Brand Name
Zemplar
Generic Name
Paricalcitol
View Brand Information FDA approval date: April 17, 1998
Classification: Vitamin D Analog
Form: Injection, Capsule
What is Zemplar (Paricalcitol)?
Paricalcitol Injection is indicated for the prevention and treatment of secondary hyperparathyroidism in patients 5 years of age and older with chronic kidney disease on dialysis. Paricalcitol Injection is a vitamin D analog indicated for the prevention and treatment of secondary hyperparathyroidism in patients 5 years of age and older with chronic kidney disease on dialysis.
Approved To Treat
Save this treatment for later
Not sure about your diagnosis?
Tired of the same old research?
Related Clinical Trials
A PiLot ClinicaL TrIal of ParicAlcitol for ChroNiC PancrEatitis
Summary: The purpose of this pilot study to examine the feasibility and acceptability of paricalcitol in adults with Chronic Pancreatitis (CP).
Window of Opportunity for Neoadjuvant Stroma Modification in Pancreatic Cancer
Summary: This proposal will investigate the effect of paricalcitol, hydroxychloroquine, and losartan (PHL) combination of 3 stroma-modifying drugs on pancreatic adenocarcinoma and its stroma.
European Alport Therapy Registry - European Initiative Towards Delaying Renal Failure in Alport Syndrome: Current and Novel Therapies
Summary: The hereditary type IV collagen disease Alport syndrome leads to kidney failure early in life. Currently there are no specific medications approved for treatment, however, several therapies have been evaluated preclinically and could improve outcome. For that reason, this non-interventional, observational study investigates, if medications (1) delay disease progression; (2) delay time to kidney fa...
Related Latest Advances
Brand Information
Zemplar (Paricalcitol)
1DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
ZEMPLAR capsules are available as 1 mcg and 2 mcg soft gelatin capsules.
- 1 mcg: oval, gray capsule imprinted with “ZA”
- 1 mcg: oval, gray capsule imprinted with the “a” logo and “ZA”
- 2 mcg: oval, orange-brown capsule imprinted with “ZF”
- 2 mcg: oval, orange-brown capsule imprinted with the “a” logo and “ZF”
2CONTRAINDICATIONS
ZEMPLAR capsules should not be given to patients with evidence of
- hypercalcemia or
- vitamin D toxicity
3WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Excessive administration of vitamin D compounds, including ZEMPLAR capsules, can cause over suppression of PTH, hypercalcemia, hypercalciuria, hyperphosphatemia, and adynamic bone disease.
3.1Hypercalcemia
Progressive hypercalcemia due to overdosage of vitamin D and its metabolites may be so severe as to require emergency attention
Prescription-based doses of vitamin D and its derivatives should be withheld during ZEMPLAR treatment to avoid hypercalcemia.
3.2Digitalis Toxicity
Digitalis toxicity is potentiated by hypercalcemia of any cause. Use caution when ZEMPLAR capsules are prescribed concomitantly with digitalis compounds.
3.3Laboratory Tests
During the initial dosing or following any dose adjustment of medication, serum calcium, serum phosphorus, and serum or plasma iPTH should be monitored at least every two weeks for 3 months, then monthly for 3 months, and every 3 months thereafter.
In pre-dialysis patients, ZEMPLAR capsules may increase serum creatinine and therefore decrease the estimated GFR (eGFR). Similar effects have also been seen with calcitriol.
3.4Aluminum Overload and Toxicity
Aluminum-containing preparations (e.g., antacids, phosphate binders) should not be administered chronically with ZEMPLAR, as increased blood levels of aluminum and aluminum bone toxicity may occur.
4ADVERSE REACTIONS
Because clinical studies are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical studies of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical studies of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
4.1Clinical Trials Experience
CKD Stages 3 and 4
Adults
The safety of ZEMPLAR capsules has been evaluated in three 24-week (approximately six-month), double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter clinical studies involving 220 CKD Stages 3 and 4 patients. Six percent (6%) of ZEMPLAR capsules treated patients and 4% of placebo treated patients discontinued from clinical studies due to an adverse event. Adverse events occurring in the ZEMPLAR capsules group at a frequency of 2% or greater and more frequently than in the placebo group are presented in Table 3:
Additional Adverse Reactions
The following additional adverse reactions occurred in <2% of the ZEMPLAR-treated patients in the above double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial.
Gastrointestinal Disorders: Dry mouth
Investigations: Hepatic enzyme abnormal
Nervous System Disorders: Dysgeusia
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders: Urticaria
Pediatric patients 10 to 16 years of age
The safety of ZEMPLAR capsules has been evaluated in one multicenter clinical study involving CKD Stages 3 and 4 patients ages 10 to 16 years. A 12-week double-blind, placebo-controlled phase was followed by an open-label phase during which all patients received ZEMPLAR capsules.
During the 12-week blinded phase, a total of 18 patients received ZEMPLAR capsules and 18 patients received placebo. Adverse events occurring more frequently in the ZEMPLAR capsules group than in the placebo group are presented in Table 4.
Additional Adverse Reactions
The following adverse reactions have occurred in ZEMPLAR-treated patients:
Gastrointestinal Disorders: Abdominal pain, constipation, vomiting
Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders: Hypercalcemia and hyperphosphatemia
Nervous System Disorders: Headache
CKD Stage 5
Adults
The safety of ZEMPLAR capsules has been evaluated in one 12-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter clinical study involving 88 CKD Stage 5 patients. Sixty-one patients received ZEMPLAR capsules and 27 patients received placebo.
The proportion of patients who terminated prematurely from the study due to adverse events was 7% for ZEMPLAR capsules treated patients and 7% for placebo patients.
Adverse events occurring in the ZEMPLAR capsules group at a frequency of 2% or greater and more frequently than in the placebo group are as follows:
Additional Adverse Reactions
The following adverse reactions occurred in <2% of the ZEMPLAR-treated patients in the above double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial.
Gastrointestinal Disorders: Gastroesophageal reflux disease
Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders: Decreased appetite, hypercalcemia, hypocalcemia
Reproductive System and Breast Disorders: Breast tenderness
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders: Acne
Pediatric patients 10 to 16 years of age
The safety of ZEMPLAR capsules has been evaluated in one 12-week, open-label, single-arm, multicenter clinical studies involving 13 CKD Stage 5 patients ages 10 to 16 years of age receiving peritoneal dialysis or hemodialysis.
The following adverse reactions were reported:
Gastrointestinal Disorders: Abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting
Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders: Hypercalcemia, hyperphosphatemia
Three of 13 patients (23%) had hypercalcemia defined as at least 2 consecutive serum calcium values >10.2 mg/dL (2.55 mmol/L).
4.2Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of ZEMPLAR capsules. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Immune System Disorders: Angioedema (including laryngeal edema)
Investigations: Blood creatinine increased
5DRUG INTERACTIONS
Table 6 shows the clinically significant drug interactions with ZEMPLAR capsules.
6OVERDOSAGE
Excessive administration of ZEMPLAR capsules can cause hypercalcemia, hypercalciuria, and hyperphosphatemia, and over suppression of PTH
Treatment of Overdosage
The treatment of acute overdosage of ZEMPLAR capsules should consist of general supportive measures. If drug ingestion is discovered within a relatively short time, induction of emesis or gastric lavage may be of benefit in preventing further absorption. If the drug has passed through the stomach, the administration of mineral oil may promote its fecal elimination. Serial serum electrolyte determinations (especially calcium), rate of urinary calcium excretion, and assessment of electrocardiographic abnormalities due to hypercalcemia should be obtained. Such monitoring is critical in patients receiving digitalis. Discontinuation of supplemental calcium and institution of a low-calcium diet are also indicated in accidental overdosage. Due to the relatively short duration of the pharmacological action of paricalcitol, further measures are probably unnecessary. If persistent and markedly elevated serum calcium levels occur, there are a variety of therapeutic alternatives that may be considered depending on the patient's underlying condition. These include the use of drugs such as phosphates and corticosteroids, as well as measures to induce an appropriate forced diuresis.
Paricalcitol is not significantly removed by dialysis.
7DESCRIPTION
Paricalcitol, USP, the active ingredient in ZEMPLAR capsules, is a synthetically manufactured, metabolically active vitamin D analog of calcitriol with modifications to the side chain (D
Paricalcitol is a white, crystalline powder with the empirical formula of C
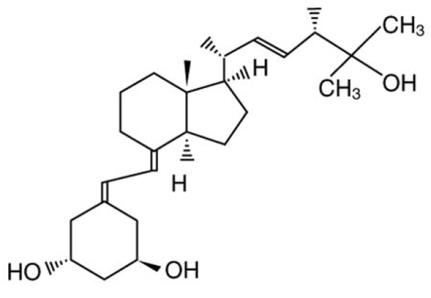
8CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Secondary hyperparathyroidism is characterized by an elevation in parathyroid hormone (PTH) associated with inadequate levels of active vitamin D hormone. The source of vitamin D in the body is from synthesis in the skin as vitamin D
8.1Mechanism of Action
Paricalcitol is a synthetic, biologically active vitamin D
8.2Pharmacodynamics
Paricalcitol decreases serum intact parathyroid hormone (iPTH) and increases serum calcium and serum phosphorous in both HD and PD patients. This observed relationship was quantified using a mathematical model for HD and PD patient populations separately. Computer-based simulations of 100 trials in HD or PD patients (N = 100) using these relationships predict slightly lower efficacy (at least two consecutive ≥ 30% reductions from baseline iPTH) with lower hypercalcemia rates (at least two consecutive serum calcium ≥ 10.5 mg/dL) for lower iPTH-based dosing regimens. Further lowering of hypercalcemia rates was predicted if the treatment with paricalcitol is initiated in patients with lower serum calcium levels at screening.
Based on these simulations, a dosing regimen of iPTH/80 with a screening serum calcium ≤ 9.5 mg/dL, approximately 76.5% (95% CI: 75.6% – 77.3%) of HD patients are predicted to achieve at least two consecutive weekly ≥ 30% reductions from baseline iPTH over a duration of 12 weeks. The predicted incidence of hypercalcemia is 0.8% (95% CI: 0.7% – 1.0%). In PD patients, with this dosing regimen, approximately 83.3% (95% CI: 82.6% – 84.0%) of patients are predicted to achieve at least two consecutive weekly ≥ 30% reductions from baseline iPTH. The predicted incidence of hypercalcemia is 12.4% (95% CI: 11.7% - 13.0%)
8.3Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
The mean absolute bioavailability of ZEMPLAR capsules under low-fat fed condition ranged from 72% to 86% in healthy adult volunteers, CKD Stage 5 patients on HD, and CKD Stage 5 patients on PD. A food effect study in healthy adult volunteers indicated that the C
Distribution
Paricalcitol is extensively bound to plasma proteins (≥ 99.8%). The mean apparent volume of distribution following a 0.24 mcg/kg dose of paricalcitol in healthy adult volunteers was 34 L. The mean apparent volume of distribution following a 4 mcg dose of paricalcitol in CKD Stage 3 and a 3 mcg dose in CKD Stage 4 patients is between 44 and 46 L.
Metabolism
After oral administration of a 0.48 mcg/kg dose of
In vitro data suggest that paricalcitol is metabolized by multiple hepatic and non-hepatic enzymes, including mitochondrial CYP24, as well as CYP3A4 and UGT1A4. The identified metabolites include the product of 24(R)-hydroxylation, 24,26- and 24,28-dihydroxylation and direct glucuronidation.
Elimination
Paricalcitol is eliminated primarily via hepatobiliary excretion; approximately 70% of the radiolabeled dose is recovered in the feces and 18% is recovered in the urine. While the mean elimination half-life of paricalcitol is 4 to 6 hours in healthy adult volunteers, the mean elimination half-life of paricalcitol in CKD Stages 3, 4, and 5 (on HD and PD) patients ranged from 14 to 20 hours.
Specific Populations
Geriatric
The pharmacokinetics of paricalcitol has not been investigated in geriatric patients greater than 65 years
Pediatric
Paricalcitol C
Gender
The pharmacokinetics of paricalcitol following single doses over the 0.06 to 0.48 mcg/kg dose range was gender independent.
Hepatic Impairment
The disposition of paricalcitol (0.24 mcg/kg) was compared in patients with mild (n = 5) and moderate (n = 5) hepatic impairment (as indicated by the Child-Pugh method) and subjects with normal hepatic function (n = 10). The pharmacokinetics of unbound paricalcitol was similar across the range of hepatic function evaluated in this study. No dose adjustment is required in patients with mild and moderate hepatic impairment. The influence of severe hepatic impairment on the pharmacokinetics of paricalcitol has not been evaluated.
Renal Impairment
Following administration of ZEMPLAR capsules, the pharmacokinetic profile of paricalcitol for CKD Stage 5 on HD or PD was comparable to that in CKD 3 or 4 patients. Therefore, no special dose adjustments are required other than those recommended in the Dosage and Administration section
Drug Interactions
An
Omeprazole
The effect of omeprazole (40 mg capsule), a strong inhibitor of CYP2C19, on paricalcitol (four 4 mcg capsules) pharmacokinetics was investigated in a single dose, crossover study in healthy subjects. The pharmacokinetics of paricalcitol was not affected when omeprazole was administered approximately 2 hours prior to the paricalcitol dose.
Ketoconazole
The effect of multiple doses of ketoconazole, a strong inhibitor of CYP3A, administered as 200 mg BID for 5 days on the pharmacokinetics of paricalcitol (4 mcg capsule) has been studied in healthy subjects. The C
9HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
ZEMPLAR capsules are available as 1 mcg and 2 mcg capsules.
The 1 mcg capsule is an oval, gray, soft gelatin capsule supplied and imprinted as follows:
Bottles of 30 – NDC 0074-9036-30 (imprinted with “ZA”)
Bottles of 30 – NDC 0074-4317-30 (imprinted with the “a” logo and “ZA”)
The 2 mcg capsule is an oval, orange-brown, soft gelatin capsule supplied and imprinted as follows:
Bottles of 30 – NDC 0074-9037-30 (imprinted with “ZF”)
Bottles of 30 – NDC 0074-4314-30 (imprinted with the “a” logo and “ZF”)
Storage
Store ZEMPLAR capsules at 25°C (77°F). Excursions permitted between 15°- 30°C (59°- 86°F). See USP Controlled Room Temperature.
10PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise patients of the following:
- The most common adverse reactions with use of ZEMPLAR capsules include diarrhea, hypertension, nausea, nasopharyngitis, dizziness, and vomiting.
- Patients should adhere to instructions regarding diet and phosphorus restriction.
- Patients should contact a health care provider if they develop symptoms of elevated calcium, (e.g. feeling tired, difficulty thinking clearly, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, constipation, increased thirst, increased urination and weight loss).
- Patients should return to the physician's office for routine monitoring. More frequent monitoring is necessary during the initiation of therapy, following dose changes or when potentially interacting medications are started or discontinued.
- Patients should inform their physician of all medications, including prescription and nonprescription drugs, supplements, and herbal preparations they are taking and any change to their medical condition. Patients should also inform their physician that they are taking ZEMPLAR capsules if a new medication is prescribed.
- Breastfeeding is not recommended during treatment with ZEMPLAR capsules
© 2024 AbbVie. All rights reserved.
ZEMPLAR and its design are trademarks of AbbVie Inc.
Manufactured for
AbbVie Inc.
North Chicago, IL 60064, U.S.A.
131899 R1 August 2024

