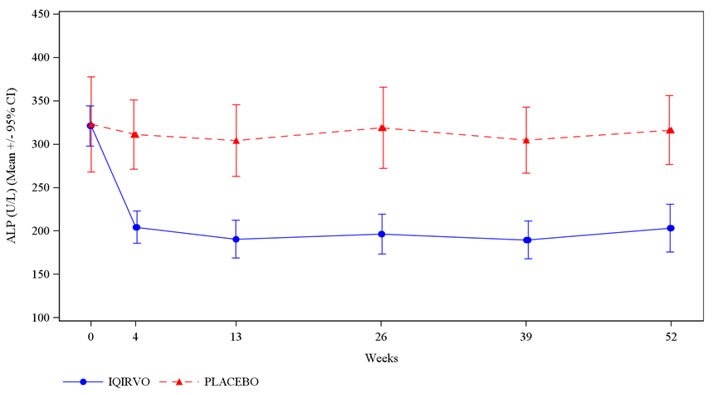
The main goal of Iqirvo is to reduce bile acid buildup and liver inflammation, thereby slowing the disease’s progression. Patients taking Iqirvo often experience improvements in liver enzyme levels particularly alkaline phosphatase (ALP), a key marker of liver damage.
Clinical studies have shown that patients who took elafibranor experienced significant reductions in ALP and other liver function markers compared with those who received a placebo, especially when added to UDCA therapy (FDA, 2024). Many patients also reported improvements in fatigue and itching, two of the most common and distressing symptoms of PBC.
Iqirvo is not a cure, but it provides meaningful control of the disease and helps preserve liver function, potentially delaying the need for a liver transplant.
How does Iqirvo work?
Iqirvo (elafibranor) works by activating two key proteins in the body, PPAR-alpha and PPAR-delta which play a major role in regulating metabolism, inflammation, and bile acid processing in the liver.
In PBC, these pathways become disrupted, leading to inflammation, accumulation of toxic bile acids, and gradual damage to liver cells. By activating PPAR-alpha and PPAR-delta, Iqirvo helps the liver:
- Increase bile acid transport and excretion, reducing harmful buildup.
- Lower liver inflammation, preventing ongoing tissue damage.
- Improve fat metabolism, which can further protect liver cells from injury.
Clinically, this mechanism matters because it tackles both inflammation and bile acid imbalance, two of the root causes of liver damage in PBC. Over time, maintaining this balance helps protect liver structure and function, supporting long-term health outcomes.
Iqirvo side effects
Like most prescription medications, Iqirvo can cause side effects. However, most patients tolerate it well when taken under medical supervision.
Common side effects may include:
- Mild stomach discomfort or diarrhea
- Headache or fatigue
- Itching (pruritus)
- Joint or muscle pain
- Weight gain or mild swelling in the legs
Serious side effects (less common):
- Elevated liver enzymes or signs of worsening liver function
- Gallstones or gallbladder-related pain
- Allergic reactions (rash, swelling, difficulty breathing)
Contact doctor immediately for jaundice, severe abdominal pain, dark urine, or persistent fatigue, as these may signal liver or gallbladder issues.
Iqirvo is not recommended for advanced liver disease, severe cirrhosis, or active gallbladder problems without specialist direction.
Pregnant or breastfeeding women should consult their doctor. Regular blood tests are necessary to monitor liver function and bile acid levels due to Iqirvo’s effect on liver metabolism.
Iqirvo dosage
Iqirvo, an oral tablet, is typically taken once daily, with or without food, at the same time each day. It’s usually combined with ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) for primary biliary cholangitis (PBC) but can be used alone if UDCA is not tolerated. Dosing is individualized based on liver function and treatment response.
Routine monitoring of liver enzyme, bilirubin, bile acid, kidney function, and lipid levels is essential. Older adults and those with mild to moderate liver impairment generally tolerate the medication well but may need more frequent follow-ups. Patients should not stop the medication suddenly without a doctor’s consultation, as this could impact disease control.
Does Iqirvo have a generic version?
As of 2025, Iqirvo (elafibranor) does not have an FDA-approved generic version. It is a brand-name medication developed by Ipsen Biopharmaceuticals and represents a new therapeutic option for primary biliary cholangitis. However, international versions may exist in other markets.
Generics are years away, but will match brand-name products in active ingredient, dosage, safety, and effectiveness. For cost concerns, ask your doctor or pharmacist about manufacturer assistance or copay support.
Conclusion
Iqirvo (elafibranor) marks a major milestone in the treatment of primary biliary cholangitis, offering a much-needed option for patients who do not respond adequately to traditional therapies. By targeting key metabolic and anti-inflammatory pathways, it helps reduce bile acid buildup, lower liver enzyme levels, and protect liver health over the long term.
While not a cure, Iqirvo significantly improves daily comfort, reduces fatigue and itching, and maintains liver function, enhancing patients’ quality of life. Consistent medication, monitoring, and communication with healthcare providers are crucial. Properly prescribed and monitored, Iqirvo offers renewed hope, enabling patients to manage PBC with greater confidence and live more fully.
References
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). (2024). FDA approves Iqirvo (elafibranor) for primary biliary cholangitis. Retrieved from https://www.fda.gov
- Mayo Clinic. (2024). Elafibranor oral route: Drug information and precautions. Retrieved from https://www.mayoclinic.org
- National Institutes of Health (NIH). (2024). Primary biliary cholangitis: Treatment and management updates. Retrieved from https://www.nih.gov
- MedlinePlus. (2024). Elafibranor: Uses, side effects, and safety. National Library of Medicine. Retrieved from https://medlineplus.gov
Approved To Treat
Top Global Experts
Related Clinical Trials
Summary: The purpose of this study is to find out about the safety and how well the study intervention (elafibranor) works in participants with PBC. The participants in this study will have confirmed PBC with inadequate response or intolerance to UDCA, which is a medication used in the management and treatment of cholestatic liver disease. PBC is a slowly progressive disease characterised by damage of the ...
Summary: This study will collect information from participants with Primary Biliary Cholangitis (PBC) as they use the drug elafibranor in real world setting. PBC is a progressive rare liver disease in which tubes in the liver called bile ducts are damaged. The liver damage in PBC may lead to scarring (cirrhosis). PBC may also be associated with multiple symptoms including pruritus (itching) and fatigue. Ma...
Summary: The participants of this study will have confirmed Primary Biliary Cholangitis (PBC) and cirrhosis (scarring of the liver). PBC is a slowly progressive disease, characterised by damage to the bile ducts in the liver, leading to a build-up of bile acids which causes further damage. The liver damage in PBC may lead to cirrhosis. PBC may also be associated with multiple symptoms. Many patients with P...
Related Latest Advances
Brand Information
- Myalgia, Myopathy, and Rhabdomyolysis
- Fractures
- Drug-Induced Liver Injury
- Hypersensitivity Reactions