Unituxin
What is Unituxin (Dinutuximab)?
Related Clinical Trials
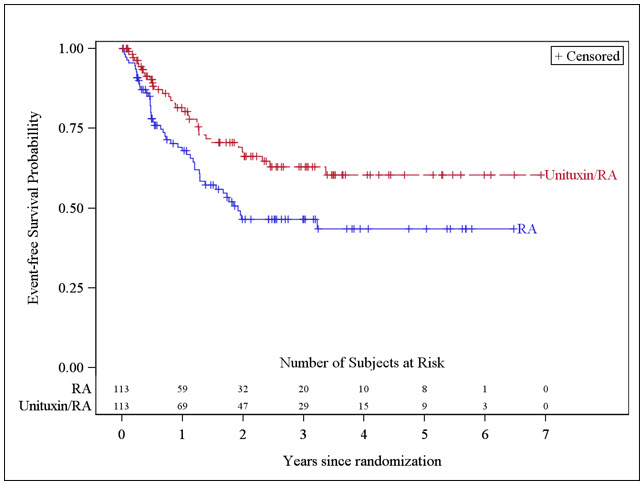
Summary: This phase III trial tests how well the addition of dinutuximab to Induction chemotherapy along with standard of care surgical resection of the primary tumor, radiation, stem cell transplantation, and immunotherapy works for treating children with newly diagnosed high-risk neuroblastoma. Dinutuximab is a monoclonal antibody that binds to a molecule called GD2, which is found on the surface of neur...
Summary: Cohort A(GAIA-102 alone): Confirm the safety of GAIA-102 alone for refractory/relapse neuroblastoma or pediatric solid tumors with lung metastases, and decide recommended dose for Phase II. Cohort B(GAIA-102 with Dinutuximab): Confirm the safety of GAIA-102 with Dinutuximab, Filgrastim, Teceleukin combination for refractory/relapse neuroblastoma and decide recommended dose for Phase II. Cohort C(G...
Summary: This is a phase II study looking at patient response to treatment with the combination dinutuximab, temozolomide, irinotecan, and GM-CSF.
Related Latest Advances
Brand Information
- Verify that patients have adequate hematologic, respiratory, hepatic, and renal function prior to initiating each course of Unituxin
- Administer required premedication and hydration prior to initiation of each Unituxin infusion
- The recommended dose of Unituxin is 17.5 mg/m
- Initiate at an infusion rate of 0.875 mg/m
- Serious Infusion Reactions
- Neurotoxicity, including Pain, Peripheral Neuropathy, Neurological Disorders of the Eye, Prolonged Urinary Retention, Transverse Myelitis, and Reversible Posterior Leukoencephalopathy Syndrome
- Capillary Leak Syndrome
- Hypotension
- Infection
- Bone Marrow Suppression
- Electrolyte Abnormalities
- Atypical Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome
- Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
- Neurotoxicity: prolonged urinary retention, transverse myelitis, and reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome (RPLS)
- Serious Infusion Reactions
Inform patients and caregivers of the risk of serious infusion reactions and anaphylaxis and to immediately report any signs or symptoms, such as facial or lip swelling, urticaria, difficulty breathing, lightheadedness, or dizziness that occur during or within 24 hours following the infusion [see . - Pain, Peripheral Neuropathy, Prolonged Urinary Retention, and Transverse Myelitis
Inform patients and caregivers of the risk of severe pain, sensory and motor neuropathy, prolonged urinary retention, and transverse myelitis, and to promptly report severe or worsening pain and signs and symptoms, such as numbness, tingling, burning, weakness, or inability to urinate [see . - Neurological Disorders of the Eye
Inform patients and caregivers of the risk of neurological disorders of the eye and to promptly report signs or symptoms, such as blurred vision, photophobia, ptosis, diplopia, or unequal pupil size [see . - Reversible Posterior Leukoencephalopathy Syndrome (RPLS)
Inform patients and caregivers of the risk of RPLS and to immediately report signs or symptoms, such as severe headache, hypertension, visual changes, lethargy, or seizures [see . - Capillary Leak Syndrome
Inform patients and caregivers of the risk of capillary leak syndrome and to immediately report any signs or symptoms [see . - Hypotension
Inform patients and caregivers of the risk of hypotension during the infusion and to immediately report any signs or symptoms [see . - Infection
Inform patients and caregivers of the risk of infection following treatment and to immediately report any signs or symptoms [see . - Bone Marrow Suppression
Inform patients and caregivers of the risk of bone marrow suppression, and to promptly report signs or symptoms of anemia, thrombocytopenia, or infection [see . - Electrolyte Abnormalities
Inform patients and caregivers of the risk of electrolyte abnormalities, including hypokalemia, hyponatremia, and hypocalcemia, and to report any signs or symptoms, such as seizures, heart palpitations, and muscle cramping [see . - Atypical Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome
Inform patients and caregivers of the risk of hemolytic uremic syndrome and to report any signs or symptoms, such as fatigue, dizziness, fainting, pallor, edema, decreased urine output, or hematuria [see . - Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Advise women of reproductive potential of the potential risk to the fetus if administered during pregnancy and the need for use of effective contraception during and for at least 2 months after completing therapy [see .


