Zolgensma
What is Zolgensma (Onasemnogene Abeparvovec-Xioi)?
Approved To Treat
Related Clinical Trials
Summary: In this observational study, researchers are looking at the effects of spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) drugs on the muscles and nerve cells in patients with SMA. Primary Objectives * To evaluate the feasibility and reliability of performing MR functional imaging in exercising muscle in patients with SMA. * To evaluate patients with SMA types 2 and 3 at baseline and longitudinally at 6 and 12 months ...
Summary: Adult SMA REACH is a data collection study aiming to gain a better understanding of the impact of standards of care and new treatments on the natural history of Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA). This study is sponsored by The Newcastle upon Tyne Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust. Adult SMA REACH is funded by Biogen and Roche. Currently, there are three drug treatments available for SMA in the UK: Zolgen...
Summary: Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) is a neurogenetic disorder caused by a loss or mutation in the survival motor neuron 1 gene (SMN1) on chromosome 5q13, which leads to reduced SMN protein levels and a selective dysfunction of motor neurons. SMA is an autosomal recessive, early childhood disease with an incidence of 1:10,000 live births. SMA is the leading cause of infant mortality due to genetic disea...
Related Latest Advances
Brand Information
- Cases of acute liver failure with fatal outcomes have been reported. Acute serious liver injury and elevated aminotransferases can also occur with ZOLGENSMA
- Patients with preexisting liver impairment may be at higher risk
- Prior to infusion, assess liver function of all patients by clinical examination and laboratory testing. Administer systemic corticosteroid to all patients before and after ZOLGENSMA infusion. Continue to monitor liver function for at least 3 months after infusion, and at other times as clinically indicated
- The safety and effectiveness of repeat administration of ZOLGENSMA have not been evaluated
- The use of ZOLGENSMA in patients with advanced SMA (e.g., complete paralysis of limbs, permanent ventilator-dependence) has not been evaluated
- Prior to ZOLGENSMA infusion:
- One day prior to ZOLGENSMA infusion, begin administration of systemic corticosteroids equivalent to oral prednisolone at 1 mg per kg of body weight per day (mg/kg/day) for a total of 30 days.
- Administer ZOLGENSMA as a single-dose intravenous infusion through a venous catheter.
- Place a primary catheter into a vein (generally a peripheral vein in the arm or leg). Insertion of a back-up catheter is recommended.
- Program syringe pump for saline priming, or prime tubing manually with saline.
- Administer ZOLGENSMA as a slow infusion over 60 minutes. DO NOT INFUSE AS AN INTRAVENOUS PUSH OR BOLUS.
- Flush line with saline following completion of infusion.
- Monitor liver function by clinical examination and by laboratory testing on a regular basis, and at other times as clinically indicated
- At the end of the 30-day period of systemic corticosteroid treatment, check liver status clinically and by assessing alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), total bilirubin, prothrombin time, and international normalized ratio (INR).
- Promptly assess and closely monitor patients with worsening liver function test results and/or signs or symptoms of acute illness (e.g., vomiting, deterioration in health)
- For patients with unremarkable findings (normal clinical exam, total bilirubin, prothrombin time, and INR and ALT and AST levels below 2 × upper limit of normal [ULN]): Taper the corticosteroid dose gradually over the next 28 days. Do not stop systemic corticosteroids abruptly
- If liver function abnormalities persist, continue systemic corticosteroids (equivalent to oral prednisolone at 1 mg/kg/day) until AST and ALT values are both below 2 × ULN and all other assessments return to normal range, and then taper the corticosteroid dose gradually over the next 28 days or longer if needed. Do not stop systemic corticosteroids abruptly
- If liver function abnormalities continue to persist ≥ 2 × ULN after the 30-day period of systemic corticosteroids, promptly consult a pediatric gastroenterologist or hepatologist
- If oral corticosteroid therapy is not tolerated, consider intravenous corticosteroids as clinically indicated
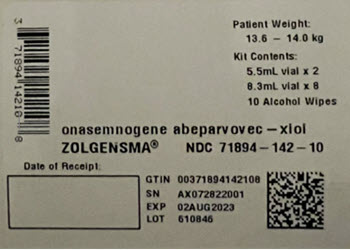
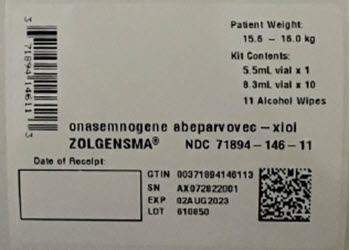
- Thaw ZOLGENSMA before use. The contents of the ZOLGENSMA kit will thaw in approximately 16 hours if placed in a refrigerator, or in approximately 6 hours if placed at room temperature. If thawed in a refrigerator, remove from refrigerator on day of dosing.
- When thawed, ZOLGENSMA is a clear to slightly opaque, colorless to faint white liquid, free of particles. Visually inspect vials for particulate matter and discoloration prior to infusion. Do not use vials if particulates or discoloration are present.
- DO NOT SHAKE.
- Draw the appropriate dose volume from all vials into a syringe, remove air from the syringe, cap the syringe, and deliver the syringe at room temperature to the patient infusion location.
- Use ZOLGENSMA within 8 hours of drawing into syringe. Discard the vector-containing syringe if the drug is not infused within the 8-hour timeframe.
- DO NOT REFREEZE.
- Liver function (clinical exam, AST, ALT, total bilirubin, albumin, prothrombin time, partial thromboplastin time [PTT], and INR) at baseline. Monitor liver function (AST, ALT, total bilirubin, prothrombin time, INR) weekly for the first month after ZOLGENSMA infusion and during the corticosteroid taper period (28 days or longer if needed). If the patient is clinically stable with unremarkable findings (normal clinical exam, total bilirubin, and prothrombin and INR results, and ALT and AST levels below 2 × ULN) at the end of the corticosteroid taper period, continue to monitor liver function every other week for another month.
- Platelet counts weekly for the first month, and then every other week for the second and third months, until platelet counts return to baseline.