Beta-1A
What is Rebif (Beta-1A)?
Approved To Treat
Top Global Experts
Related Clinical Trials
Summary: In this study, researchers will learn more about the effects of diroximel fumarate (DRF), also known as VUMERITY®, when taken during pregnancy in people with multiple sclerosis, also known as MS. In MS, the immune system attacks the nerves in the brain and spinal cord. The affected areas are called lesions. The damage makes it difficult for the brain and spinal cord to function and send messages t...
Summary: The primary objectives of the study are to estimate the risk of major congenital malformations (MCMs) in infants born to women with multiple sclerosis (MS) who were exposed to diroximel fumarate (DRF) at any time from 2 weeks after the first day of their last menstrual period (LMP) up through the first trimester of pregnancy and to comparatively evaluate pregnancy outcomes with MCMs in women with ...
Summary: West Nile virus (WNV) is a mosquito-borne virus which in majority of cases causes only self-limited disease. Despite that, in minority of cases (\ 0.5%) it can infect the brain and cause severe and even life-threatening disease (neuroinvasive disease). Recent study has shown that up to 40% of WNV patients who develop neuroinvasive disease, have antibodies against Interferons (anti-Type I interfero...
Related Latest Advances
Brand Information
- Injection: 8.8 mcg per 0.2 mL in a graduated, single-dose REBIF prefilled syringe
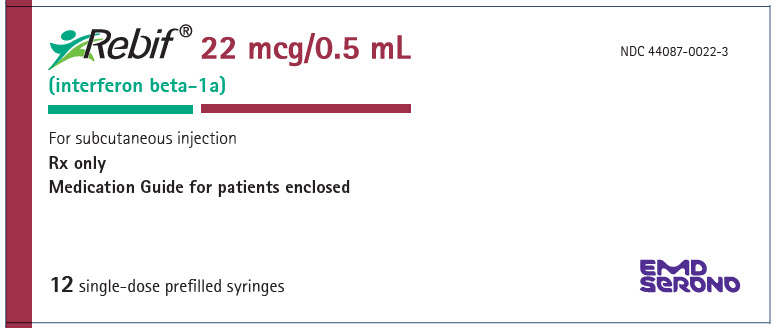
- Injection: 22 mcg per 0.5 mL in a graduated, single-dose REBIF prefilled syringe
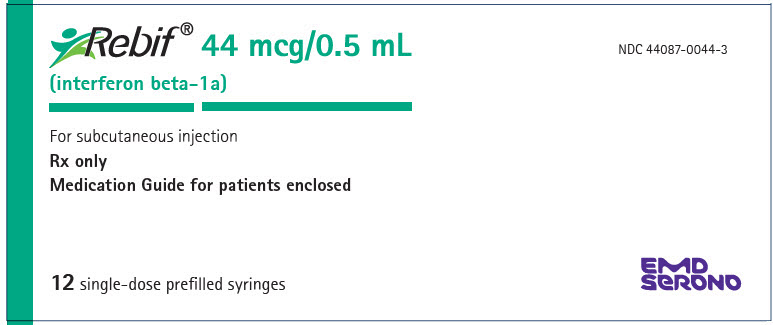
- Injection: 44 mcg per 0.5 mL in a graduated, single-dose REBIF prefilled syringe
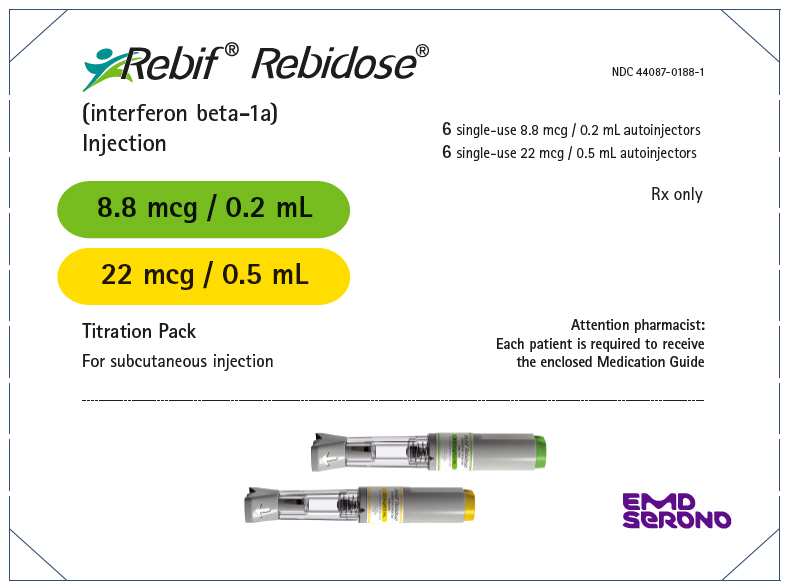
- Injection: 8.8 mcg per 0.2 mL in a single-dose prefilled REBIF Rebidose autoinjector
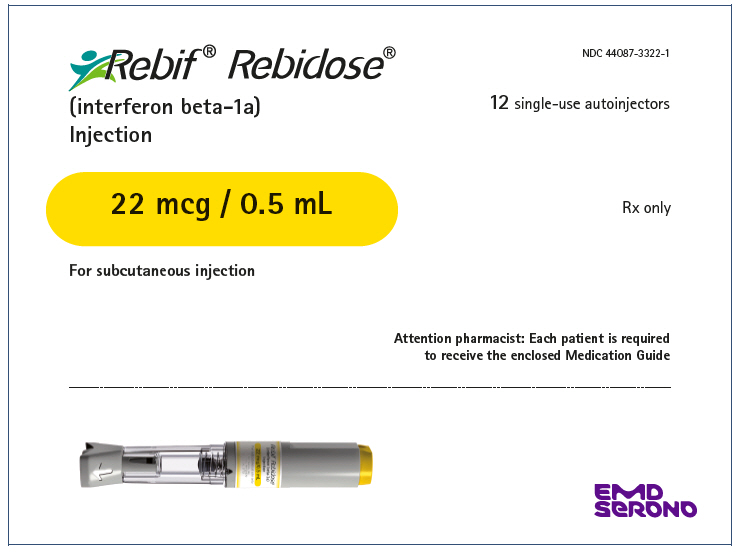
- Injection: 22 mcg per 0.5 mL in a single-dose prefilled REBIF Rebidose autoinjector
- Injection: 44 mcg per 0.5 mL in a single-dose prefilled REBIF Rebidose autoinjector
- Depression and Suicide [see
- Hepatic Injury [see
- Anaphylaxis and Other Allergic Reactions [see
- Injection Site Reactions including Necrosis [see
- Decreased Peripheral Blood Counts [see
- Thrombotic Microangiopathy
- Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
- Seizures [see
- Laboratory Tests [see
- Behavioral health problems including depression and suicidal thoughts. You may have mood problems including:
- depression (feeling hopeless or feeling bad about yourself)
- thoughts of hurting yourself or suicide
- Liver problems or worsening of liver problems including liver failure. Symptoms may include:
- nausea
- loss of appetite
- tiredness
- dark colored urine and pale stools
- yellowing of your skin or the white part of your eye
- bleeding more easily than normal
- confusion
- sleepiness
During your treatment with REBIF you will need to see your healthcare provider regularly and have regular blood tests to check for side effects.
- Serious allergic and skin reactions. Symptoms may include:
- itching
- swelling of your face, eyes, lips, tongue or throat
- trouble breathing
- anxiousness
- feeling faint
- skin rash, hives, sores in your mouth, or skin blisters and peels
- Injection site problems. REBIF may cause redness, pain, itching or swelling at the place where your injection was given. Call your healthcare provider right away if an injection site becomes swollen and painful or the area looks infected. You may have a skin infection or an area of severe skin damage (necrosis) requiring treatment by a healthcare provider.
- are allergic to interferon beta, human albumin, or any of the ingredients in REBIF. See the end of this Medication Guide for a complete list of ingredients in REBIF.
- mental illness, including depression and suicidal behavior
- liver problems
- bleeding problems or blood clots
- low blood cell counts
- seizures (epilepsy)
- thyroid problems
- drink alcohol
- you are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if REBIF can harm your unborn baby.
- you are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. REBIF may pass into your breastmilk. Talk with your healthcare provider about the best way to feed your baby if you take REBIF.
- See the Instructions for Use at the end of this Medication Guide on how to prepare and give an injection of REBIF using a prefilled syringe. For the REBIF Rebidose autoinjector, read the Instructions for Use that comes with the REBIF Rebidose autoinjector.
- Your healthcare provider should show you how to prepare and measure your dose of REBIF and how to inject your REBIF before you use it for the first time.
- REBIF is given by injection under the skin (subcutaneous injection) on the same 3 days a week, for example, Monday, Wednesday and Friday.
- Your injections should be at least 48 hours apart. Take them the same time each day.
- Inject REBIF exactly as your healthcare provider tells you.
- Your healthcare provider will tell you how much REBIF to inject, and may change the dose based on how your body responds. Do not inject more than your healthcare provider tells you to.
- Do not change your dose unless your healthcare provider tells you to.
- Change (rotate) your injection site you choose with each injection. This will help decrease the chance that you will have an injection site reaction.
- Do not inject REBIF into an area of the body where the skin is irritated, reddened, bruised, infected or scarred in any way.
- REBIF comes as a:
- See "
- Blood problems. REBIF can affect your bone marrow and cause low red and white blood cell, and platelet counts. In some people, these blood cell counts may fall to dangerously low levels. If your blood cell counts become very low, you can get infections and problems with bleeding and bruising. Your healthcare provider may ask you to have regular blood tests to check for blood problems.
- Pulmonary arterial hypertension. Pulmonary arterial hypertension can occur with interferon beta products, including REBIF. Symptoms may include new fatigue or shortness of breath. Contact your healthcare provider right away if you develop these symptoms.
- Seizures. Some people have had seizures while taking REBIF.
- flu-like symptoms. You may have flu-like symptoms when you first start taking REBIF. You may be able to manage these flu-like symptoms by taking over-the-counter pain and fever reducers. For many people, these symptoms lessen or go away over time. Symptoms may include:
- stomach pain
- change in liver blood tests
- Store REBIF in the refrigerator between 36°F to 46°F (2°C to 8°C).
- Do not freeze REBIF.
- If you cannot refrigerate your REBIF, you can store your REBIF at temperatures above 36°F and below 77°F (2°C to 25°C) for up to 30 days.
- Keep REBIF away from heat and light.
- REBIF prefilled syringe
- alcohol pad or cotton balls and rubbing alcohol
- small adhesive bandage strip if desired
- puncture resistant safety container for disposal of used syringes. See "
- antibacterial soap
- an over-the-counter pain or fever reducing medicine, if your healthcare provider has recommended that you take this before, at the same time, or after you give yourself REBIF to help decrease the fever, chills, sweating and muscle aches (flu-like symptoms) that may happen.
- When first starting treatment with REBIF, your healthcare provider may prescribe either the 22 mcg or 44 mcg dose of REBIF. You should gradually increase the dose over 4 weeks, starting at 20% of the prescribed dose for the first 2 weeks, half-dose for the second 2 weeks (weeks 3 and 4), and then the full dose prescribed by your healthcare provider.
- Check the expiration date
- Remove your REBIF syringe from the refrigerator at least 30 minutes before you plan to use it so it can warm to room temperature.
- Be sure that the dose, either, 8.8 mcg, 22 mcg or 44 mcg, described on the carton is the same as the dose prescribed by your healthcare provider.
- Remove the REBIF syringe from the plastic packaging. Keep the needle capped.
- Look at the contents of the syringe carefully. The liquid should be clear to slightly yellow.
- The best sites for giving yourself an injection are those areas with a layer of fat between the skin and muscle, like your thigh, the outer surface of your upper arm, your stomach or buttocks.
- Do not use the area near your waistline or within 2 inches of your navel. If you are very thin, use only the thigh or outer surface of the arm for injection.
- Use a different site each time you inject such as the thigh, hip, stomach or upper arm
- Do not inject REBIF into an area of your body where the skin is irritated, reddened, bruised, infected or abnormal in any way.
- Wash your hands thoroughly with antibacterial soap before preparing to inject the medicine.
- Clean the injection site with an alcohol pad or cotton ball with rubbing alcohol using a circular motion. To avoid stinging, you should let your skin dry before you inject REBIF.
- Remove the needle cap from the syringe needle.
- If your healthcare provider has told you to use less than the full 0.5 mL dose, slowly push the plunger in until the amount of medicine left in the syringe is the amount healthcare provider told you to use.
- Use your thumb and forefinger to pinch a pad of skin surrounding the cleaned injection site (
- While still pinching the skin, quickly insert the needle like a dart at about a 90 degree angle (just under the skin) into the pad of tissue as shown
- After the needle is in, remove the hand that you used to pinch your skin and inject the medicine using a slow, steady push on the plunger until all the medicine is injected and the syringe is empty
- Withdraw the needle and apply gentle pressure to the injection site with a dry cotton ball or sterile gauze. Applying a cold compress or ice pack to the injection site after injection may help reduce local skin reactions.
- Put a small adhesive bandage strip over the injection site, if desired.
- Keep a record of the date and location of each injection.
- After 2 hours, check the injection site for redness, swelling, or tenderness. If you have a skin reaction and it does not clear up in a few days, call your healthcare provider.
- Put your used needles, syringes, and autoinjectors, including REBIF, in an FDA-cleared sharps container right away after use.
- When your sharps disposal container is almost full, you will need to follow your community guidelines for the right way to dispose of your sharps disposal container. There may be state or local laws about how you should throw away used autoinjectors and syringe needles. For more information about safe sharps disposal, and for specific information about sharps disposal in the state that you live in, go to the FDA's website at: http://www.fda.gov/safesharpsdisposal.
- Do not dispose of your used sharps disposal container in your household trash unless your community guidelines permit this. Do not recycle your used sharps disposal container.