Netspot
What is Netspot (68GA-Dotatate)?
For people living with certain rare cancers, getting an accurate diagnosis can be one of the most challenging steps in their journey. Neuroendocrine tumors (NETs), which can develop in the pancreas, gastrointestinal tract, or lungs, often grow slowly and may not cause clear symptoms at first. Detecting and understanding these tumors requires precise imaging and that’s where Netspot (68Ga-Dotatate) plays a critical role.
Netspot is a radiopharmaceutical imaging agent used in positron emission tomography (PET) scans to locate and evaluate somatostatin receptor–positive neuroendocrine tumors in adults and children. It belongs to a class of diagnostic agents known as somatostatin analogs, which bind to specific receptors on neuroendocrine tumor cells. Introduced as a specialized diagnostic tool, Netspot helps physicians visualize the extent and activity of NETs more clearly than traditional imaging methods, guiding more accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
Approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2016, Netspot marked a major advancement in nuclear medicine by offering improved precision in detecting these complex tumors.
What does Netspot do?
Netspot is not a cancer treatment. Instead, it is a diagnostic imaging agent that helps doctors detect and monitor neuroendocrine tumors (NETs). These tumors often express a protein called the somatostatin receptor, which is found in higher concentrations on the surface of NET cells.
When used during a PET scan, Netspot helps physicians see where these receptors and therefore, the tumors are located in the body. This can include tumors in the pancreas, intestines, or lungs, and areas where cancer may have spread.
By providing high-resolution, whole-body images, Netspot allows healthcare teams to:
- Identify the location, size, and number of NET lesions
- Assess whether the cancer has metastasized (spread to other organs)
- Determine eligibility for targeted treatments, such as peptide receptor radionuclide therapy (PRRT)
Clinical studies have shown that Netspot PET imaging is significantly more accurate than older imaging techniques like octreotide scans, leading to better-informed treatment decisions and improved patient outcomes (NIH, 2023).
How does Netspot work?
Netspot works through a combination of molecular targeting and advanced imaging technology. The active ingredient, 68Ga-Dotatate, is a radioactive tracer made by attaching the radioactive isotope gallium-68 to a somatostatin analog called Dotatate.
When injected into the body, 68Ga-Dotatate travels through the bloodstream and attaches to somatostatin receptors found on neuroendocrine tumor cells. Once bound, it emits tiny signals of positron radiation, which are detected by the PET scanner. The scanner then converts these signals into detailed, three-dimensional body images, highlighting areas where NETs are active.
In simpler terms, Netspot “lights up” the tumor cells that have somatostatin receptors, allowing doctors to see the precise location and spread of the disease. This level of clarity is crucial for choosing the most appropriate therapy whether surgery, targeted therapy, or radiotherapy.
Clinically, this mechanism matters because accurate tumor mapping helps avoid unnecessary procedures and ensures that treatment is directed at the most affected areas.
Netspot side effects
Netspot is generally very well tolerated, and side effects are uncommon. Because the drug is used only for diagnostic purposes and is quickly cleared from the body, the amount of radiation exposure is low.
Common side effects may include:
- Mild nausea
- Headache or dizziness
- Injection site pain or redness
- Flushing or warmth sensation
Less common or serious side effects may include:
- Allergic reactions (such as rash, itching, or swelling)
- Low blood pressure or fainting during injection
- Temporary changes in heart rate
Allergic or hypersensitivity reactions are rare but can occur, particularly in people who have had reactions to similar contrast agents. The injection is administered by trained medical professionals in a controlled environment, allowing for immediate management of any adverse response.
Netspot’s radiation dose is carefully controlled and safe for diagnosis. Pregnant or breastfeeding women should inform their doctors due to potential risks to the baby.
Netspot dosage
Netspot is administered as a single IV injection just before a PET scan, prepared by nuclear medicine professionals. Patients wait 30-90 minutes for the tracer to circulate, then undergo a 30-minute PET scan requiring stillness.
Netspot dosage is standardized, not based on body weight or age. Patients should drink fluids and urinate frequently post-scan to eliminate the tracer. Immediate side effects are rare. Long-term or repeated use is typically not needed unless follow-up imaging is required.
Does Netspot have a generic version?
As of 2025, there is no FDA-approved generic version of Netspot (68Ga-Dotatate). It is currently available only under the brand name Netspot, manufactured by Advanced Accelerator Applications USA, Inc., a subsidiary of Novartis. However, international versions may exist in other markets.
While other approved imaging agents like Locametz (68Ga-PSMA-11) for prostate cancer and 68Ga-DOTATOC (for somatostatin receptors) exist, they serve different diagnostic purposes and aren’t Netspot substitutes. A generic Netspot will need to prove identical purity, effectiveness, and safety. Currently, Netspot is used in specialized centers for neuroendocrine tumor PET scans.
Conclusion
Netspot (68Ga-Dotatate) represents a breakthrough in neuroendocrine tumor detection and management. By combining targeted molecular imaging with PET technology, it allows doctors to see tumors with remarkable clarity, improving diagnostic accuracy and guiding more effective treatment strategies.
Netspot is crucial for understanding and monitoring neuroendocrine tumors, from diagnosis to ongoing care. It boasts a strong safety record, minimal side effects, and precise imaging. This diagnostic tool empowers both patients and clinicians by providing detailed information for confident, personalized decisions, ultimately leading to better outcomes.
References
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). (2024). Netspot (68Ga-Dotatate) prescribing information. Retrieved from https://www.accessdata.fda.gov
- Mayo Clinic. (2024). Gallium Ga 68 Dotatate (intravenous route): Description and precautions. Retrieved from https://www.mayoclinic.org
- MedlinePlus. (2024). Gallium Ga 68 Dotatate injection: Uses and safety information. National Library of Medicine. Retrieved from https://medlineplus.gov
- National Institutes of Health (NIH). (2023). Advances in molecular imaging of neuroendocrine tumors using Ga-68-labeled tracers. Retrieved from https://www.nih.gov
Approved To Treat
Top Global Experts
Related Clinical Trials
Summary: Antineutrophil cytoplasm antibody (ANCA)-associated vasculitis (AAV) is a severe autoimmune condition characterised by inflammation of small blood vessels. The condition causes multi-organ dysfunction and, if left untreated, is usually fatal. AAV is difficult to diagnose and the degree of disease activity is challenging to monitor. Current methods of disease activity assessment are either inaccura...
Background: About 5% to 10% of differentiated thyroid cancers become resistant to standard treatment with radioactive iodine. In these cases, treatment options are limited and generally not effective. Researchers want to see if they can better detect thyroid tumors by using a compound called 68Gallium-DOTATATE. This compound may bind to a tumor and make it visible during a positron emission tomography/compute...
Summary: This trial studies how well 68Ga-DOTATATE digital PET/CT work in diagnosing soft tissue sarcoma. 68Ga-DOTATATE is a radiotracer that may improve image quality of PET imaging. PET is an established imaging technique that utilizes small amounts of radioactivity attached to very minimal amounts of tracer, in the case of this research, 68Ga-DOTATATE. CT images provide an exact outline of organs and po...
Related Latest Advances
Brand Information
- Vial 1 (reaction vial with lyophilized powder): 40 mcg of dotatate, 5 mcg of 1,10-phenanthroline, 6 mcg gentisic acid and 20 mg D-mannitol for injection as a white lyophilized powder in a 10 mL glass vial with light-blue flip-off cap
- Vial 2 (buffer vial): clear, and colorless reaction buffer solution (60 mg formic acid, 56.5 mg sodium hydroxide in approximately 1 mL volume) in a 10 mL olefin polymer vial with a yellow flip-off cap
- Eckert & Ziegler GalliaPharm (
- IRE ELiT Galli Eo (
- Hypersensitivity reactions
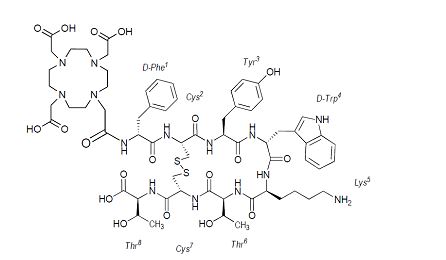
- Vial 1 (reaction vial with lyophilized powder) contains: 40 mcg dotatate, 5 mcg 1,10-phenanthroline; 6 mcg gentisic acid; 20 mg mannitol.
- Vial 2 (buffer vial) contains: 60 mg formic acid; 56.5 mg sodium hydroxide and water for injection.


