Generic Name
Norethindrone Acetate
Brand Names
Sharobel, Galbriela, Junel, Blisovi, Necon, Wera, Norethindrone, Nortrel, Dasetta, Microgestin, Nexesta, Mimvey, Deblitane, Cyonanz, Nylia, Zenchent, Hailey, Orquidea, Mibelas 24, Wymzya, Nortrel 21, Camila, Tri-Legest, Hailey 24, Rhuzdah, ERRIN, Affodel, Xelria, Abigale, Alyacen, Philith, Microgestin 24, Nortrel 28, Loestrin, Taytulla, Junel 21, Aurovela 24, Merzee, Kaitlib, Melodetta 24, Lopreeza, Gallifrey, Blisovi 24, Femlyv, Layolis, XARAH, Feirza, Meleya, Jinteli, Lyleq, Loestrin 21, Briellyn, Activella, Aurovela, 24FE, OSHIH, Finzala, Luizza, Emzahh, Incassia, Tarina, Balziva, Tarina 24, Aranelle, Vyfemla, Etyqa, Jencycla, Myfembree, Fyavolv
FDA approval date: May 25, 2001
Classification: Progestin
Form: Tablet, Kit
What is Sharobel (Norethindrone Acetate)?
Aurovela.
Approved To Treat
Top Global Experts
There are no experts for this drug
Save this treatment for later
Not sure about your diagnosis?
Tired of the same old research?
Related Clinical Trials
There is no clinical trials being done for this treatment
Related Latest Advances
There is no latest advances for this treatment
Brand Information
SHAROBEL (Norethindrone)
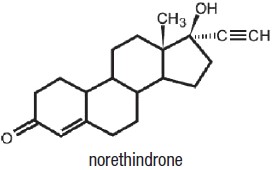
1DESCRIPTION
SHAROBEL
Each tablet contains 0.35 mg norethindrone. Inactive ingredients include FD&C Blue No. 1 Aluminum Lake, FD&C Yellow No. 6 Aluminum Lake, titanium dioxide, polyvinyl alcohol, talc, macrogol/polyethylene glycol 3350 NF, lecithin (soya), hypromellose, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, and pregelatinized starch.
Meets USP Dissolution Test 3.
2INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1. Indications
Progestin-only oral contraceptives are indicated for the prevention of pregnancy.
2. Efficacy
If used perfectly, the first-year failure rate for progestin-only oral contraceptives is 0.3%. However, the typical failure rate is estimated to be closer to 9%, due to late or omitted pills. Table 1 lists the pregnancy rates for users of all major methods of contraception.
Table 1: Percentage of Women Experiencing an Unintended Pregnancy During the First Year of Typical Use and the First Year of Perfect Use of Contraception and the Percentage Continuing Use at the End of the First Year. United States.
Emergency Contraception: Emergency contraceptive pills or insertion of a copper intrauterine contraceptive after unprotected intercourse substantially reduces the risk of pregnancy.
Lactational Amenorrhea Method: LAM is a highly effective, temporary method of contraception.
Source: Trussell J. Contraceptive Effi cacy. In Hatcher RA, Trussell J, Nelson AL, Cates W, Kowal D, Policar M. Contraceptive Techology: Twentieth Revised Edition. New York NY: Ardent Media, 2011.
1 Among typical couples who initiate use of a method (not necessarily for the first time), the percentage who experience an accidental pregnancy during the first year if they do not stop use for any other reason. Estimates of the probability of pregnancy during the first year of typical use for spermicides, withdrawal, fertility awareness-based methods, the diaphragm, the male condom, the oral contraceptive pill, and Depo-Provera are taken from the 1995 National Survey of Family Growth corrected for underreporting of abortion; see the text for the derivation of estimates for the other methods.
SHAROBEL ™ Tablets have not been studied for and are not indicated for use in emergency contraception.
3CONTRAINDICATIONS
Progestin-only oral contraceptives (POPs) should not be used by women who currently have the following conditions:
- Known or suspected pregnancy
- Known or suspected carcinoma of the breast
- Undiagnosed abnormal genital bleeding
- Hypersensitivity to any component of this product
- Benign or malignant liver tumors
- Acute liver disease
4WARNINGS
Cigarette smoking increases the risk of serious cardiovascular disease. Women who use oral contraceptives should be strongly advised not to smoke.
SHAROBEL
4.1Ectopic Pregnancy
The incidence of ectopic pregnancies for progestin-only oral contraceptive users is 5 per 1000 woman-years. Up to 10% of pregnancies reported in clinical studies of progestin-only oral contraceptive users are extrauterine. Although symptoms of ectopic pregnancy should be watched for, a history of ectopic pregnancy need not be considered a contraindication to use of this contraceptive method. Healthcare professionals should be alert to the possibility of an ectopic pregnancy in women who become pregnant or complain of lower abdominal pain while on progestin-only oral contraceptives.
4.2Delayed Follicular Atresia/Ovarian Cysts
If follicular development occurs, atresia of the follicle is sometimes delayed and the follicle may continue to grow beyond the size it would attain in a normal cycle. Generally these enlarged follicles disappear spontaneously. Often they are asymptomatic; in some cases they are associated with mild abdominal pain. Rarely they may twist or rupture, requiring surgical intervention.
4.3Irregular Genital Bleeding
Irregular menstrual patterns are common among women using progestin-only oral contraceptives. If genital bleeding is suggestive of infection, malignancy or other abnormal conditions, such nonpharmacologic causes should be ruled out. If prolonged amenorrhea occurs, the possibility of pregnancy should be evaluated.
4.4Carcinoma of the Breast and Reproductive Organs
Some epidemiological studies of oral contraceptive users have reported an increased relative risk of developing breast cancer, particularly at a younger age and apparently related to duration of use. These studies have predominantly involved combined oral contraceptives and there is insufficient data to determine whether the use of POPs similarly increases the risk.
A meta-analysis of 54 studies found a small increase in the frequency of having breast cancer diagnosed for women who were currently using combined oral contraceptives or had used them within the past ten years.
This increase in the frequency of breast cancer diagnosis, within ten years of stopping use, was generally accounted for by cancers localized to the breast. There was no increase in the frequency of having breast cancer diagnosed ten or more years after cessation of use.
Women with breast cancer should not use oral contraceptives because the role of female hormones in breast cancer has not been fully determined.
Some studies suggest that oral contraceptive use has been associated with an increase in the risk of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia in some populations of women. However, there continues to be controversy about the extent to which such findings may be due to differences in sexual behavior and other factors. There is insufficient data to determine whether the use of POPs increases the risk of developing cervical intraepithelial neoplasia.
4.5Hepatic Neoplasia
Benign hepatic adenomas are associated with combined oral contraceptive use, although the incidence of benign tumors is rare in the United States. Rupture of benign, hepatic adenomas may cause death through intra-abdominal hemorrhage.
Studies have shown an increased risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma in combined oral contraceptive users. However, these cancers are rare in the U.S. There is insufficient data to determine whether POPs increase the risk of developing hepatic neoplasia.
5ADVERSE REACTIONS
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Northstar Rx LLC at 1-800-206-7821 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or
Adverse reactions reported with the use of POPs include:
- Menstrual irregularity is the most frequently reported side effect.
- Frequent and irregular bleeding are common, while long duration of bleeding episodes and amenorrhea are less likely.
- Headache, breast tenderness, nausea, and dizziness are increased among progestin-only oral contraceptive users in some studies.
- Androgenic side effects such as acne, hirsutism, and weight gain occur rarely.
The following adverse reactions were also reported in clinical trials or during post-marketing experience:
6OVERDOSAGE
There have been no reports of serious ill effects from overdosage, including ingestion by children.
7DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
To achieve maximum contraceptive effectiveness, SHAROBEL™ must be taken exactly as directed. One tablet is taken every day, at the same time. Administration is continuous, with no interruption between pill packs. See Detailed Patient Labeling for detailed instruction.
8HOW SUPPLIED
SHAROBEL™ (0.35 mg Norethindrone Tablets, USP) is available in a compact card (NDC 16714-441-01) containing 28 green, biconvex, round tablets imprinted "V2" on one side.
SHAROBEL™ is available in the following configurations:
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F). [See USP Controlled Room Temperature.]
Keep out of the reach of children.
REFERENCE
1. McCann M, and Potter L. Progestin-Only Oral Contraceptives: A Comprehensive Review. Contraception, 50:60 (Suppl. 1), December 1994.
2. Van Giersbergen PLM, Halabi A, Dingemanse J. Pharmacokinetic interaction between bosentan and the oral contraceptives norethisterone and ethinyl estradiol. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther 2006;44(3):113-118.
3. Truitt ST, Fraser A, Gallo ME, Lopez LM, Grimes DA and Schulz KF. Combined hormonal versus nonhormonal versus progestin-only contraception in lactation (Review). The Cochrane Collaboration. 2007, Issue 3.
4. Halderman, LD and Nelson AL. Impact of early postpartum administration of progestin-only hormonal contraceptives compared with nonhormonal contraceptives on short-term breast-feeding patterns. Am J Obstet Gynecol.; 186 (6): 1250-1258.
5. Ostrea EM, Mantaring III JB, Silvestre MA. Drugs that affect the fetus and newborn infant via the placenta or breast milk. Pediatr Clin N Am; 51(2004): 539-579.
6. Cooke ID, Back DJ, Shroff NE: Norethisterone concentration in breast milk and infant and maternal plasma during ethynodiol diactetate administration. Contraception 1985; 31:611-21.
7. 2008 USPC Official:12/1/08-4/30/09, USP Monographs: Norethindrone Tablets (page 1 of 5).
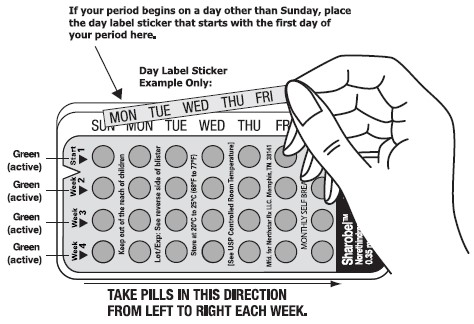
9INSTRUCTIONS FOR USING YOUR BLISTER PACK FOR THE 28 TABLETS
Please Read Me!
Save these Instructions.
- It’s best to take your fi rst POP on the fi rst day of your menstrual period (Day 1 Start). If you use a Day 1 Start, you are protected from becoming pregnant as soon as you take your first pill.
- If you decide to take your first POP on another day, use a backup method (such as a condom and/or a spermicide) every time you have sex during the next 48 hours.
SET THE DAY:
Day 1 Start:
- Pick the day label sticker that starts with the fi rst day of your period.
- Place this day label sticker over the area on the plastic compact which already has the days of the week (starting with Sunday) imprinted and press firmly.
Note: if the fi rst day of your period is a Sunday, you can skip step #1 and #2.
If you decide to take your first POP on another day, use a backup method (such as a condom and/or a spermicide) every time you have sex during the next 48 hours.
- To remove a tablet, i) ensure the blister is properly placed into the compact with the entire blister locked on the right V notch and placed under the six plastic lips of the compact, ii) press down the tablet with even pressure with your thumb or fi nger. The tablet will be pushed through the back of the compact tablet dispenser. Do not press with your thumbnail, fi ngernail, or any other sharp object.
- Swallow the pill. You will take one pill each day. POPs must be taken at the same time every day, so choose a time and then take the pill at that same time every day. Every time you take a pill late, and especially if you miss a pill, you are more likely to get pregnant.
- Wait 24 hours to take your next pill. POPs must be taken at the same time every day, so choose a time and then take the pill at that same time every day. Every time you take a pill late, and especially if you miss a pill, you are more likely to get pregnant. Continue to take one pill each day whether bleeding or not until all the pills have been taken.
- Take your pill at the same time every day. It is important to take the correct pill eachday and not miss any pills. To help you remember, take your pill at the same time as another daily activity, like turning off your alarm clock or brushing your teeth.
- You will start a new blister pack on the day after your blister pack is empty.
- THE FIRST PILL IN EVERY BLISTER PACK WILL ALWAYS BE TAKEN ON THE SAME DAY OF THE WEEK, NO MATTER WHEN YOUR NEXT PERIOD STARTS.
If you are late or you miss taking your POPs:
- If you are more than 3 hours late or you miss one or more POPs:
1)
2)
3)
- If you are not sure what to do about the pills you have missed, keep taking POPs and use a backup method until you can talk to your healthcare professional.
Important points to remember:
- POPs must be taken at the same time every day, so choose a time and then take the pill at that same time every day. Every time you take a pill late, and especially if you miss a pill, you are more likely to get pregnant.
- Start the next pack the day after the last pack is finished. There is no break between packs. Always have your next pack of pills ready.
- You may have some menstrual spott ing between periods. Do not stop taking your pills if this happens.
- If you vomit soon after taking a pill, use a backup method (such as a condom and/or a spermicide) for 48 hours.
- If you want to stop taking POPs, you can do so at any time, but, if you remain sexually active and don’t wish to become pregnant, be certain to use another birth control method.
- If you are not sure about how to take POPs, ask your healthcare professional.

Manufactured for: Northstar Rx LLC
I 0066 Rev.06/2023 Rev.B
10PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
SHAROBEL™ (Norethindrone Tablets USP, 0.35 mg)
Rx only