Sorafenib
What is Nexavar (Sorafenib)?
Approved To Treat
Top Global Experts
Related Clinical Trials
Summary: Recently, the positive results of the Imbrave 150 study (randomized study comparing Atezolizumab+Bevacizumab versus Sorafenib) prompted investigators to redefine their management strategy for advanced HCC by proposing the combination Atezolizumab+ Bevacizumab as first-line treatment in these patients. Identifying new predictive biomarkers of response is essential to optimize the identification of ...
Summary: This is a multi-center, observational, retrospective study designed to characterize the effectiveness and safety of sunitinib or sorafenib monotherapy in the treatment of Chinese adult patients with unresectable and locally advanced or metastatic PRCC, who have not received any prior systemic anticancer therapy in the metastatic setting. Electronic medical record (EMR) data of patients with 1L sun...
Summary: This is an observational study in which only data will be collected from adults with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. These adults should be prescribed a different treatment after treatment with atezolizumab and bevacizumab, or another similar combination of drugs, by their doctors. Unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (uHCC) is a type of liver cancer that cannot be treated with surgery. In...
Related Latest Advances
Brand Information
- 200 mg sorafenib, round, biconvex, red film-coated tablets, debossed with the “Bayer cross” on one side and “200” on the other side.
- 200 mg sorafenib, round, faceted biconvex, red film-coated tablets, debossed with the “Bayer cross” on one side and “200” on the other side.
- NEXAVAR is contraindicated in patients with known severe hypersensitivity to sorafenib or any other component of NEXAVAR.
- NEXAVAR in combination with carboplatin and paclitaxel is contraindicated in patients with squamous cell lung cancer
- Cardiovascular events
- Hemorrhage
- Hypertension
- Dermatologic toxicities
- Gastrointestinal perforation
- QT interval prolongation
- Drug-induced liver injury
- Impairment of TSH suppression in DTC
- Adverse reactions graded according to National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events version 3.0 (NCI CTCAE v3.0).
- Laboratory parameters graded according to National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events version 3.0 (NCI CTCAE v3.0).
- Adverse reactions graded according to National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events version 3.0 (NCI CTCAE v3.0).
- Laboratory parameters graded according to National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events version 3.0 (NCI CTCAE v3.0).
- National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events Version 3.0
- Includes the following terms: abdominal pain, abdominal discomfort, hepatic pain, esophageal pain, esophageal discomfort, abdominal pain lower, abdominal pain upper, abdominal tenderness, abdominal rigidity
- Includes the following terms: stomatitis, aphthous stomatitis, mouth ulceration, mucosal inflammation
- Includes the following terms: oral pain, oropharyngeal discomfort, glossitis, burning mouth syndrome, glossodynia
- Palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia syndrome (Hand-foot skin reaction)
- Includes the following terms: hypertension, blood pressure increased, blood pressure systolic increased
- Laboratory parameters graded according to National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events version 3.0 (NCI CTCAE v3.0).
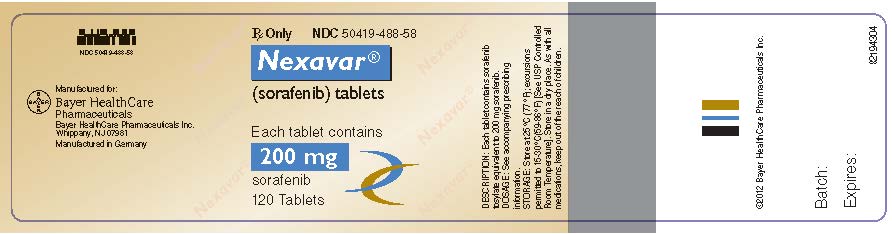
- 200 mg, round, biconvex, red film-coated tablets, debossed with the “Bayer cross” on one side and “200” on the other side. NDC 50419-488-58
- 200 mg, round, faceted, biconvex, red film-coated tablets, debossed with the “Bayer cross” on one side and “200” on the other side. NDC 50419-489-01
(sorafenib) tablets

(sorafenib) tablets