Generic Name
RopivacaIne
Brand Names
Naropin, Ropidex
FDA approval date: September 24, 1996
Classification: Amide Local Anesthetic
Form: Injection, Kit
What is Naropin (RopivacaIne)?
Ropivacaine hydrochloride injection is indicated for the production of local or regional anesthesia for surgery and for acute pain management. Surgical Anesthesia : epidural block for surgery including cesarean section; major nerve block; local infiltration Acute Pain Management : epidural continuous infusion or intermittent bolus, e.g., postoperative or labor; local infiltration Ropivacaine hydrochloride injection is an amide local anesthetic indicated in adults for the production of local or regional anesthesia for surgery and for acute pain management. Surgical Anesthesia : epidural block for surgery including cesarean section; major nerve block; local infiltration Acute Pain Managemen t: epidural continuous infusion or intermittent bolus, e.g., postoperative or labor; local infiltration.
Approved To Treat
Top Global Experts
There are no experts for this drug
Save this treatment for later
Not sure about your diagnosis?
Tired of the same old research?
Related Clinical Trials
There is no clinical trials being done for this treatment
Related Latest Advances
Brand Information
Naropin (ROPIVACAINE HYDROCHLORIDE)
1INDICATIONS AND USAGE
NAROPIN is indicated for the production of local or regional anesthesia for surgery and for acute pain management.
Surgical Anesthesia: epidural block for surgery including cesarean section; major nerve block; local infiltration
Acute Pain Management: epidural continuous infusion or intermittent bolus, e.g., postoperative or labor; local infiltration
2DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
NAROPIN
NAROPIN
- 0.2%, 20 mg per 10 mL (2 mg/mL), in 10 mL single-dose vial
- 0.2%, 40 mg per 20 mL (2 mg/mL), in 20 mL single-dose vial
- 0.5%, 100 mg per 20 mL (5 mg/mL), 20 mL single-dose vial
- 0.5%, 150 mg per 30 mL (5 mg/mL), 30 mL single-dose vial
- 0.75%, 150 mg per 20 mL (7.5 mg/mL), 20 mL single-dose vial
- 1%, 100 mg per 10 mL (10 mg/mL), 10 mL single-dose vial
- 1%, 200 mg per 20 mL (10 mg/mL), 20 mL single-dose vial
NAROPIN
- 0.2%, 200 mg per 100 mL (2 mg/mL), 100 mL single-dose infusion bottle
- 0.2%, 400 mg per 200 mL (2 mg/mL ), 200 mL single-dose infusion bottle
- 0.5%, 500 mg per 100 mL (5 mg/mL), 100 mL single-dose infusion bottle
- 0.5%, 1,000 mg per 200 mL (5 mg/mL ), 200 mL single-dose infusion bottle
NAROPIN®Plastic Polypropylene Ampule
- 0.2%, 20 mg per 10 mL (2 mg/mL), 10 mL single-dose polypropylene ampule
- 0.2%, 40 mg per 20 mL (2 mg/mL), 20 mL single-dose polypropylene ampule
- 0.5%, 100 mg per 20 mL (5 mg/mL), 20 mL single-dose polypropylene ampule
- 0.75%, 150 mg per 20 mL (7.5 mg/mL), 20 mL single-dose polypropylene ampule
- 1%, 100 mg per 10 mL (10 mg/mL), 10 mL single-dose polypropylene ampule
- 1%, 200 mg per 20 mL (10 mg/mL), 20 mL single-dose polypropylene ampule
NAROPIN®Single-Dose, Ready-to-Use, Polypropylene Flexible Bags
- 0.2%, 200 mg per 100 mL (2 mg/mL), 100 mL single-dose, ready-to-use, polypropylene flexible bag
- 0.2%, 400 mg per 200 mL (2 mg/mL), 200 mL fill in 250 mL single-dose, ready-to-use, polypropylene flexible bag.
3CONTRAINDICATIONS
NAROPIN is contraindicated in patients with a known hypersensitivity to ropivacaine or to any local anesthetic agent of the amide type.
4ADVERSE REACTIONS
Reactions to ropivacaine are characteristic of those associated with other amide-type local anesthetics. A major cause of adverse reactions to this group of drugs may be associated with excessive plasma levels, which may be due to overdosage, unintentional intravascular injection or slow metabolic degradation.
The reported adverse events are derived from clinical studies conducted in the U.S. and other countries. The reference drug was usually bupivacaine. The studies used a variety of premedications, sedatives, and surgical procedures of varying length. A total of 3,988 patients have been exposed to NAROPIN at concentrations up to 1% in clinical trials. Each patient was counted once for each type of adverse event.
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely conditions, adverse reactions rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Incidence ≥ 5%
For the indications of epidural administration in surgery, cesarean section, postoperative pain management, peripheral nerve block, and local infiltration, the following treatment-emergent adverse events were reported with an incidence of ≥ 5% in all clinical studies (N=3988): hypotension (37%), nausea (24.8%), vomiting (11.6%), bradycardia (9.3%), fever (9.2%), pain
(8%), postoperative complications (7.1%), anemia (6.1%), paresthesia (5.6%), headache (5.1%), pruritus (5.1%), and back
pain (5%).
Incidence 1 to 5%
Urinary retention, dizziness, rigors, hypertension, tachycardia, anxiety, oliguria, hypoesthesia, chest pain, hypokalemia, dyspnea, cramps, and urinary tract infection.
Incidence in Controlled Clinical Trials
The reported adverse events are derived from controlled clinical studies with NAROPIN (concentrations ranged from 0.125% to 1% for NAROPIN and 0.25% to 0.75% for bupivacaine) in the U.S. and other countries involving 3,094 patients.
Incidence <1%
The following adverse events were reported during the NAROPIN clinical program in more than one patient (N=3988), occurred at an overall incidence of <1%, and were considered relevant:
Application Site Reactions - injection site pain
Cardiovascular System - vasovagal reaction, syncope, postural hypotension, non-specific ECG abnormalities
Female Reproductive - poor progression of labor, uterine atony
Gastrointestinal System - fecal incontinence, tenesmus, neonatal vomiting
General and Other Disorders - hypothermia, malaise, asthenia, accident and/or injury
Hearing and Vestibular - tinnitus, hearing abnormalities
Heart Rate and Rhythm - extrasystoles, non-specific arrhythmias, atrial fibrillation
Liver and Biliary System - jaundice Metabolic Disorders - hypomagnesemia Musculoskeletal System - myalgia
Myo/Endo/Pericardium - ST segment changes, myocardial infarction
Nervous System - tremor, Horner's syndrome, paresis, dyskinesia, neuropathy, vertigo, coma, convulsion, hypokinesia, hypotonia, ptosis, stupor
Psychiatric Disorders - agitation, confusion, somnolence, nervousness, amnesia, hallucination, emotional lability, insomnia, nightmares
Respiratory System - bronchospasm, coughing
Skin Disorders - rash, urticaria
Urinary System Disorders - urinary incontinence, micturition disorder Vascular - deep vein thrombosis, phlebitis, pulmonary embolism Vision - vision abnormalities
For the indication epidural anesthesia for surgery, the 15 most common adverse events were compared between different concentrations of NAROPIN and bupivacaine.
Using data from the same studies, the number (%) of patients experiencing hypotension is displayed by patient age, drug and concentration in
5DRUG INTERACTIONS
Patients who are administered local anesthetics are at increased risk of developing methemoglobinemia when concurrently exposed to the following drugs, which could include other local anesthetics
NAROPIN should be used with caution in patients receiving other local anesthetics or agents structurally related to amide- type local anesthetics, since the toxic effects of these drugs are additive. Cytochrome P4501A2 is involved in the formation of 3-hydroxy ropivacaine, the major metabolite. In vivo, the plasma clearance of ropivacaine was reduced by 70% during coadministration of fluvoxamine (25 mg bid for 2 days), a selective and potent CYP1A2 inhibitor. Thus strong inhibitors of cytochrome P4501A2, such as fluvoxamine, given concomitantly during administration of NAROPIN, can interact with NAROPIN leading to increased ropivacaine plasma levels. Caution should be exercised when CYP1A2 inhibitors are coadministered. Possible interactions with drugs known to be metabolized by CYP1A2 via competitive inhibition such as theophylline and imipramine may also occur. Coadministration of a selective and potent inhibitor of CYP3A4, ketoconazole (100 mg bid for 2 days with ropivacaine infusion administered 1 hour after ketoconazole) caused a 15% reduction in in vivo plasma clearance of ropivacaine.
Specific trials studying the interaction between ropivacaine and class III antiarrhythmic drugs (e.g., amiodarone) have not been performed, but caution is advised
6OVERDOSAGE
Acute emergencies from local anesthetics are generally related to high plasma levels encountered, or large doses administered, during therapeutic use of local anesthetics or to unintended subarachnoid or intravascular injection of local anesthetic solution
6.1Treatment
Therapy with NAROPIN should be discontinued at the first sign of toxicity. No specific information is available for the treatment of toxicity with NAROPIN; therefore, treatment should be symptomatic and supportive. The first consideration is prevention, best accomplished by incremental injection of NAROPIN, careful and constant monitoring of cardiovascular and respiratory vital signs and the patient's state of consciousness after each local anesthetic and during continuous infusion. At the first sign of change in mental status, oxygen should be administered.
The first step in the management of systemic toxic reactions, as well as underventilation or apnea due to unintentional subarachnoid injection of drug solution, consists of immediate attention to the establishment and maintenance of a patent airway and effective assisted or controlled ventilation with 100% oxygen with a delivery system capable of permitting immediate positive airway pressure by mask. Circulation should be assisted as necessary. This may prevent convulsions if they have not already occurred.
If necessary, use drugs to control convulsions. Intravenous barbiturates, anticonvulsant agents, or muscle relaxants should only be administered by those familiar with their use. Immediately after the institution of these ventilatory measures, the adequacy of the circulation should be evaluated. Supportive treatment of circulatory depression may require administration of intravenous fluids, and, when appropriate, a vasopressor dictated by the clinical situation (such as ephedrine or epinephrine to enhance myocardial contractile force).
Should cardiac arrest occur, prolonged resuscitative efforts may be required to improve the probability of a successful outcome.
The mean dosages of ropivacaine producing seizures, after intravenous infusion in dogs, nonpregnant and pregnant sheep were 4.9, 6.1 and 5.9 mg/kg, respectively. These doses were associated with peak arterial total plasma concentrations of 11.4, 4.3 and 5 mcg/mL, respectively.
In human volunteers given intravenous NAROPIN, the mean (min-max) maximum tolerated total and free arterial plasma concentrations were 4.3 (3.4 to 5.3) and 0.6 (0.3 to 0.9) mcg/mL respectively, at which time moderate CNS symptoms (muscle twitching) were noted.
Clinical data from patients experiencing local anesthetic induced convulsions demonstrated rapid development of hypoxia, hypercarbia and acidosis within a minute of the onset of convulsions. These observations suggest that oxygen consumption and carbon dioxide production are greatly increased during local anesthetic convulsions and emphasize the importance of immediate and effective ventilation with oxygen which may avoid cardiac arrest.
If difficulty is encountered in the maintenance of a patent airway or if prolonged ventilatory support (assisted or controlled) is indicated, endotracheal intubation, employing drugs and techniques familiar to the clinician, may be indicated after initial administration of oxygen by mask.
The supine position is dangerous in pregnant women at term because of aortocaval compression by the gravid uterus. Therefore, during treatment of systemic toxicity, maternal hypotension or fetal bradycardia following regional block, the parturient should be maintained in the left lateral decubitus position if possible, or manual displacement of the uterus off the great vessels should be accomplished. Resuscitation of obstetrical patients may take longer than resuscitation of non- pregnant patients and closed-chest cardiac compression may be ineffective. Rapid delivery of the fetus may improve the response to resuscitative efforts.
7DESCRIPTION
NAROPIN
Ropivacaine hydrochloride is chemically described as S-(-)-1-propyl-2',6'-pipecoloxylidide hydrochloride monohydrate. The drug substance is a white crystalline powder, with the following structural formula:
At 25 °C ropivacaine hydrochloride has a solubility of 53.8 mg/mL in water, a distribution ratio between
NAROPIN (ropivacaine hydrochloride) injection is a clear, colorless, and preservative-free solution. Each mL contains 2.1 mg, 5.3 mg, 7.9 mg or 10.6 mg ropivacaine hydrochloride monohydrate (equivalent to 2.0 mg, 5.0 mg, 7.5 mg or 10 mg of ropivacaine hydrochloride anhydrous), and 8.6 mg, 8.0 mg, 7.5 mg or 7.1 mg of sodium chloride; respectively, and sodium hydroxide and hydrochloric acid as pH adjusters, in water for injection. The pH is adjusted between 4.0 to 6.0. The specific gravity of NAROPIN Injection solutions range from 1.002 to 1.005 at 25°C.
8CLINICAL STUDIES
Ropivacaine was studied as a local anesthetic both for surgical anesthesia and for acute pain management
The onset, depth and duration of sensory block are, in general, similar to bupivacaine. However, the depth and duration of motor block, in general, are less than that with bupivacaine.
8.1Epidural Administration in Surgery
There were 25 clinical studies performed in 900 patients to evaluate NAROPIN epidural injection for general surgery. NAROPIN was used in doses ranging from 75 to 250 mg. In doses of 100 to 200 mg, the median (1st to 3rd quartile) onset time to achieve a T10 sensory block was 10 (5 to 13) minutes and the median (1st to 3rd quartile) duration at the T10 level was 4 (3 to 5) hours
8.2Epidural Administration in Cesarean Section
A total of 12 studies were performed with epidural administration of NAROPIN for cesarean section. Eight of these studies involved 218 patients using the concentration of 5 mg/mL (0.5%) in doses up to 150 mg. Median onset measured at T6 ranged from 11 to 26 minutes. Median duration of sensory block at T6 ranged from 1.7 to 3.2 h, and duration of motor block ranged from 1.4 to 2.9 h. NAROPIN provided adequate muscle relaxation for surgery in all cases.
In addition, 4 active controlled studies for cesarean section were performed in 264 patients at a concentration of 7.5 mg/mL (0.75%) in doses up to 187.5 mg. Median onset measured at T6 ranged from 4 to 15 minutes. Seventy-seven to 96% of NAROPIN-exposed patients reported no pain at delivery. Some patients received other anesthetic, analgesic, or sedative modalities during the course of the operative procedure.
8.3Epidural Administration in Labor and Delivery
A total of 9 double-blind clinical studies, involving 240 patients were performed to evaluate NAROPIN for epidural block for management of labor pain. When administered in doses up to 278 mg as intermittent injections or as a continuous infusion, NAROPIN produced adequate pain relief.
A prospective meta-analysis on 6 of these studies provided detailed evaluation of the delivered newborns and showed no difference in clinical outcomes compared to bupivacaine. There were significantly fewer instrumental deliveries in mothers receiving ropivacaine as compared to bupivacaine.
8.4Epidural Administration in Postoperative Pain Management
There were 8 clinical studies performed in 382 patients to evaluate NAROPIN 2 mg/mL (0.2%) for postoperative pain management after upper and lower abdominal surgery and after orthopedic surgery. The studies utilized intravascular morphine via PCA as a rescue medication and quantified as an efficacy variable.
Epidural anesthesia with NAROPIN 5 mg/mL, (0.5%) was used intraoperatively for each of these procedures prior to initiation of postoperative NAROPIN. The incidence and intensity of the motor block were dependent on the dose rate of NAROPIN and the site of injection. Cumulative doses of up to 770 mg of ropivacaine were administered over 24 hours (intraoperative block plus postoperative continuous infusion). The overall quality of pain relief, as judged by the patients, in the ropivacaine groups was rated as good or excellent (73% to 100%). The frequency of motor block was greatest at 4 hours and decreased during the infusion period in all groups. At least 80% of patients in the upper and lower abdominal studies and 42% in the orthopedic studies had no motor block at the end of the 21-hour infusion period. Sensory block was also dose rate dependent and a decrease in spread was observed during the infusion period.
A double-blind, randomized, clinical trial compared lumbar epidural infusion of NAROPIN (n=26) and bupivacaine (n=26) at 2 mg/mL (8 mL/h), for 24 hours after knee replacement. In this study, the pain scores were higher in the NAROPIN group, but the incidence and the intensity of motor block were lower.
Continuous epidural infusion of NAROPIN 2 mg/mL (0.2%) during up to 72 hours for postoperative pain management after major abdominal surgery was studied in 2 multicenter, double-blind studies. A total of 391 patients received a low thoracic epidural catheter, and NAROPIN 7.5 mg/L (0.75%) was given for surgery, in combination with GA. Postoperatively, NAROPIN 2 mg/mL (0.2%), 4 to 14 mL/h, alone or with fentanyl 1, 2, or 4 mcg/mL was infused through the epidural catheter and adjusted according to the patient's needs. These studies support the use of NAROPIN 2 mg/mL (0.2%) for epidural infusion at 6 to 14 mL/h (12 to 28 mg) for up to 72 hours and demonstrated adequate analgesia with only slight and nonprogressive motor block in cases of moderate to severe postoperative pain.
Clinical studies with 2 mg/mL (0.2%) NAROPIN have demonstrated that infusion rates of 6 to 14 mL (12 to 28 mg) per hour provide adequate analgesia with nonprogressive motor block in cases of moderate to severe postoperative pain. In these studies, this technique resulted in a significant reduction in patients' morphine rescue dose requirement. Clinical experience supports the use of NAROPIN epidural infusions for up to 72 hours.
8.5Peripheral Nerve Block
NAROPIN, 5 mg/mL (0.5%), was evaluated for its ability to provide anesthesia for surgery using the techniques of Peripheral Nerve Block. There were 13 studies performed including a series of 4 pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic studies performed on minor nerve blocks. From these, 235 NAROPIN-treated patients were evaluable for efficacy.
NAROPIN was used in doses up to 275 mg. When used for brachial plexus block, onset depended on technique used. Supraclavicular blocks were consistently more successful than axillary blocks. The median onset of sensory block (anesthesia) produced by ropivacaine 0.5% via axillary block ranged from 10 minutes (medial brachial cutaneous nerve) to 45 minutes (musculocutaneous nerve). Median duration ranged from 3.7 hours (medial brachial cutaneous nerve) to 8.7 hours (ulnar nerve). The 5 mg/mL (0.5%) NAROPIN solution gave success rates from 56% to 86% for axillary blocks, compared with 92% for supraclavicular blocks.
In addition, NAROPIN, 7.5 mg/mL (0.75%), was evaluated in 99 NAROPIN-treated patients, in 2 double-blind studies, performed to provide anesthesia for surgery using the techniques of Brachial Plexus Block. NAROPIN 7.5 mg/mL was compared to bupivacaine 5 mg/mL. In 1 study, patients underwent axillary brachial plexus block using injections of 40 mL (300 mg) of NAROPIN, 7.5 mg/mL (0.75%) or 40 mL injections of bupivacaine, 5 mg/mL (200 mg). In a second study, patients underwent subclavian perivascular brachial plexus block using 30 mL (225 mg) of NAROPIN, 7.5 mg/mL (0.75%) or 30 mL of bupivacaine 5 mg/mL (150 mg). There was no significant difference between the NAROPIN and bupivacaine groups in either study with regard to onset of anesthesia, duration of sensory blockade, or duration of anesthesia.
The median duration of anesthesia varied between 11.4 and 14.4 hours with both techniques. In one study, using the axillary technique, the quality of analgesia and muscle relaxation in the NAROPIN group was judged to be significantly superior to bupivacaine by both investigator and surgeon. However, using the subclavian perivascular technique, no statistically significant difference was found in the quality of analgesia and muscle relaxation as judged by both the investigator and surgeon. The use of NAROPIN 7.5 mg/mL for block of the brachial plexus via either the subclavian perivascular approach using 30 mL (225 mg) or via the axillary approach using 40 mL (300 mg) both provided effective and reliable anesthesia.
8.6Local Infiltration
A total of 7 clinical studies were performed to evaluate the local infiltration of NAROPIN to produce anesthesia for surgery and analgesia in postoperative pain management. In these studies 297 patients who received NAROPIN in doses up to 200 mg (concentrations up to 5 mg/mL, 0.5%) were evaluable for efficacy. With infiltration of 100 to 200 mg NAROPIN, the time to first request for analgesic was 2 to 6 hours. When compared to placebo, NAROPIN produced lower pain scores and a reduction of analgesic consumption.
9HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
NAROPIN (ropivacaine hydrochloride) Injection is a clear colorless, and preservative-free solution, available in single-dose containers in 2 mg/mL (0.2%), 5 mg/mL (0.5%), 7.5 mg/mL (0.75%) and 10 mg/mL (1%) concentrations.
10PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - Naropin 10 mL Single Dose Vial Label
NDC 63323-285-03 278513
Naropin
(ropivacaine hydrochloride) Injection, USP
0.2% 20 mg per 10 mL
(2 mg per mL)
For Infiltration, Nerve Block, and
Epidural Administration Only.
Not for Intravenous Administration.
10 mL Single-Dose Vial Rx only

11PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - Naropin 10 mL Single Dose Vial Tray Label
NDC 63323-285-13 278513
Naropin
(ropivacaine hydrochloride) Injection, USP
0.2% 20 mg per 10 mL
(2 mg per mL)
For Infiltration, Nerve Block, and
Epidural Administration Only.
Not for Intravenous Administration.
Rx only
Twenty-five

12PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - Naropin 20 mL Single Dose Vial Label
NDC 63323-285-07 278523
Naropin
(ropivacaine hydrochloride) Injection, USP
0.2% 40 mg per 20 mL
(2 mg per mL)
For Infiltration, Nerve Block, and
Epidural Administration Only.
Not for Intravenous Administration.
20 mL Single-Dose Vial Rx only

13PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - Naropin 20 mL Single Dose Vial Tray Label
NDC 63323-285-23 278523
Naropin
(ropivacaine hydrochloride) Injection, USP
0.2% 40 mg per 20 mL
(2 mg per mL)
For Infiltration, Nerve Block, and
Epidural Administration Only.
Not for Intravenous Administration.
Rx only
Twenty-five

14PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - Naropin 20 mL Single Dose Vial Label
NDC 63323-286-05 278623
Naropin
(ropivacaine hydrochloride) Injection, USP
0.5% 100 mg per 20 mL
(5 mg per mL)
For Infiltration, Nerve Block, and
Epidural Administration Only.
Not for Intravenous Administration.
20 mL Single-Dose Vial Rx only

15PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - Naropin 20 mL Single Dose Vial Tray Label
NDC 63323-286-23 278623
Naropin
(ropivacaine hydrochloride) Injection, USP
0.5% 100 mg per 20 mL
(5 mg per mL)
For Infiltration, Nerve Block, and
Epidural Administration Only.
Not for Intravenous Administration.
Rx only
Twenty-five

16PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - Naropin 30 mL Single Dose Vial Label
NDC 63323-286-09 278631
Naropin
(ropivacaine HCl Injection, USP)
0.5% 150 mg per 30 mL
(5 mg per mL)
For Infiltration, Nerve Block, and
Epidural Administration Only.
Not for Intravenous Administration.
30 mL Single Dose Vial Rx only

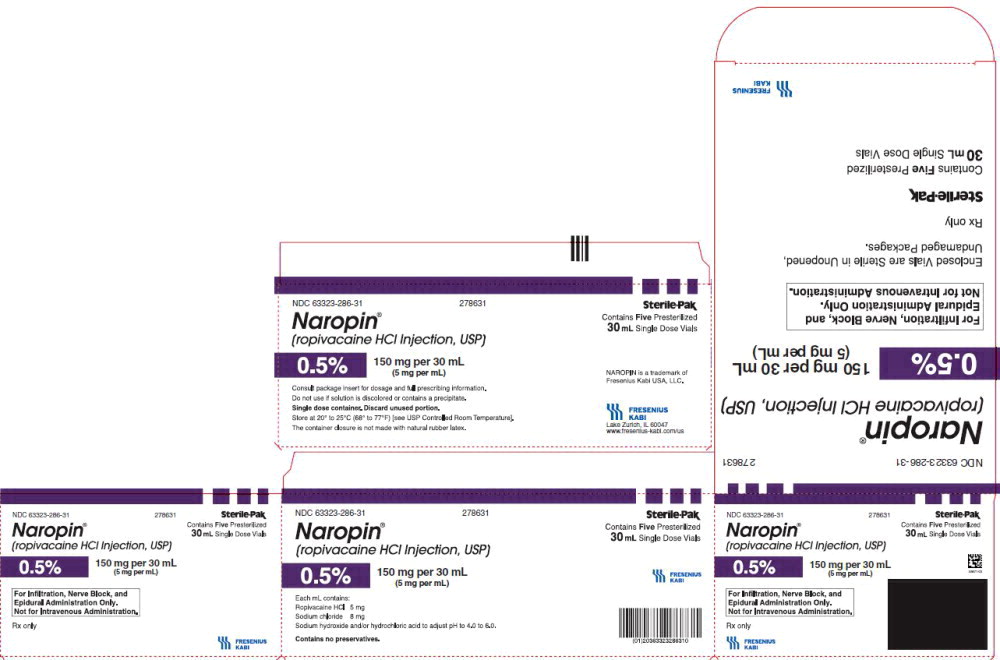
17PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - Naropin 30 mL Single Dose Vial Carton Panel
NDC 63323-286-31 278631
Naropin
(ropivacaine HCl Injection, USP)
0.5% 150 mg per 30 mL
(5 mg per mL)
For Infiltration, Nerve Block, and
Epidural Administration Only.
Not for Intravenous Administration.
Rx only
Contains
18PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - Naropin 30 mL Single Dose Vial Label
NDC 63323-286-11 278635
Naropin
(ropivacaine hydrochloride) Injection, USP
0.5% 150 mg per 30 mL
(5 mg per mL)
For Infiltration, Nerve Block, and
Epidural Administration Only.
Not for Intravenous Administration.
30 mL Single-Dose Vial Rx only

19PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - Naropin 30 mL Single Dose Vial Tray Label
NDC 63323-286-35 278635
Naropin
(ropivacaine hydrochloride) Injection, USP
0.5% 150 mg per 30 mL
(5 mg per mL)
For Infiltration, Nerve Block, and
Epidural Administration Only.
Not for Intravenous Administration.
Rx only
Twenty-five
30 mL Single-Dose Vials

20PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - Naropin 20 mL Single Dose Vial Label
NDC 63323-287-03 278721
Naropin
(ropivacaine hydrochloride) Injection, USP
0.75% 150 mg per 20 mL
(7.5 mg per mL)
For Nerve Block and Epidural Administration
Only. Not for Intravenous Administration.
20 mL Single-Dose Vial Rx only

21PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - Naropin 20 mL Single Dose Vial Tray Label
NDC 63323-287-21 278721
Naropin
(ropivacaine hydrochloride) Injection, USP
0.75% 150 mg per 20 mL
(7.5 mg per mL)
For Nerve Block and Epidural Administration
Only. Not for Intravenous Administration.
Rx only
Twenty-five

22PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - Naropin 10 mL Single Dose Vial Label
NDC 63323-288-03 278811
Naropin
(ropivacaine hydrochloride) Injection, USP
1% 100 mg per 10 mL
(10 mg per mL)
For Epidural Administration Only.
Not for Intravenous Administration.
10 mL Single-Dose Vial Rx only

23PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - Naropin 10 mL Single Dose Vial Tray Label
NDC 63323-288-11 278811
Naropin
(ropivacaine hydrochloride) Injection, USP
1% 100 mg per 10 mL
(10 mg per mL)
For Epidural Administration Only.
Not for Intravenous Administration.
Rx only
Twenty-five

24PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - Naropin 20 mL Single Dose Vial Label
NDC 63323-288-07 278821
Naropin
(ropivacaine hydrochloride) Injection, USP
1% 200 mg per 20 mL
(10 mg per mL)
For Epidural Administration Only.
Not for Intravenous Administration.
20 mL Single-Dose Vial Rx only

25PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - Naropin 20 mL Single Dose Vial Tray Label
NDC 63323-288-21 278821
Naropin
(ropivacaine hydrochloride) Injection, USP
1% 200 mg per 20 mL
(10 mg per mL)
For Epidural Administration Only.
Not for Intravenous Administration.
Rx only
Twenty-five
20 mL Single-Dose Vials

26PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - Naropin 200 mL Single Dose Bottle Label
NDC 63323-285-57 278564
Naropin
(ropivacaine hydrochloride) Injection, USP
0.2% 400 mg per 200 mL
(2 mg per mL)
For Infiltration, Nerve Block, and
Epidural Administration Only.
Not for Intravenous Administration.
Single Dose Only - Discard unused portion.
For continuous infiltration or epidural infusion only.
200 mL Rx only

27PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - Naropin 100 mL Single Dose Bottle Label
NDC 63323-285-51 278565
Naropin
(ropivacaine hydrochloride) Injection, USP
0.2% 200 mg per 100 mL
(2 mg per mL)
For Infiltration, Nerve Block, and
Epidural Administration Only.
Not for Intravenous Administration.
Single Dose Only - Discard unused portion.
For continuous infiltration or epidural infusion only.
100 mL Rx only

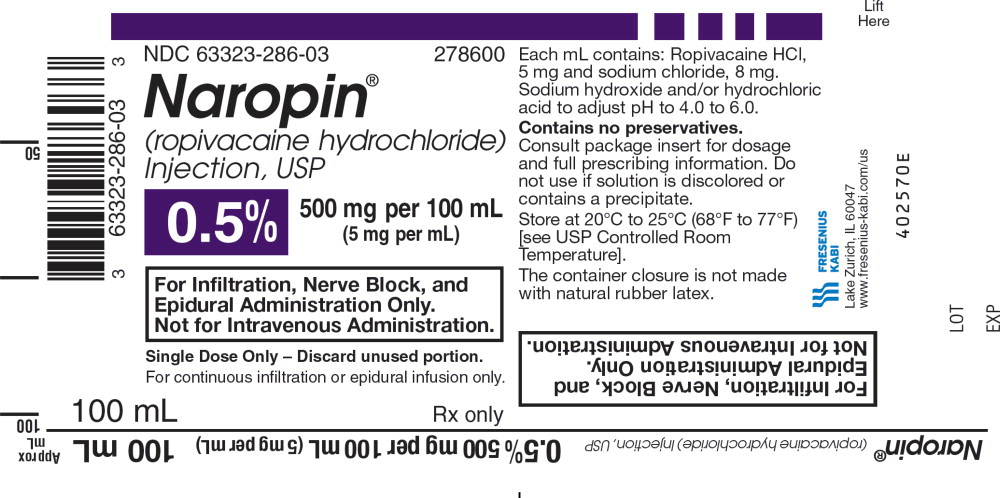
28PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - Naropin 100 mL Single Dose Bottle Label
NDC 63323-286-03 278600
Naropin
(ropivacaine hydrochloride) Injection, USP
0.5% 500 mg per 100 mL
(5 mg per mL)
For Infiltration, Nerve Block, and
Epidural Administration Only.
Not for Intravenous Administration.
Single Dose Only - Discard unused portion.
For continuous infiltration or epidural infusion only.
100 mL Rx only
29PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - Naropin 200 mL Single Dose Bottle Label
NDC 63323-286-33 278663
Naropin
(ropivacaine hydrochloride) Injection, USP
0.5% 1,000 mg per 200 mL
(5 mg per mL)
For Infiltration, Nerve Block, and
Epidural Administration Only.
Not for Intravenous Administration.
Single Dose Only - Discard unused portion.
For continuous infiltration or epidural infusion only.
200 mL Rx only

30PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - Naropin 10 mL Ampule Label
NDC 63323-285-01 278510
Naropin
(ropivacaine HCl Injection, USP)
0.2% 20 mg per 10 mL
(2 mg per mL)
Not for Inhalation.
10 mL ampule Rx only

31PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - Naropin 10 mL Ampule Lidding Label
NDC 63323-285-01 278510
Naropin
(ropivacaine HCl Injection, USP)
0.2% 20 mg per 10 mL
(2 mg per mL)
For Infiltration, Nerve Block, and
Epidural Administration Only.
Not for Intravenous Administration.

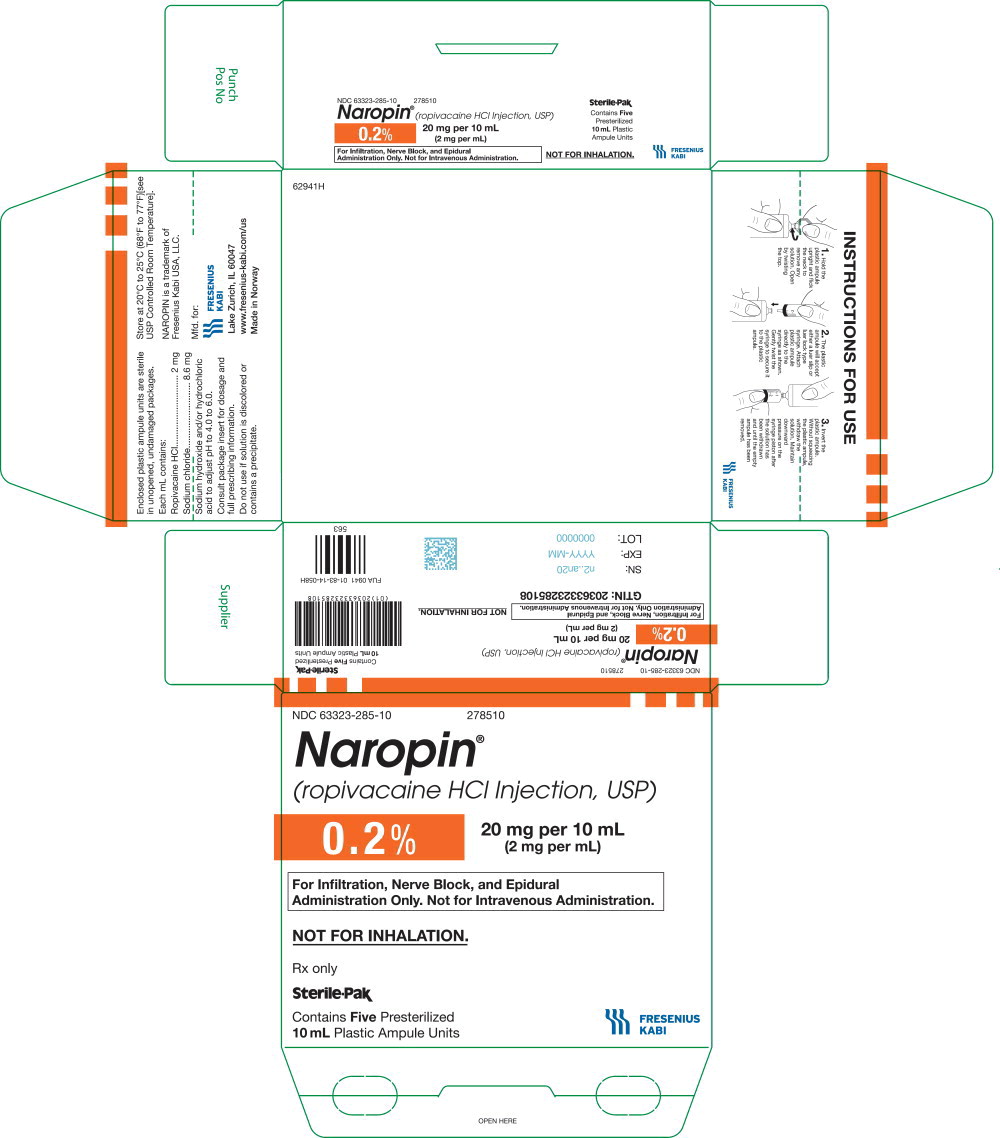
32PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - Naropin 10 mL Ampule Carton Label
NDC 63323-285-10 278510
Naropin
(ropivacaine HCl Injection, USP)
0.2% 20 mg per 10 mL
(2 mg per mL)
For Infiltration, Nerve Block, and
Epidural Administration Only.
Not for Intravenous Administration.
Not for Inhalation.
Rx only
Sterile-Pak
Contains
33PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - Naropin 20 mL Ampule Label
NDC 63323-285-06 278520
Naropin
(ropivacaine HCl Injection, USP)
0.2% 40 mg per 20 mL
(2 mg per mL)
Not for Inhalation.
20 mL ampule Rx only

34PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - Naropin 20 mL Ampule Lidding Label
NDC 63323-285-06 278520
Naropin
(ropivacaine HCl Injection, USP)
0.2% 40 mg per 20 mL
(2 mg per mL)
For Infiltration, Nerve Block, and
Epidural Administration Only.
Not for Intravenous Administration.

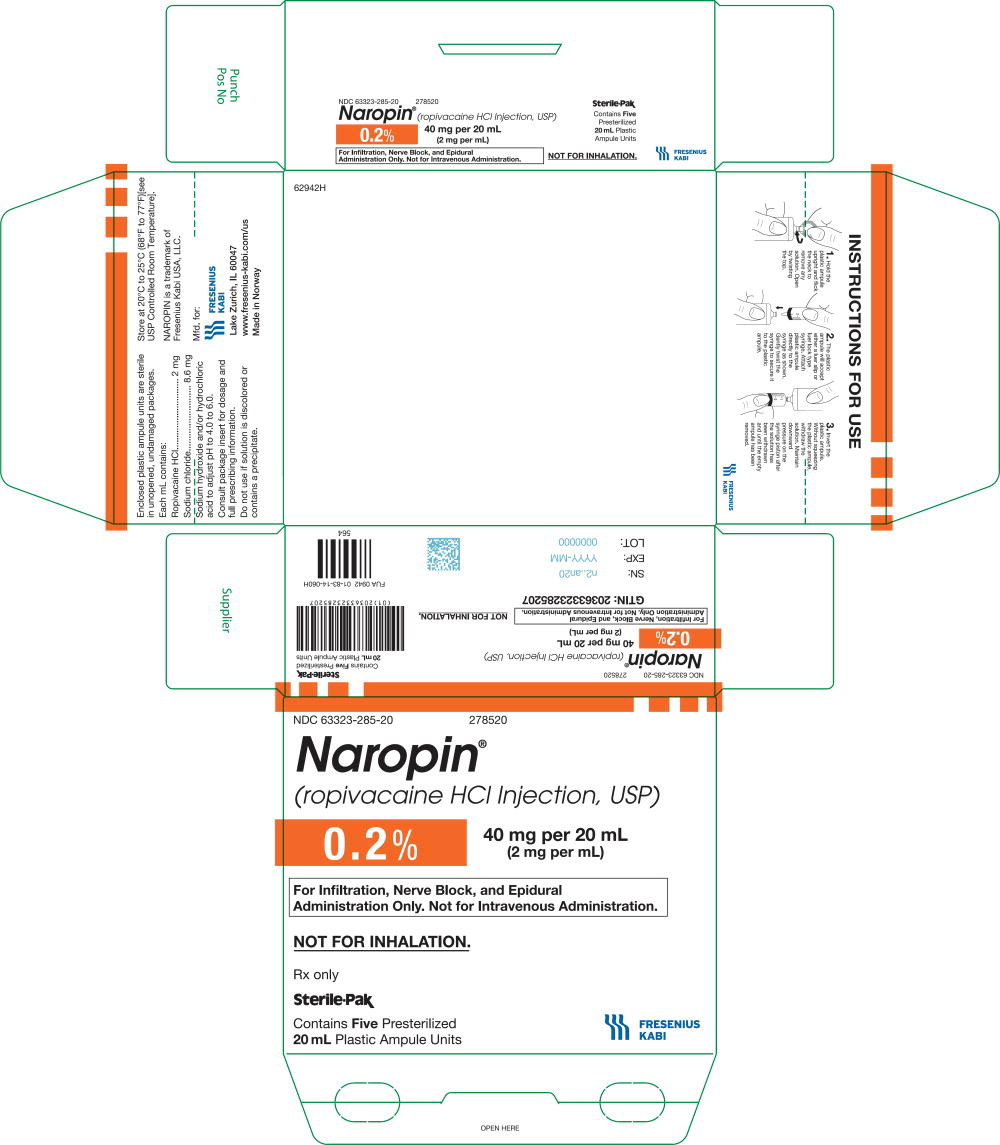
35PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - Naropin 20 mL Ampule Carton Label
NDC 63323-285-20 278520
Naropin
(ropivacaine HCl Injection, USP)
0.2% 40 mg per 20 mL
(2 mg per mL)
For Infiltration, Nerve Block, and
Epidural Administration Only.
Not for Intravenous Administration.
Not for Inhalation.
Rx only
Sterile-Pak
Contains
36PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - Naropin 20 mL Ampule Label
NDC 63323-287-01 278720
Naropin
(ropivacaine HCl Injection, USP)
0.75% 150 mg per 20 mL
(7.5 mg per mL)
Not for Inhalation.
20 mL ampule Rx only

37PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - Naropin 20 mL Ampule Lidding Label
NDC 63323-287-01 278720
Naropin
(ropivacaine HCl Injection, USP)
0.75% 150 mg per 20 mL
(7.5 mg per mL)
For Nerve Block and Epidural
Administration Only.
Not for Intravenous Administration.
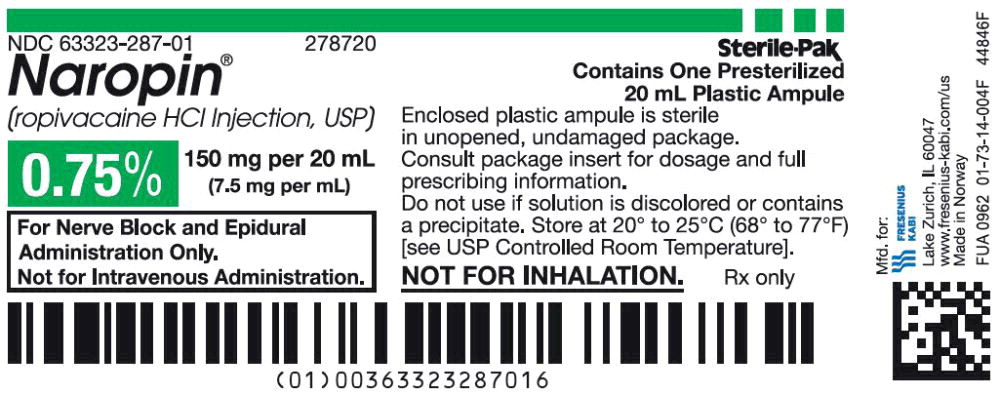
38PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - Naropin 20 mL Ampule Carton Label
NDC 63323-287-20 278720
Naropin
(ropivacaine HCl Injection, USP)
0.75% 150 mg per 20 mL
(7.5 mg per mL)
For Nerve Block and Epidural
Administration Only.
Not for Intravenous Administration.
Not for Inhalation.
Rx only
Sterile-Pak
Contains
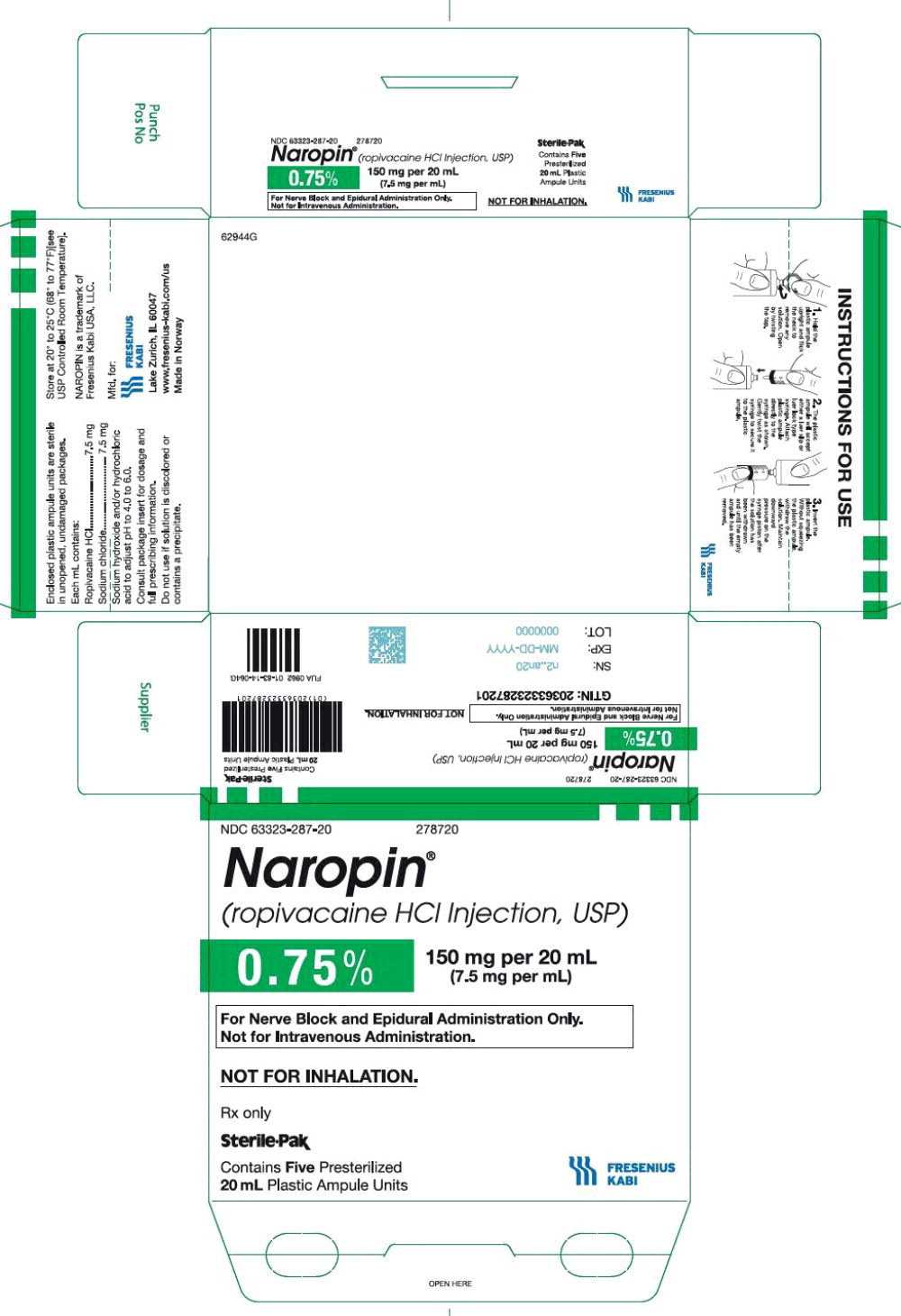
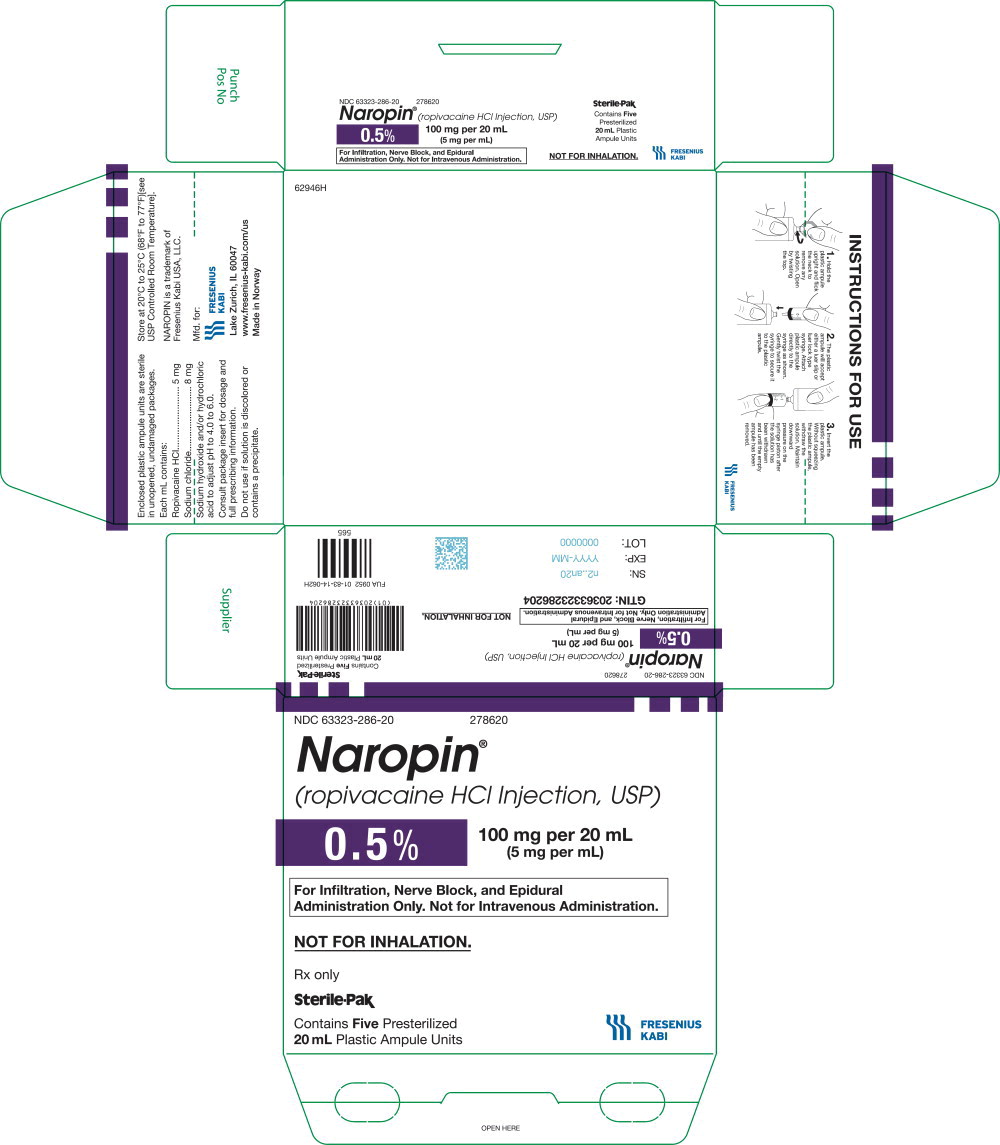
39PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - Naropin 20 mL Ampule Label
NDC 63323-286-01 278620
Naropin
(ropivacaine HCl Injection, USP)
0.5% 100 mg per 20 mL
(5 mg per mL)
Not for Inhalation.
20 mL ampule Rx only

40PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - Naropin 20 mL Ampule Lidding Label
NDC 63323-286-01 278620
Naropin
(ropivacaine HCl Injection, USP)
0.5% 100 mg per 20 mL
(5 mg per mL)
For Infiltration, Nerve Block, and
Epidural Administration Only.
Not for Intravenous Administration.

41PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - Naropin 20 mL Ampule Carton Label
NDC 63323-286-20 278620
Naropin
(ropivacaine HCl Injection, USP)
0.5% 100 mg per 20 mL
(5 mg per mL)
For Infiltration, Nerve Block, and
Epidural Administration Only.
Not for Intravenous Administration.
Not for Inhalation.
Rx only
Sterile-Pak
Contains
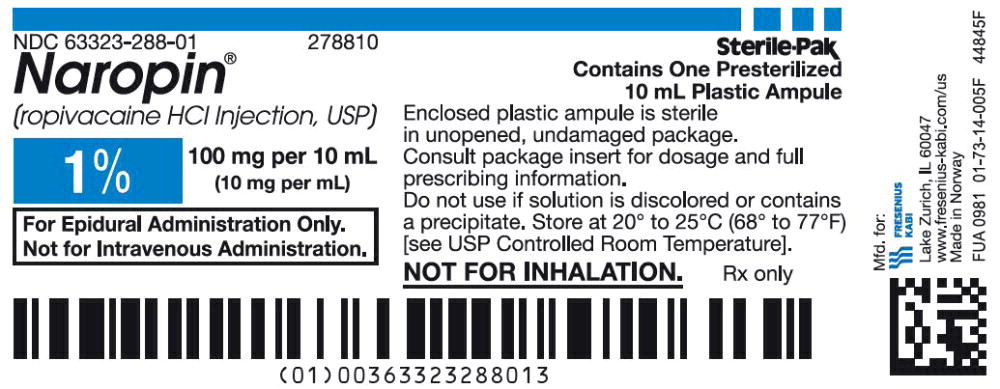
42PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - Naropin 10 mL Ampule Label
NDC 63323-288-01 278810
Naropin
(ropivacaine HCl Injection, USP)
1% 100 mg per 10 mL
(10 mg per mL)
Not for Inhalation.
10 mL ampule Rx only

43PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - Naropin 10 mL Ampule Lidding Label
NDC 63323-288-01 278810
Naropin
(ropivacaine HCl Injection, USP)
1% 100 mg per 10 mL
(10 mg per mL)
For Epidural Administration Only.
Not for Intravenous Administration.
44PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - Naropin 10 mL Ampule Carton Label
NDC 63323-288-10 278810
Naropin
(ropivacaine HCl Injection, USP)
1% 100 mg per 10 mL
(10 mg per mL)
For Epidural Administration Only.
Not for Intravenous Administration.
Not for Inhalation.
Rx only
Sterile-Pak
Contains

45PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - Naropin 20 mL Ampule Label
NDC 63323-288-06 278820
Naropin
(ropivacaine HCl Injection, USP)
1% 200 mg per 20 mL
(10 mg per mL)
Not for Inhalation.
20 mL ampule Rx only

46PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - Naropin 20 mL Ampule Lidding Label
NDC 63323-288-06 278820
Naropin
(ropivacaine HCl Injection, USP)
1% 200 mg per 20 mL
(10 mg per mL)
For Epidural Administration Only.
Not for Intravenous Administration.

47PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - Naropin 20 mL Ampule Carton Label
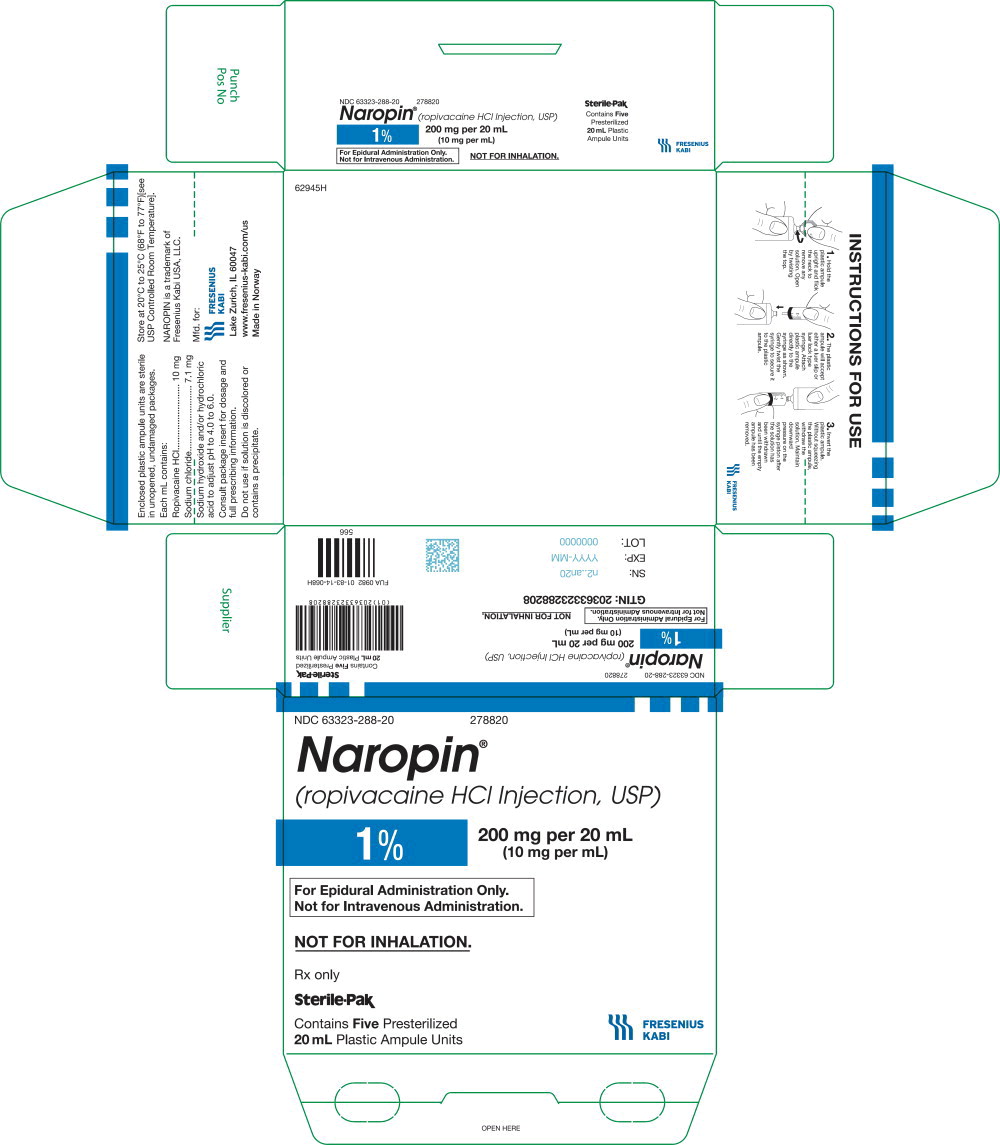
NDC 63323-288-20 278820
Naropin
(ropivacaine HCl Injection, USP)
1% 200 mg per 20 mL
(10 mg per mL)
For Epidural Administration Only.
Not for Intravenous Administration.
Not for Inhalation.
Rx only
Sterile-Pak
Contains
20 mL Plastic Ampule Units
48PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - Naropin 100 mL Bag Label
NDC 63323-285-02
278561
Naropin
(ropivacaine HCl Injection, USP)
0.2% 200 mg per 100 mL
(2 mg per mL)
For Infiltration, Nerve Block, and
Epidural Administration Only

49PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - Naropin 100 mL Bag Shipper Label
Product No. 278561
Naropin
(ropivacaine HCl Injection, USP)
200 mg/100 mL (2 mg/mL)
Rx only
For Infiltration, Nerve Block, and Epidural Administration Only.
NDC 63323-285-61

50PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - Naropin 200 mL Bag Label
NDC 63323-285-04
278563
Naropin
(ropivacaine HCl Injection, USP)
0.2% 400 mg per 200 mL
(2 mg per mL)
For Infiltration, Nerve Block, and
Epidural Administration Only

51PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - Naropin 200 mL Bag Shipper Label
Product No. 278563
Naropin
(ropivacaine HCl Injection, USP)
400 mg/200 mL (2 mg/mL)
Rx only
For Infiltration, Nerve Block, and Epidural Administration Only.
NDC 63323-285-63
