Provocholine
What is Provocholine (Methacholine)?
Approved To Treat
Related Clinical Trials
Summary: The purpose of this study is to look at children with PCD and see if they have another condition called bronchial hyperresponsiveness.
Summary: The primary objectives of the study are: Part 1: to characterize the potency and variability of dose response on efficacy (Provocative concentration of methacholine causing at least a 20% fall in forced expiratory volume (FEV1) \[PC20\]) of salbutamol administered via MDI with salbutamol HFA-134a or salbutamol HFA-152a in participants with mild asthma. Part 2: to compare the comparative dose respo...
Summary: Background and study aims: The purpose of this research registry is to understand how asthma varies from person to person and monitor changes that may occur over time. The effects that asthma has on the body will be assessed, by looking at different causes/triggers of flare-ups/exacerbations, asthma symptoms, and how inflammation of the airways may affect respiratory health over time. The informat...
Related Latest Advances
Brand Information
7. Repeat steps 2 through 5 for each Provocholine concentration, emptying the nebulizer between each concentration. To keep the cumulative effect of Provocholine relatively constant, the time interval between the commencement of two subsequent concentrations should be kept to 5 minutes.
Administration of the Diluent or Base Solution to Obtain Post-Diluent FEV1 Value
Calculate PC20 using one of the following methods. Determine the percent decrease in FEV1 using the mean post-diluent FEV1 and the lowest FEV1 post-dose, as shown below:
% fall in FEV1 = mean post-diluent FEV
mean post-diluent FEV1
Plot the percent decrease in FEV1 against the increasing methacholine concentration using a log scale and obtain the PC20 by linear interpolation between the last two points, as shown in Figure 1.
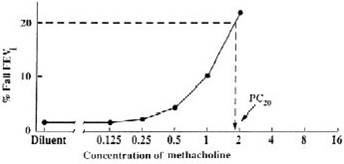
Alternatively, calculate the PC20 as follows:
PC20 = antilog [log C1+ (log C2 - log C1)(20 - R1)]
(R2- R1)
Calculate the PD20 as follows:
PD20 = antilog [log D1+ (log D2 - log D1)(20 - R1)]
(R2- R1)
A negative (normal) methacholine challenge result is defined as FEV1 reduction of < 20% after all the doses (doubling or quadrupling dose increments) in Table 1 (for 5-breath dosimeter method) or Table 2 (for the 2-minute tidal breathing method) have been administered.
- Hypersensitivity to methacholine or other parasympathomimetic agents. Reactions have included rash, itching/swelling (especially of the face/tongue/throat), severe dizziness, trouble breathing.
- Baseline FEV
Beta-agonists, anticholinergics, and theophylline inhibit the response of airways to Provocholine; therefore, hold these drugs before Provocholine use for the following duration:
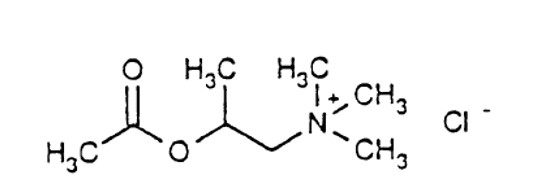
Each kit is packaged in a carton with six plastic vials with twist-off cap each containing 3 mL of the following concentrations of methacholine chloride solution. Each solution also contains: Sodium Acetate Trihydrate, Sodium Chloride, glacial acetic acid as pH adjuster.
- Provocholine (methacholine chloride) Powder for Inhalation Solution: in amber glass vials that contain 100 mg of methacholine chloride powder, white to off-white in color. Cartons have 6 vials (NDC 64281-100-06).
- Provocholine (methacholine chloride) Inhalation Solution Kit (Sterile):
- Powder for inhalation solution: Store the supplied powder at 59
- Provocholine inhalation solution kit: Store between 59
Inform the patient or caregiver that severe bronchoconstriction can result from Provocholine administration [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Inform the patient or caregiver that Provocholine may produce mild cough, chest tightness or shortness of breath.

®Provocholine is a registered trademark of Methapharm Inc.

