Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
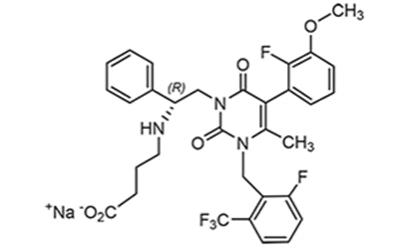
The safety of ORIAHNN was evaluated in two 6-month, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials (Studies UF-1 and UF-2), in which 790 premenopausal women received at least 1 dose of ORIAHNN (n=395), elagolix 300 mg twice daily (n=199), or placebo (n=196)
Serious Adverse Events
Serious adverse events were reported in three (0.8%) ORIAHNN-treated women in Studies UF-1 and UF-2. Two women had heavy menstrual bleeding and required blood transfusion due to anemia (0.5%) and one woman with history of bariatric surgery had a laparoscopic cholecystectomy due to cholelithiasis.
In Study UF-3, two women were diagnosed with breast cancer. One woman had completed 6 months of treatment with ORIAHNN in Study UF-1 and received 34 additional days of ORIAHNN in Study UF-3 when diagnosed. The second woman had received placebo in Study UF-2 and completed 6 months of ORIAHNN in Study UF-3 when diagnosed
Adverse Reactions Leading to Study Discontinuation
In Studies UF-1 and UF-2, the discontinuation rate due to adverse reactions was 10% among ORIAHNN-treated women and 7% among placebo-treated women. The most common adverse reactions leading to study drug discontinuation in the ORIAHNN group were nausea (1%), headache (1%), alopecia (1%), metrorrhagia (1%), menorrhagia (1%), and hot flush (1%). One event each of the following adverse reactions led to study drug discontinuation: affect lability, angina pectoris, depression, hepatic enzyme increased, homicidal ideation, hypertension, irritability, thrombosis.
In women who received ORIAHNN in Studies UF-1 or UF-2 and then in Study UF-3, 4% discontinued treatment due to adverse reactions. Three women discontinued due to serious adverse events (one each for breast cancer, menorrhagia with pelvic pain, and hysterectomy).
Common Adverse Reactions
Adverse reactions reported in ≥5% of ORIAHNN-treated women in Studies UF-1 and UF-2 and at a greater frequency than placebo-treated women are presented in Table 1.
The most commonly reported adverse reactions in the blinded extension trial (Study UF-3) were consistent with those in the placebo-controlled trials.
Less Common Adverse Reactions
In Studies UF-1 and UF-2, adverse reactions reported in ≥3% and <5% in the ORIAHNN group and greater incidence than the placebo group included: libido decreased, arthralgia, hypertension, alopecia, mood swings, influenza, abdominal distension, upper respiratory tract infection, menorrhagia, vomiting, and weight increased.
Thromboembolic and Vascular Events
In the Studies UF-1, UF-2, and UF-3, two (0.4%) thrombotic events occurred in 453 ORIAHNN-treated patients (thrombosis in the calf and pulmonary embolism)
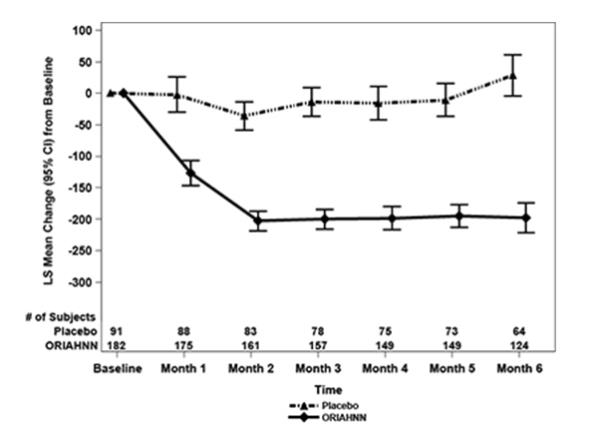
Bone Loss
The effect of ORIAHNN on BMD was assessed by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA).
In Studies UF-1 and UF-2, there was a greater decrease in BMD in women treated with ORIAHNN for 6 months compared to women treated with placebo. In Study UF-3, continued bone loss was observed in some women who received ORIAHNN for 12 consecutive months. The mean percent change from baseline in lumbar spine BMD at Month 6 (Studies UF-1 and UF-2) and Month 12 (Study UF-3) is presented in Table 2.
Following 12 months of ORIAHNN treatment in Study UF-3, a decline in lumbar spine BMD of >3% was seen in 27% (48/175) of women and a decline of ≥8% was seen in 1.7% (3/175) of women.
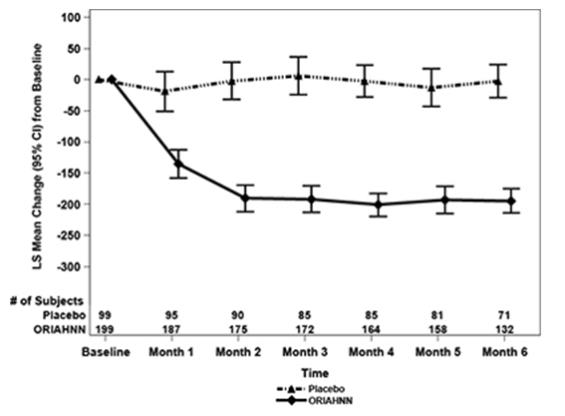
To assess for recovery, the change in BMD over time was analyzed for women who received continuous ORIAHNN treatment for up to 12 months and were then followed after cessation of therapy for an additional 12 months in Study UF-3 (Figure 1). The LS mean percent change from baseline in BMD 12 months after cessation of therapy was -0.72 (95% CI -1.2, -0.2), -0.59 (-1.0, -0.2), and -0.95 (-1.6, -0.3) at the lumbar spine, total hip, and femoral neck, respectively. Twelve months after cessation of ORIAHNN, continued bone loss was observed at the lumbar spine, total hip, and femoral neck in 24%, 32%, and 40% of women, respectively. Partial recovery was observed in 46%, 33%, and 38% and full recovery was observed in 30%, 35%, and 22% of women at these same sites. The time to maximum recovery in women who partially recovered is unknown.
Figure 1. Mean Percent Change From Baseline in Lumbar Spine BMD in Women Who Received 12 Months of ORIAHNN (On-Treatment) and 12 Months of Follow Up (Off Treatment)
Suicidal Ideation, Suicidal Behavior, and Exacerbation of Mood Disorders
In the placebo-controlled trials (Studies UF-1 and UF-2), ORIAHNN was associated with adverse mood changes. Depression, depressed mood, and/or tearfulness were reported in 3% of ORIAHNN-treated women compared to 1% of placebo-treated women. One woman treated with lower dose elagolix alone for another disease completed suicide 2 days after elagolix discontinuation.
Hepatic Transaminase Elevations
In Studies UF-1 and UF-2, elevations of serum ALT and AST with no concurrent elevations of bilirubin were reported.
- ALT elevations to at least 3 times the upper limit of normal (ULN) occurred in 1.1% (4/379) of ORIAHNN-treated women and no placebo-treated women. Peak elevation of ALT almost 8 times the ULN was reported in 1 ORIAHNN-treated woman.
- AST elevations to at least 3 times the ULN occurred in 5/379 (1.3%) in ORIAHNN-treated women and no placebo-treated women. Peak elevation of AST 6 times the ULN was reported in 1 ORIAHNN-treated woman.
Blood Pressure Elevations
There were more ORIAHNN-treated women with systolic blood pressure ≥ 160 mmHg (7.1%) and diastolic blood pressure ≥ 100 mmHg (11.3%) compared to placebo-treated women (3.7% and 6.3%, respectively). The incidence of hypertensive adverse reactions was 3.8% in ORIAHNN-treated women and 3.1% placebo-treated women. One ORIAHNN-treated woman in Study UF-1, with no prior history but with elevated cholesterol levels, had severe hypertension (BP 204/112) and chest pain. ECG was negative. Her hypertension was controlled with anti-hypertensives and she completed Study UF-3.
Changes in Lipid Parameters
Increases in total cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), serum triglycerides, and apolipoprotein B were noted during ORIAHNN treatment in Studies UF-1 and UF-2.
Of the women with Grade 0 LDL-C (<130 mg/dL) at baseline, 1/313 (0.3%) ORIAHNN-treated woman shifted to Grade 3 (≥ 190 mg/dL) compared to no placebo-treated woman. Of those with Grade 1 LDL-C (130 to <160 mg/dL) at baseline, 9/54 (16.7%) ORIAHNN-treated women shifted to Grade 3 compared to no placebo-treated woman. Of those with Grade 2 LDL-C (160 to <190 mg/dL) at baseline, 7/10 (70%) ORIAHNN-treated women shifted to Grade 3 compared to 1/5 (20%) placebo-treated woman.
Alopecia
In Phase 3 placebo-controlled clinical trials (Studies UF-1 and UF-2), 3.5% (14/395) of ORIAHNN-treated women experienced alopecia, hair loss, or hair thinning compared to 1.0% (2/196) of placebo-treated women. No specific pattern in hair loss was observed. In almost one-third (4/14) of affected ORIAHNN-treated women, alopecia was a reason for study drug discontinuation; no placebo-treated women discontinued because of alopecia. In ORIAHNN-treated women, 79% of the cases were mild and 21% were moderate in severity. Hair loss was ongoing at the end of the study for 4 out of 14 women (29%). Of these 4 women, one discontinued treatment due to hair loss, two had ongoing hair loss 12 months after discontinuing ORIAHNN, and one was lost to follow-up. In the remaining 10 women (71%), hair loss either resolved while on treatment or resolved within 24 days to approximately 9 months after discontinuing ORIAHNN.
Resumption of Menses after Discontinuation
After six months of ORIAHNN treatment, resumption of menses was reported by 39%, 68%, and 73% of women within 1, 2, and 6 months, respectively, in Study UF-1 and 39%, 85%, and 92% within 1, 2, and 6 months, respectively, in Study UF-2.
After 12 months of therapy with ORIAHNN (Study UF-1 or Study UF-2 then Study UF-3), resumption of menses was reported by 43%, 82%, and 90% of women within 1, 2, and 6 months after stopping treatment, respectively.
Whether those who did not resume having menses transitioned to a peri-postmenopausal status is unknown.