Brand Name
Pamidronate
View Brand InformationFDA approval date: July 28, 2003
Classification: Bisphosphonate
Form: Injection
What is Pamidronate?
Hypercalcemia of Malignancy Pamidronate disodium, in conjunction with adequate hydration, is indicated for the treatment of moderate or severe hypercalcemia associated with malignancy, with or without bone metastases. Patients who have either epidermoid or non-epidermoid tumors respond to treatment with pamidronate disodium. Vigorous saline hydration, an integral part of hypercalcemia therapy, should be initiated promptly and an attempt should be made to restore the urine output to about 2 L/day throughout treatment. Mild or asymptomatic hypercalcemia may be treated with conservative measures . Patients should be hydrated adequately throughout the treatment, but overhydration, especially in those patients who have cardiac failure, must be avoided. Diuretic therapy should not be employed prior to correction of hypovolemia. The safety and efficacy of pamidronate disodium in the treatment of hypercalcemia associated with hyperparathyroidism or with other non-tumor-related conditions has not been established. Paget’s Disease Pamidronate disodium is indicated for the treatment of patients with moderate to severe Paget’s disease of bone. The effectiveness of pamidronate disodium was demonstrated primarily in patients with serum alkaline phosphatase ≥ 3 times the upper limit of normal. Pamidronate disodium therapy in patients with Paget’s disease has been effective in reducing serum alkaline phosphatase and urinary hydroxyproline levels by ≥ 50% in at least 50% of patients, and by ≥ 30% in at least 80% of patients. Pamidronate disodium therapy has also been effective in reducing these biochemical markers in patients with Paget’s disease who failed to respond, or no longer responded to other treatments. Osteolytic Bone Metastases of Breast Cancer and Osteolytic Lesions of Multiple Myeloma Pamidronate disodium is indicated, in conjunction with standard antineoplastic therapy, for the treatment of osteolytic bone metastases of breast cancer and osteolytic lesions of multiple myeloma. The pamidronate disodium treatment effect appeared to be smaller in the study of breast cancer patients receiving hormonal therapy than in the study of those receiving chemotherapy, however, overall evidence of clinical benefit has been demonstrated.
Approved To Treat
Top Global Experts
There are no experts for this drug
Save this treatment for later
Not sure about your diagnosis?
Tired of the same old research?
Related Clinical Trials
There is no clinical trials being done for this treatment
Related Latest Advances
Brand Information
Pamidronate Disodium (Pamidronate Disodium)
1DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Injection: 30 mg/10 mL (3 mg/mL) and 90 mg/10 mL (9 mg/mL) solution in single-dose vials
2CONTRAINDICATIONS
Pamidronate disodium is contraindicated in patients with hypersensitivity to pamidronate disodium, other bisphosphonates, or mannitol. Reactions to pamidronate disodium injection and to mannitol have included anaphylaxis.
3ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions are described, or described in greater detail, in other sections:
- Deterioration in renal function
- Electrolyte disorders
- Osteonecrosis of the jaw
- Atypical fractures of the femur
3.1Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
3.1.1Hypercalcemia of Malignancy
Transient elevation of temperature by at least 1°C was noted 24 to 48 hours after administration of pamidronate disodium in 34% of patients in clinical trials. Local soft-tissue reactions (redness, swelling or induration and pain on palpation) at the site of catheter insertion were observed, most commonly in patients treated with 90 mg of pamidronate disodium. Symptomatic treatment resulted in resolution in all patients.
Cases of uveitis, iritis, scleritis, and episcleritis have been reported, including one case of scleritis and one case of uveitis upon separate rechallenges.
Five of 231 patients (2%) who received pamidronate disodium while enrolled on controlled
clinical trials for management of hypercalcemia were reported to have seizures, including two patients with pre-existing seizure disorders. One patient on the control (saline arm) also had a seizure. At least 15% of patients treated with pamidronate disodium for hypercalcemia of malignancy experienced the following adverse reactions during a clinical trial:
General: Fluid overload, generalized pain
Cardiovascular: Hypertension
Gastrointestinal: Abdominal pain, anorexia, constipation, nausea, vomiting
Genitourinary: Urinary tract infection
Musculoskeletal: Bone pain
Laboratory abnormality: Anemia, hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, hypophosphatemia
Table 1 lists the adverse reactions reported during comparative, controlled trials.
3.1.2Paget’s Disease
Adverse reactions that occurred in at least 5% of patients with Paget’s disease treated with
90 mg of pamidronate disodium in two clinical trials included fever, nausea, back pain, and bone pain. Dizziness, headaches, parathesias, and increased sweating were also reported and occurred more frequently than reported in patients treated with pamidronate for hypercalcemia of malignancy.
At least 10% of all pamidronate disodium-treated patients with Paget’s disease also experienced the following adverse reactions during clinical trials:
Cardiovascular: Hypertension
Musculoskeletal: Arthrosis, bone pain
Nervous system: Headache
3.1.3Osteolytic Bone Metastases of Breast Cancer and Osteolytic Lesions of Multiple Myeloma
The most commonly reported (> 15%) adverse reactions occurred with similar frequencies in the pamidronate disodium and in the placebo group (see Table 2).
In the breast cancer trials, four pamidronate disodium-related adverse reactions, interstitial pneumonitis, malaise and dyspnea, symptomatic hypocalcemia, and severe bone pain, resulted in discontinuation of therapy.
3.2Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during postapproval pamidronate sodium use. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
General: reactivation of Herpes simplex and Herpes zoster, influenza-like symptoms
CNS: confusion and visual hallucinations, sometimes in the presence of electrolyte imbalance
Skin: rash, pruritus
Special senses: conjunctivitis, orbital inflammation
Renal and urinary disorders: focal segmental glomerulosclerosis including the collapsing variant, nephrotic syndrome; renal tubular disorders (RTD); tubulointerstitial nephritis, and glomerulonephropathies.
Laboratory abnormalities: hyperkalemia, hypernatremia, hematuria. Cases of allergic manifestations have been reported, including hypotension, dyspnea, or angioedema, and anaphylactic shock. Pamidronate disodium is contraindicated in patients with clinically significant hypersensitivity to pamidronate disodium or other bisphosphonates
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders: adult respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), interstitial lung disease (ILD).
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders: severe, occasionally incapacitating bone, joint, and/or muscle pain.
4OVERDOSAGE
Cases of drug overdose have been reported in hypercalcemia patients treated with total doses of 225 mg to 300 mg pamidronate disodium given over 2.5 to 4 days. All patients survived, but all developed hypocalcemia that required intravenous and/or oral administration of calcium. If overdosage occurs, treat symptomatic hypocalcemia patients with short-term intravenous calcium.
Single doses of pamidronate disodium should not exceed 90 mg, and the duration of the intravenous infusion should be no less than 2 hours
In addition, one obese woman (95 kg) who was treated with 285 mg of pamidronate disodium/day for 3 days experienced high fever (39.5°C), hypotension (from 170/90 mmHg to 90/60 mmHg), and transient taste perversion, occurring about 6 hours after the first infusion. Fever and hypotension reversed with steroid therapy.
5DESCRIPTION
Pamidronate Disodium Injection is a bisphosphonate available in 30 mg and 90 mg vials for intravenous administration. Each mL of the 30 mg/10 mL vial contains 3 mg pamidronate disodium, 47 mg mannitol; water for injection, q.s.; and phosphoric acid to adjust pH 6.0 to 7.0. Each mL of the 90 mg/10 mL vial contains, 9 mg pamidronate disodium, 37.5 mg mannitol; water for injection, q.s.; and phosphoric acid to adjust pH 6.0 to 7.0.
The pH of a 1% solution of pamidronate disodium in distilled water is approximately 8.3.
Pamidronate disodium, a member of the group of chemical compounds known as bisphosphonates, is an analog of pyrophosphate. Pamidronate disodium is designated chemically as phosphonic acid (3-amino-1-hydroxypropylidene) bis-, disodium salt, and its structural formula is:
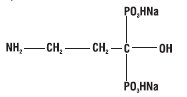
Pamidronate disodium is a white powder. It is soluble in water and in 2N sodium hydroxide, sparingly soluble in 0.1N hydrochloric acid and in 0.1N acetic acid, and practically insoluble in organic solvents. Its molecular formula is C
6HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Pamidronate Disodium Injection is available as follows:
30 mg/10 mL (3 mg/mL) single-dose vial as a clear-colorless solution containing 30 mg of pamidronate disodium and 470 mg of mannitol in 10 mL water for injection.
NDC 67457-430-10
90 mg/10 mL (9 mg/mL) single-dose vial as a clear-colorless solution containing 90 mg of pamidronate disodium and 375 mg of mannitol in 10 mL water for injection.
NDC 67457-446-10
Storage: Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature].
7PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- Advise pregnant women and females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus and to inform their healthcare provider of a known or suspected pregnancy
- Advise women not to breastfeed during and after pamidronate disodium treatment
- Advise males and females of reproductive potential that pamidronate may impair fertility
- Inform patients that the risk of osteonecrosis of the jaw is increased in patients undergoing invasive dental procedures. Advise patients to avoid such procedures, if possible, and to maintain good dental hygiene and routine dental care
- Inform patients that atypical femur fractures have occurred in patients taking bisphosphonates. Advise patients to report any thigh or groin pain
Manufactured for:
Manufactured by:
50107390
Revised: 12/2025
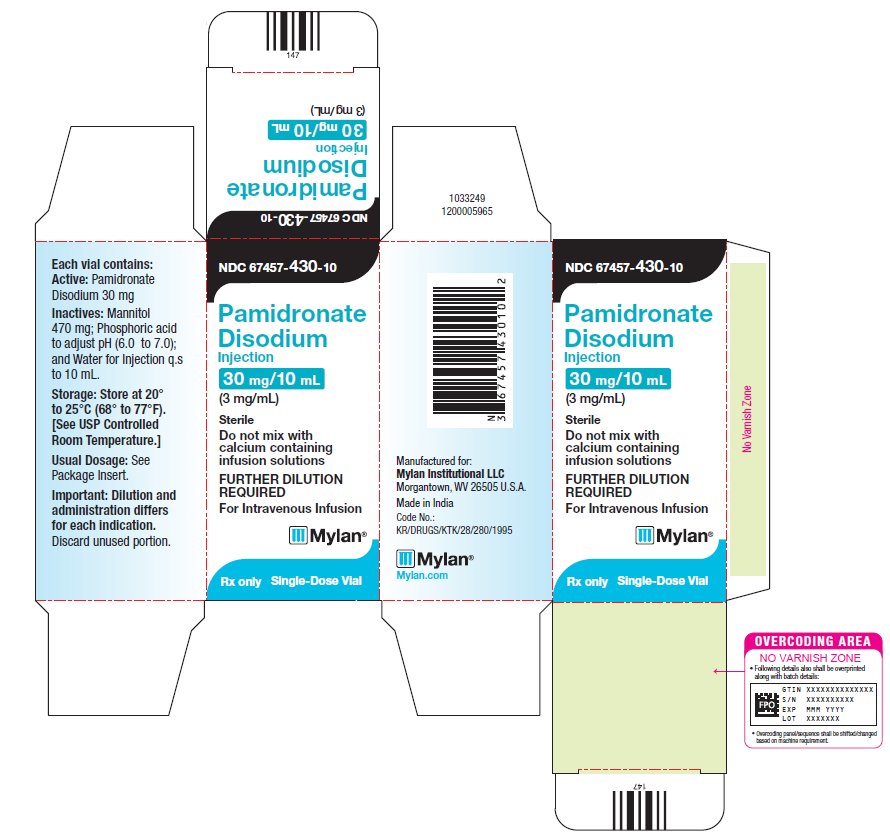
8PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL – 3 mg/mL
NDC 67457-430-10
Pamidronate
30 mg/10 mL
Sterile
Do not mix with
FURTHER DILUTION
For Intravenous Infusion
Mylan
Rx only
Single-Dose Vial
Each vial contains:
Active: Pamidronate
Disodium 30 mg
Active: Pamidronate
Disodium 30 mg
Inactives: Mannitol
Storage: Store at 20°
Usual Dosage: See
Package Insert.
Package Insert.
Important: Dilution and
Discard unused portion.
Manufactured for:
Made in India
Code No.:
KR/DRUGS/KTK/28/280/1995
Mylan.com
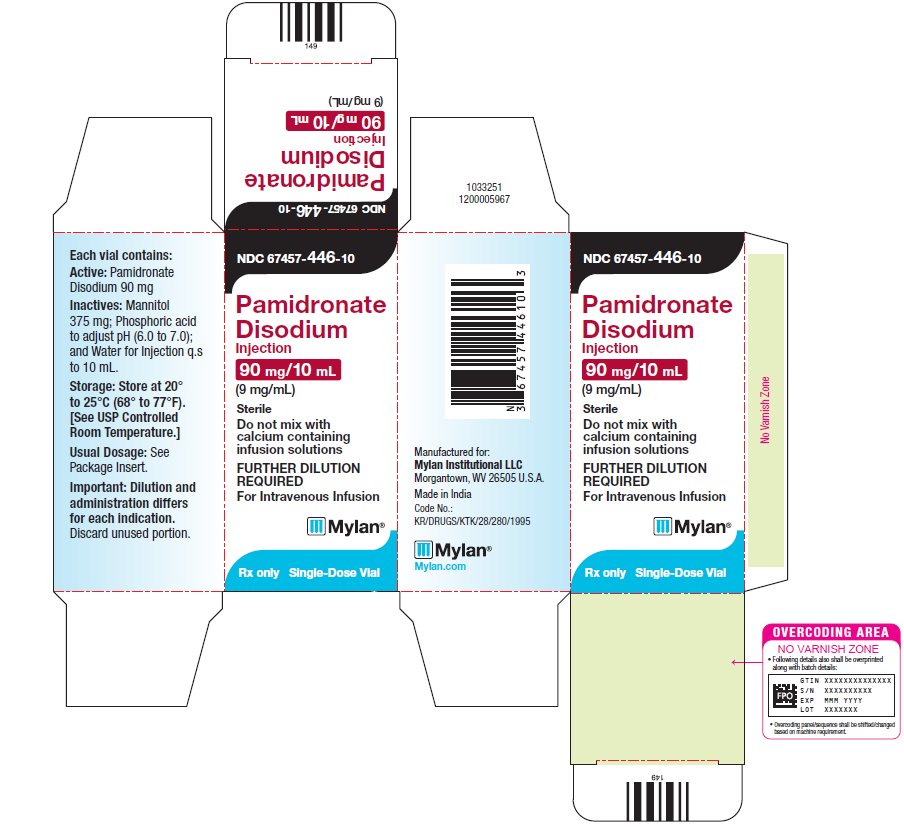
9PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL – 9 mg/mL
NDC 67457-446-10
Pamidronate
90 mg/10 mL
Sterile
Do not mix with
FURTHER DILUTION
For Intravenous Infusion
Mylan
Rx only
Single-Dose Vial
Each vial contains:
Active: Pamidronate
Disodium 90 mg
Active: Pamidronate
Disodium 90 mg
Inactives: Mannitol
375 mg; Phosphoric acid
to adjust pH (6.0 to 7.0);
and Water for Injection q.s
to 10 mL.
375 mg; Phosphoric acid
to adjust pH (6.0 to 7.0);
and Water for Injection q.s
to 10 mL.
Storage: Store at 20°
Usual Dosage: See
Package Insert.
Package Insert.
Important: Dilution and
Discard unused portion.
Manufactured for:
Made in India
Code No.:
KR/DRUGS/KTK/28/280/1995
Mylan.com