Cholestyramine
What is Choleystyramine (Cholestyramine)?
For many people, high cholesterol feels like a silent problem, there are no symptoms, yet the risk of heart disease grows quietly over time. For others, liver or intestinal problems can cause persistent itching or diarrhea due to excess bile acids. In both cases, finding safe, effective relief can significantly improve quality of life.
Cholestyramine is a long-established medication that helps lower cholesterol and manage bile acid related conditions. Belonging to a class of drugs called bile acid sequestrants, it works inside the intestines rather than in the bloodstream. It has been used safely for decades to improve heart health, relieve bile acid induced itching, and even control certain types of chronic diarrhea.
By reducing cholesterol and supporting liver function, Cholestyramine helps patients take an active step toward preventing complications like atherosclerosis, gallstones, or bile acid diarrhea, offering both protection and relief.
What does Cholestyramine do?
Cholestyramine is primarily prescribed to lower LDL (“bad”) cholesterol levels in the blood, helping to prevent heart attack and stroke. Doctors often recommend it for patients who cannot tolerate statins or who need additional cholesterol control alongside diet and exercise.
Beyond cholesterol management, Cholestyramine also treats bile acid–related disorders, including:
- Itching caused by partial bile duct blockage (cholestatic pruritus)
- Bile acid diarrhea, which can occur after gallbladder removal or intestinal surgery
By binding bile acids in the intestine, the medication helps remove excess bile from the body. This process reduces itching and stabilizes bowel movements.
Clinical studies and real-world experience have shown that Cholestyramine can lower LDL cholesterol by 15–30% when taken regularly with dietary changes (Mayo Clinic, 2024; MedlinePlus, 2024). Patients often report not just better cholesterol readings but improved digestive comfort in bile acid–related conditions.
How does Cholestyramine work?
Cholestyramine works within the digestive tract, not the bloodstream. It acts like a sponge, binding bile acids, natural substances made by the liver from cholesterol and preventing them from being reabsorbed in the intestines.
When bile acids are trapped and excreted in stool, the liver must use more cholesterol to produce new bile acids. This process lowers the cholesterol level in the blood over time.
In bile acid disorders, the same mechanism helps by reducing excess bile that can irritate the intestines or skin. By removing these irritating substances, Cholestyramine provides relief from chronic itching and diarrhea.
Clinically, this mechanism is important because it offers a non-systemic treatment, meaning the drug doesn’t enter the bloodstream, making it safe even for patients with liver or kidney concerns. However, it can affect the absorption of other medications and vitamins, so timing doses carefully is essential.
Cholestyramine side effects
Because Cholestyramine acts locally in the intestines, it doesn’t cause many systemic side effects. However, it can lead to gastrointestinal symptoms, especially when first starting treatment.
Common side effects include:
- Constipation or bloating
- Gas and abdominal discomfort
- Nausea or loss of appetite
Less common but notable effects:
- Indigestion or heartburn
- Diarrhea (in some individuals)
- Unpleasant taste or gritty texture
Long-term or serious effects:
- Deficiency of fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, and K) if taken for extended periods
- Interference with absorption of other medications (e.g., warfarin, thyroid medicines, diuretics)
Who should avoid or use caution with Cholestyramine:
- People with complete bile duct blockage or severe constipation
- Those with phenylketonuria (certain formulations may contain phenylalanine)
To reduce constipation, doctors often recommend drinking plenty of fluids, adding fiber, and adjusting diet as needed. If itching, severe abdominal pain, or yellowing of the skin occurs, medical review is advised.
Cholestyramine dosage
Cholestyramine is usually available as an oral powder that must be mixed with water, juice, or soft food before swallowing. It is not absorbed into the bloodstream and must always be taken by mouth as directed.
Because it can affect the absorption of other medicines, doctors typically recommend taking other medications 1 hour before or 4–6 hours after Cholestyramine to prevent interactions.
Monitoring during therapy may include:
- Lipid panel tests (to track cholesterol levels)
- Liver function tests (if used long-term)
- Vitamin levels, especially for fat-soluble vitamins, in extended use
Patients who experience constipation may benefit from stool softeners or dietary adjustments. For children and older adults, dosages are adjusted carefully based on tolerance and response.
Does Cholestyramine have a generic version?
Yes. Cholestyramine is available in generic form, approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Brand names include Questran, Questran Light, and Prevalite, but the generic version contains the same active ingredient and provides identical therapeutic effects.
Generic Cholestyramine is typically more affordable, and since it acts locally in the intestine, there’s no difference in absorption or efficacy compared to brand-name versions. Patients can safely switch between formulations under a healthcare provider’s guidance.
Conclusion
Cholestyramine has been a trusted medication for decades, offering dual benefits for people with high cholesterol and bile acid–related conditions. By binding bile acids and lowering cholesterol levels, it not only supports cardiovascular health but also brings meaningful relief from itching and digestive discomfort linked to liver or gallbladder issues.
Although it can cause mild digestive side effects or affect vitamin absorption, these risks are manageable with good hydration, balanced nutrition, and regular medical follow-up.
When prescribed and monitored by a qualified healthcare provider, Cholestyramine remains a safe, effective, and non-systemic therapy that helps patients take proactive steps toward better heart and digestive health.
References
- Mayo Clinic. (2024). Cholestyramine (oral route) – Description and precautions. Retrieved from https://www.mayoclinic.org
- MedlinePlus. (2024). Cholestyramine – Drug information. U.S. National Library of Medicine. Retrieved from https://medlineplus.gov/druginfo/meds/a682672.html
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). (2023). Cholestyramine resin labeling and safety information. Retrieved from https://www.accessdata.fda.gov
- National Institutes of Health. (2023). Cholestyramine – Drug summary. LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury. https://www.nih.gov/
- American Heart Association. (2024). Lowering cholesterol through bile acid sequestrants. Retrieved from https://www.heart.org
Approved To Treat
Top Global Experts
Related Clinical Trials
Summary: The purpose of each study is to independently measure the annualized relapse rate (ARR) with administration of frexalimab compared to a daily oral dose of teriflunomide in male and female participants with relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis (aged 18 to 55 years at the time of enrollment). People diagnosed with relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis are eligible for enrollment as long as they mee...
Summary: This phase I trial tests the safety and side effects of leflunomide in combination with steroids in treating patients with acute graft versus host disease who have undergone done stem cell transplant for blood cancers (hematologic malignancies). Sometimes the transplanted cells from a donor can attack the body's normal cells (called graft-versus-host disease). Leflunomide and steroids are immunosu...
Summary: This phase Ib trial tests the safety, side effects, and best dose of leflunomide in combination with gemcitabine in treating patients with pancreatic cancer that may have spread from where it first started to nearby tissue, lymph nodes, or distant parts of the body (advanced) and cannot be removed by surgery (unresectable). Improving the effectiveness of gemcitabine without increasing side effects...
Related Latest Advances
Brand Information
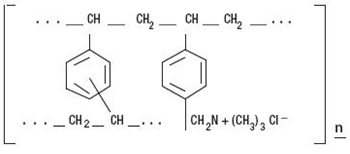
Inactive Ingredients: mannitol, fructose, sorbitol, aspartame, citric acid, lake pigment 6010 D&C yellow #10 aluminum lake and FD&C yellow #6/sunset yellow FCF AI 15% - 18%, orange flavour, propylene glycol alginate, xanthan gum, pectin, silicon dioxide.
In a large, placebo-controlled, multi-clinic study, LRC-CPPT1 , hypercholesterolemic subjects treated with cholestyramine resin had mean reductions in total and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) which exceeded those for diet and placebo treatment by 7.2% and 10.4%, respectively. Over the seven year study period the cholestyramine resin group experienced a 19% reduction (relative to the incidence in the placebo group) in the combined rate of coronary heart disease death plus non-fatal myocardial infarction (cumulative incidences of 7% cholestyramine resin and 8.6% placebo). The subjects included in the study were men aged 35 to 59 with serum cholesterol levels above 265 mg/dL and no previous history of heart disease. It is not clear to what extent these findings can be extrapolated to females and other segments of the hypercholesterolemic population. (See also PRECAUTIONS, Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility.)
Preliminary evidence suggests that the lipid-lowering effects of cholestyramine on total and LDL-cholesterol are enhanced when combined with a HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor, e.g., pravastatin, lovastatin, simvastatin and fluvastatin. Additive effects on LDL-cholesterol are also seen with combined nicotinic acid/cholestyramine therapy. See the PRECAUTIONS, Drug Interactions for recommendations on administering concomitant therapy.
The color of Cholestyramine for Oral Suspension USP Light powder may vary somewhat from batch to batch but this variation does not affect the performance of the product. Place the contents of one single-dose pouch or one level scoopful of Cholestyramine for Oral Suspension USP Light powder in a glass or cup. Add at least 2 to 6 ounces of water or other noncarbonated beverage of your choice. Stir to a uniform consistency and drink.
Cholestyramine for Oral Suspension USP Light powder may also be mixed with highly fluid soups or pulpy fruits with a high moisture content such as applesauce or crushed pineapple.
Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
1. The Lipid Research Clinics Coronary Primary Prevention Trial Results: (I) Reduction in Incidence of Coronary Heart Disease; (II) The Relationship of Reduction in Incidence of Coronary Heart Disease to Cholesterol Lowering. JAMA. 1984; 251:351-374.
Alkem Laboratories Ltd.,
INDIA.
339 Jefferson Road,
Parsippany, NJ 07054
Cholestyramine for Oral Suspension USP Light Powder
4 grams cholestyramine resin USP, per scoopful.
Orange Flavor

Cholestyramine for Oral Suspension USP Light Powder
4 grams cholestyramine resin USP, per pouch.
Orange Flavor
NDC 67877-422-57
Cholestyramine for Oral Suspension USP Light Powder
4 grams cholestyramine resin USP, per pouch.
Orange Flavor