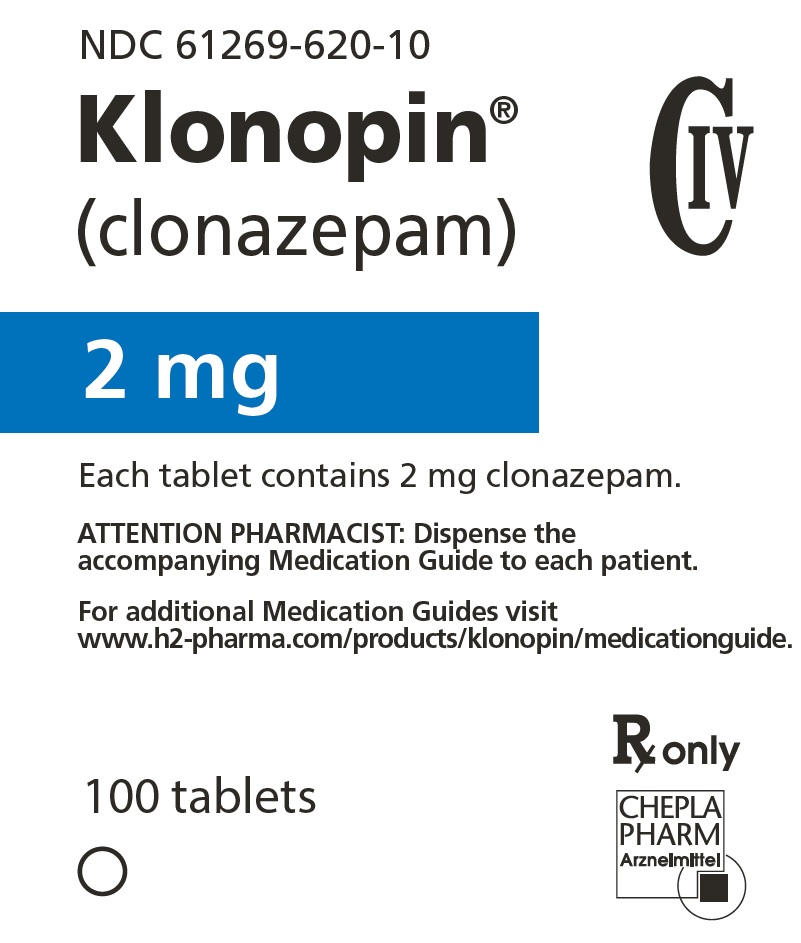
Klonopin
What is Klonopin (ClonazePAM)?
Approved To Treat
Related Clinical Trials
Summary: The effectiveness and efficacy of the combination of pharmacotherapy with the two new recovery-oriented programs, RECOVERYTRSGR for patients with treatment- resistant schizophrenia and RECOVERYTRSBDGR for patients with treatment- resistant bipolar disorder.
Summary: \# Brief Summary (English Version) Tardive Dyskinesia (TD) is a hyperkinetic movement disorder induced by long-term use of dopamine receptor blockers and related drugs. Characterized by involuntary spasms or choreiform movements involving the tongue, lower face, jaw, and limbs (persisting for at least several weeks), TD causes irreversible neurological damage that persists even after discontinuing...
Summary: Hereditary hyperekplexia is a rare neuronal disorder, caused by genetic defects leading to dysfunction of glycinergic neurotransmission. The clinical presentation is characterized by stiffness and exaggerated startle responses to unexpected stimuli, that appear shortly after birth. The generalised stiffness can lead to apnea and sudden infant death syndrome. Several genes are known to be associate...
Related Latest Advances
Brand Information
- Concomitant use of benzodiazepines and opioids may result in profound sedation, respiratory depression, coma, and death. Reserve concomitant prescribing of these drugs for patients for whom alternative treatment options are inadequate. Limit dosages and durations to the minimum required. Follow patients for signs and symptoms of respiratory depression and sedation (see
- The use of benzodiazepines, including Klonopin, exposes users to risks of abuse, misuse, and addiction, which can lead to overdose or death. Abuse and misuse of benzodiazepines commonly involve concomitant use of other medications, alcohol, and/or illicit substances, which is associated with an increased frequency of serious adverse outcomes. Before prescribing Klonopin and throughout treatment, assess each patient's risk for abuse, misuse, and addiction (see
- The continued use of benzodiazepines, including Klonopin, may lead to clinically significant physical dependence. The risks of dependence and withdrawal increase with longer treatment duration and higher daily dose. Abrupt discontinuation or rapid dosage reduction of Klonopin after continued use may precipitate acute withdrawal reactions, which can be life-threatening. To reduce the risk of withdrawal reactions, use a gradual taper to discontinue Klonopin or reduce the dosage (see
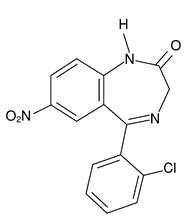
- History of sensitivity to benzodiazepines
- Clinical or biochemical evidence of significant liver disease
- Acute narrow angle glaucoma (it may be used in patients with open angle glaucoma who are receiving appropriate therapy).
For additional Medication Guides visit
www.h2-pharma.com/products/klonopin/medicationguide.
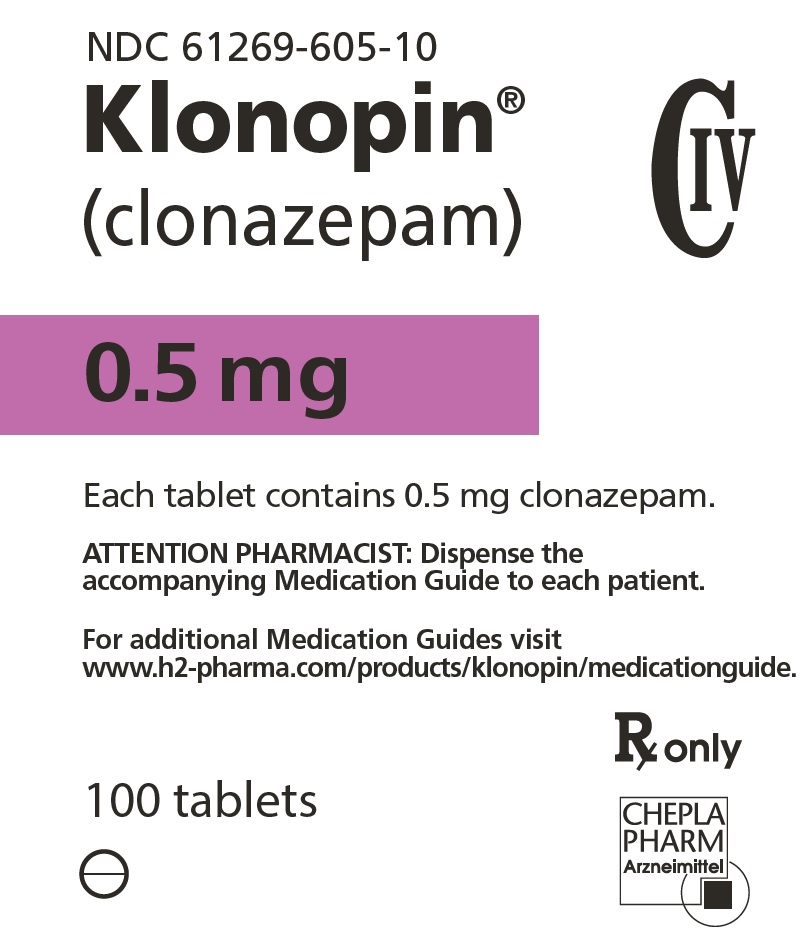
For additional Medication Guides visit
www.h2-pharma.com/products/klonopin/medicationguide.
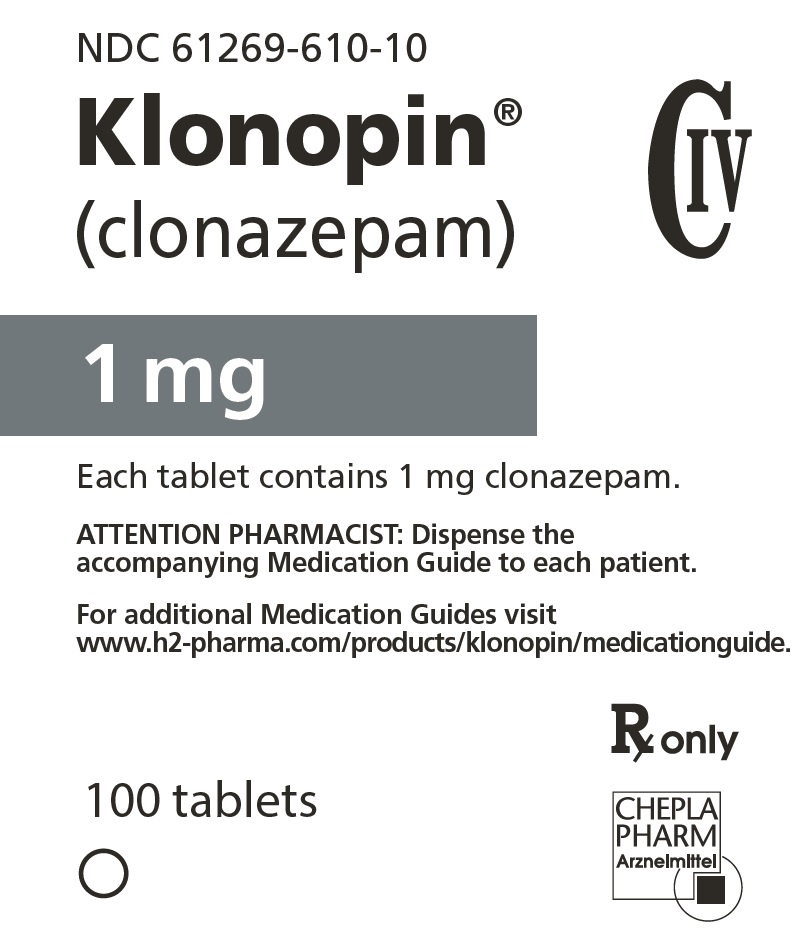
For additional Medication Guides visit
www.h2-pharma.com/products/klonopin/medicationguide.