Glatiramer Acetate
What is Copaxone (Glatiramer Acetate)?
Approved To Treat
Related Clinical Trials
Summary: This study is a single-country, non-interventional, multicenter, observational study, mainly based on primary data collection to assess the effect of ofatumumab on clinical parameters of Multiple Sclerosis (MS) in a routine medical care setting, as compared to the standard of care (SoC) arm of a closely monitored phase-IIIb study (STHENOS, which includes glatiramer acetate, interferons, teriflunom...
Summary: The primary objective of the study is to estimate the prevalence of major congenital malformations (MCMs) and compare the prevalence between the diroximel fumarate (DRF) and comparator groups. The secondary objectives of the study are to estimate the incidence of spontaneous abortion (SA) and compare the incidence between the DRF and comparator groups; to estimate the incidence of preterm birth an...
Summary: The purpose of this research study is to investigate the effectiveness of MS Disease modifying medications on cognitive fatigue in persons with relapsing remitting multiple sclerosis (RRMS). Cognitive fatigue is the kind of fatigue that occurs after intense mental concentration as after a session of problem solving.
Related Latest Advances
Brand Information
- Make patients aware of the symptoms of anaphylaxis, which may overlap with those of an immediate post-injection reaction; instruct them to seek immediate medical care should these symptoms occur. Prompt identification of anaphylaxis is important to avoid a delay in treatment
- COPAXONE is
- Injection: 20 mg per mL in a single-dose, prefilled syringe with a white plunger. For subcutaneous use only.
- Injection: 40 mg per mL in a single-dose, prefilled syringe with a blue plunger. For subcutaneous use only.
- Anaphylactic Reactions
- Immediate Post-Injection Reaction
- Chest Pain
- Lipoatrophy and Skin Necrosis
- Potential Effects on Immune Response
- Hepatic Injury
- 20 mg per mL in a single-dose, prefilled syringe with a white plunger, in individual blister packages supplied in 30-count cartons (NDC 68546-317-30).
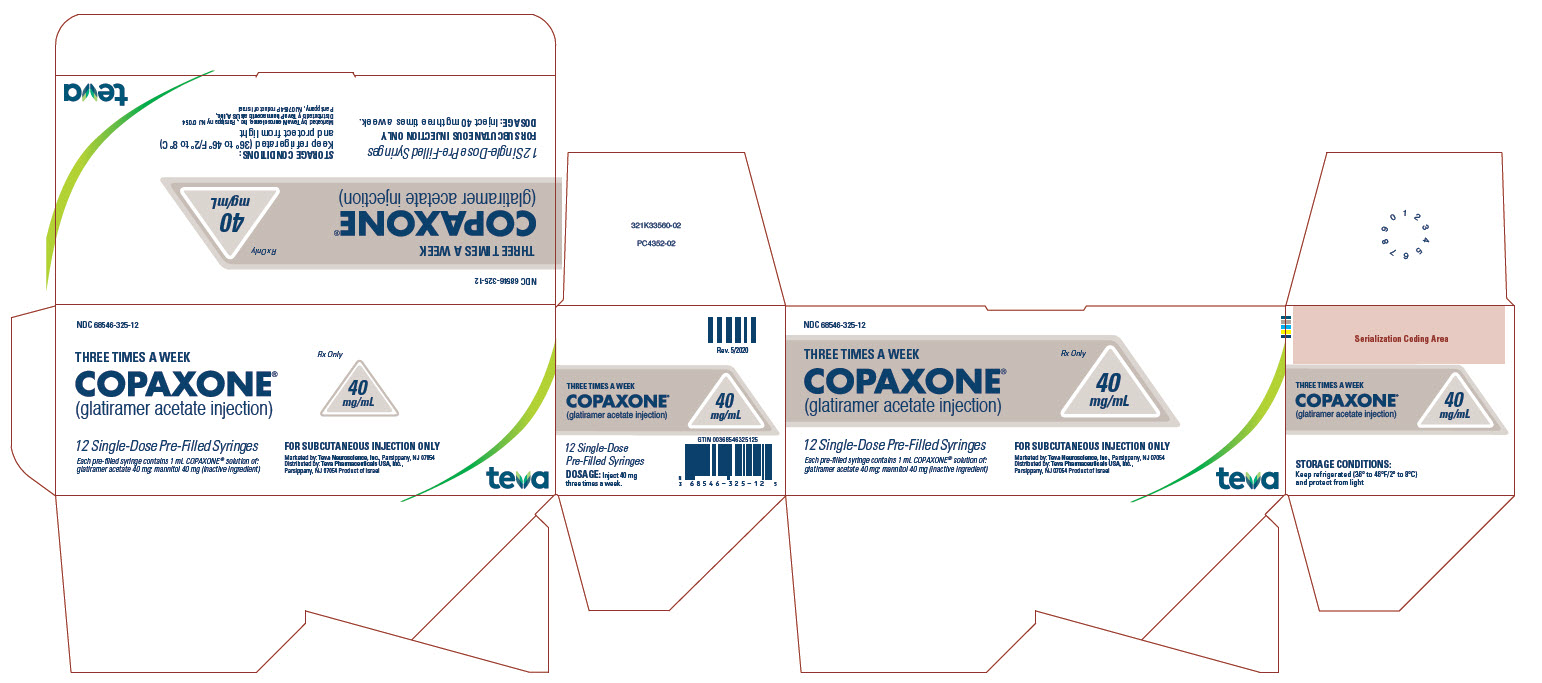
- 40 mg per mL in a single-dose, prefilled syringe with a blue plunger, in individual blister packages supplied in 12-count cartons (NDC 68546-325-12).
- COPAXONE 20 mg is injected 1 time each day, in the fatty layer under your skin (subcutaneously).
- Each COPAXONE 20 mg prefilled syringe is for single use (1 time use) only.
- The COPAXONE 20 mg dose is packaged in boxes of 30 prefilled syringes with needles attached. COPAXONE 20 mg prefilled syringes have
- COPAXONE 40 mg is injected 3 times each week, in the fatty layer under your skin (subcutaneously).
- COPAXONE 40 mg should be given on the same 3 days each week, if possible, for example, Monday, Wednesday, and Friday. Give your COPAXONE injections at least 48 hours (2 days) apart.
- Each COPAXONE 40 mg prefilled syringe is for single use (1 time use) only.
- The COPAXONE 40 mg dose is packaged in boxes of 12 prefilled syringes with needles attached. COPAXONE 40 mg prefilled syringes have
- 1 blister pack with a COPAXONE Prefilled Syringe with needle attached
- Alcohol wipe (not supplied)
- Dry cotton ball (not supplied)
- A place to record your injections, like a notebook (not supplied)
- Sharps disposal container (not supplied).
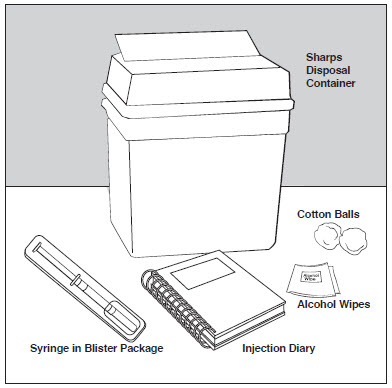
- Place the supplies you will need on a clean, flat surface in a well-lit area.
- After you remove 1 blister pack from the carton, keep all unused syringes in the carton and store them in the refrigerator.
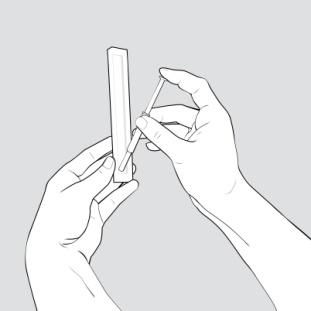
- Let the blister pack, with the syringe inside, warm to room temperature for about 20 minutes.
- Wash your hands. Be careful not to touch your face or hair after washing your hands.
- There may be small air bubbles in the syringe.
- Check the liquid medicine in the syringe before you give your injection. The liquid in the syringe should look clear, and colorless, and may look slightly yellow. If the liquid is cloudy or contains any particles, do not use the syringe and throw it away in a sharps disposal container.
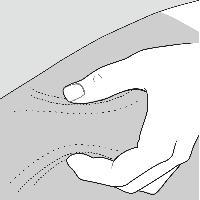
- The possible injection areas on your body include
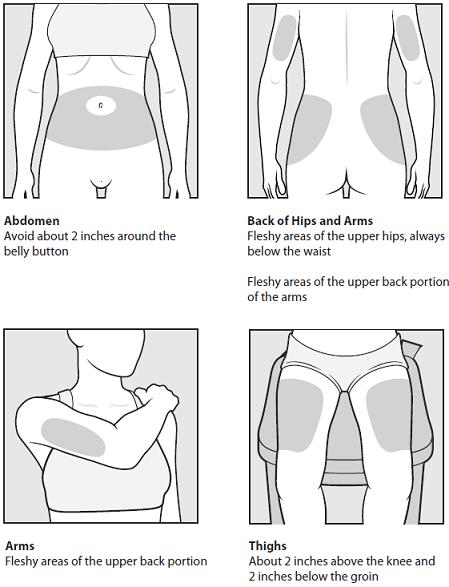
- For each COPAXONE dose, choose a different injection area from 1 of the areas shown above.
- Do not stick the needle in the same place (site) more than 1 time each week. Each injection area contains multiple injection sites for you to choose from. Avoid injecting in the same site over and over again.
- Keep a record of the sites where you give your injection each day so you will remember where you already injected
- There are some injection areas on your body that are hard to reach (like the back of your arm). You may need help from someone who has been instructed on how to give your injection if you cannot reach certain injection areas.
- Do not inject in sites where the skin has scarring or “dents”. Using scarred or dented skin for your injections may make your skin worse.
- Clean the injection site using the alcohol wipe and allow your skin to air dry.
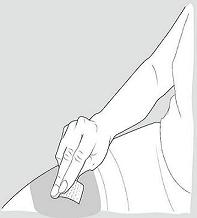
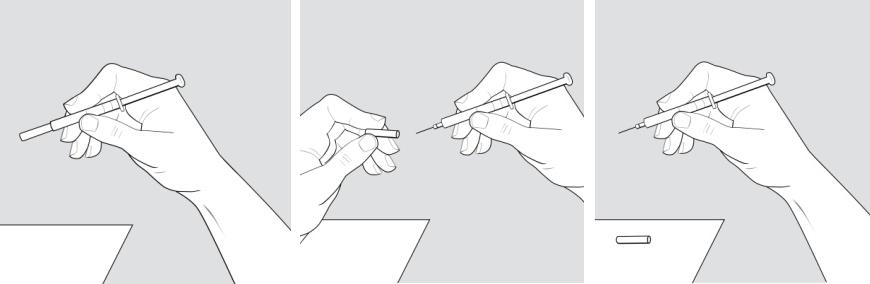
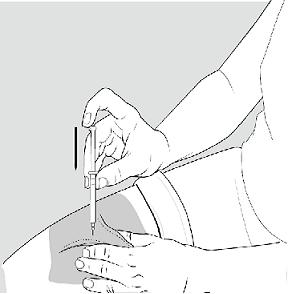
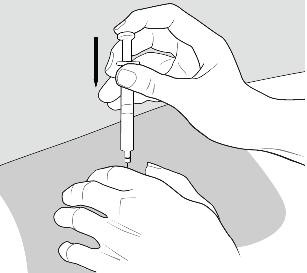
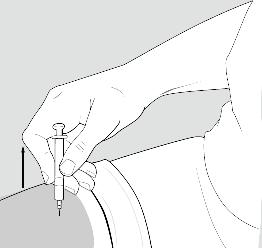
- Rest the heel of your hand holding the syringe against your skin at the injection site. Insert the needle at a 90 degree angle straight into your skin.
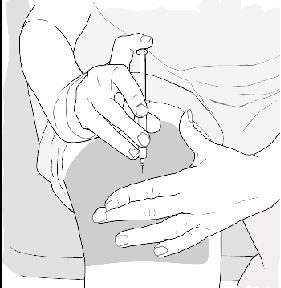
- When the needle is all the way into your skin, release the fold of skin.
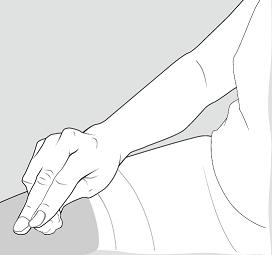
- Put your used needles and syringes in a FDA-cleared sharps disposal container right away after use.
- If you do not have a FDA-cleared sharps disposal container, you may use a household container that is:
- When your sharps disposal container is almost full, you will need to follow your community guidelines for the right way to dispose of your sharps disposal container. There may be state or local laws about how you should throw away used needles and syringes. For more information about safe sharps disposal, and for specific information about sharps disposal in the state that you live in, go to the FDA’s website at: http://www.fda.gov/safesharpsdisposal.
- Do not dispose of your used sharps disposal container in your household trash unless your community guidelines permit this. Do not recycle your used sharps disposal container.