Brand Name
Natazia
Generic Name
Dienogest
View Brand Information FDA approval date: May 06, 2010
Form: Kit
What is Natazia (Dienogest)?
Natazia is an estrogen/progestin COC indicated for use by women to prevent pregnancy. , Treatment of heavy menstrual bleeding in women without organic pathology who choose to use an oral contraceptive as their method of contraception.
Approved To Treat
Top Global Experts
There are no experts for this drug
Save this treatment for later
Not sure about your diagnosis?
Related Clinical Trials
There is no clinical trials being done for this treatment
Related Latest Advances
There is no latest advances for this treatment
Brand Information
Natazia (estradiol valerate and estradiol valerate/dienogest)
WARNING: CIGARETTE SMOKING AND SERIOUS CARDIOVASCULAR EVENTS
Cigarette smoking increases the risk of serious cardiovascular events from combination oral contraceptives (COC) use. This risk increases with age, particularly in women over 35 years of age, and with the number of cigarettes smoked. For this reason, COCs should not be used by women who are over 35 years of age and smoke.
1DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Natazia (estradiol valerate and estradiol valerate/dienogest) tablets are available in blister packs.
Each blister pack contains 28 round, biconvex, film-coated tablets in the following order:
- 2 dark yellow tablets, with an embossed “DD” in a regular hexagon on one side, each containing 3 mg estradiol valerate
- 5 medium red tablets, with an embossed “DJ” in a regular hexagon on one side, each containing 2 mg estradiol valerate and 2 mg dienogest
- 17 light yellow tablets, with an embossed “DH” in a regular hexagon on one side, each containing 2 mg estradiol valerate and 3 mg dienogest
- 2 dark red tablets, with an embossed “DN” in a regular hexagon on one side, each containing 1 mg estradiol valerate
- 2 white tablets (inert), with an embossed “DT” in a regular hexagon on one side
2CONTRAINDICATIONS
Natazia is contraindicated in females who are known to have or develop the following conditions:
- A high risk of arterial or venous thrombotic diseases. Examples include women who are known to:
- Undiagnosed abnormal uterine bleeding
- Current diagnosis of, or history of, breast cancer, which may be hormone sensitive
- Liver tumors, benign or malignant, or liver disease
3ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious adverse reactions with the use of COCs are discussed elsewhere in the labeling:
- Serious cardiovascular events and stroke
- Vascular events
- Liver disease
Adverse reactions commonly reported by COC users are:
- Irregular uterine bleeding
- Nausea
- Breast tenderness
- Headache
3.1Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
3.1.1Contraception and Heavy Menstrual Bleeding Studies
A total of 2,131 women, 18 to 54 years of age, who took at least one dose of Natazia were enrolled in four clinical phase 3 trials. A total of 1,867 subjects were included in two clinical phase 3 studies with a treatment duration up to 28 cycles with Natazia as an oral contraceptive and 264 subjects in the two phase 3 clinical trials with a treatment duration of 7 cycles evaluating Natazia in the treatment of heavy, prolonged, and/or frequent menstrual bleeding in women without organic pathology
Adverse Reactions Leading to Study Discontinuation: 11.4% of the women discontinued from the clinical trials due to an adverse reaction; the most frequent adverse reactions leading to discontinuation were menstrual disorder (metrorrhagia, menorrhagia, menstruation irregular, genital hemorrhage, vaginal hemorrhage, dysfunctional uterine bleeding) (2.3%); mood changes (depression, mood swings, mood altered, depressed mood, dysthymic disorder, crying) (1.2%); acne (1.1%), headache (including migraines) (1.1%), and weight increased (0.7 %).
Common Adverse Reactions (≥ 2%): headache (including migraines) (12.7%), breast pain, discomfort or tenderness (7.0%), menstrual disorders (metrorrhagia, menstruation irregular, menorrhagia, vaginal hemorrhage, dysfunctional uterine bleeding, genital hemorrhage, abnormal withdrawal bleeding, uterine hemorrhage) (6.9%), nausea or vomiting (6.0%), acne (3.9%), mood changes (depression, mood swings, depressed mood, mood altered, affect lability, dysthymic disorder, crying) (3.0%) and increased weight (2.9%).
Serious Adverse Reactions: myocardial infarction (2 cases), ruptured ovarian cyst (2 cases), deep vein thrombosis, focal nodular hyperplasia of the liver, uterine leiomyoma, acute cholecystitis, and chronic acalculous cholecystitis.
3.2Postmarketing Experience
Five studies that compared breast cancer risk between ever-users (current or past use) of COCs and never-users of COCs reported no association between ever use of COCs and breast cancer risk, with effect estimates ranging from 0.90 - 1.12 (Figure 1).
Three studies compared breast cancer risk between current or recent COC users (<6 months since last use) and never users of COCs (Figure 1). One of these studies reported no association between breast cancer risk and COC use. The other two studies found an increased relative risk of 1.19–1.33 with current or recent use. Both of these studies found an increased risk of breast cancer with current use of longer duration, with relative risks ranging from 1.03 with less than one year of COC use to approximately 1.4 with more than 8–10 years of COC use.
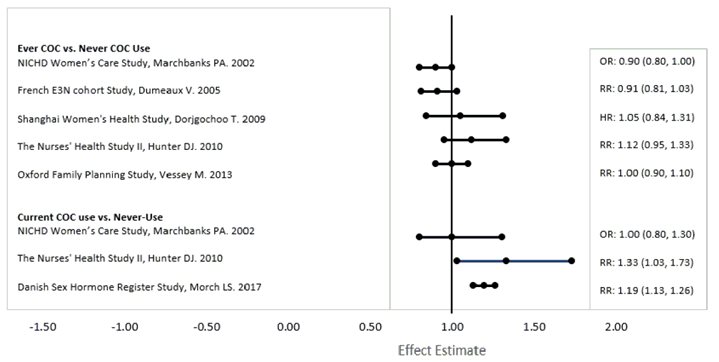
RR = relative risk; OR = odds ratio; HR = hazard ratio. “ever COC” are females with current or past COC use; “never COC use” are females that never used COCs.
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of Natazia. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Vascular disorders: Venous and arterial thromboembolic events (including pulmonary emboli, deep vein thrombosis, cerebral thrombosis, myocardial infarction and stroke), hypertension
Hepatobiliary disorders: Gallbladder disease, hepatitis
Immune system disorders: Hypersensitivity
Metabolism and nutrition disorders: Fluid retention, hypertriglyceridemia
Nervous system disorders: Dizziness
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: Chloasma, angioedema, erythema nodosum, erythema multiforme
Gastrointestinal disorders: Gastrointestinal symptoms (for example, abdominal pain)
Infections and infestations: Vulvovaginal candidiasis
4DRUG INTERACTIONS
Consult the labeling of all concurrently-used drugs to obtain further information about interactions with hormonal contraceptives or the potential for enzyme alterations
4.1Effects of Other Drugs on Combined Oral Contraceptives
Substances diminishing the efficacy of COCs: Dienogest is a substrate of CYP3A4. Women who take medications that are strong CYP3A4 inducers should not choose Natazia as their oral contraceptive while using these inducers and for at least 28 days after discontinuation of these inducers due to the possibility of increased breakthrough bleeding and/or decreased contraceptive efficacy.
Drugs or herbal products that induce certain enzymes, including CYP3A4, may decrease the effectiveness of COCs or increase breakthrough bleeding. Some drugs or herbal products that may decrease the effectiveness of hormonal contraceptives include phenytoin, barbiturates, carbamazepine, bosentan, felbamate, griseofulvin, oxcarbazepine, rifampin, topiramate and products containing St. John’s wort. Interactions between oral contraceptives and other drugs may lead to breakthrough bleeding and/or contraceptive failure. Counsel women to use an alternative method of contraception or a back-up method when enzyme inducers are used with COCs, and to continue back-up contraception for 28 days after discontinuing the enzyme inducer to ensure contraceptive reliability.
Multiple dose co-administration of the strong CYP3A4 inducer rifampin with estradiol valerate/dienogest tablets in healthy postmenopausal women led to a decrease in dienogest and estradiol systemic exposure at steady state.
Substances Increasing the Systemic Exposure of COCs (enzyme inhibitors): Concomitant administration of moderate or strong CYP3A4 inhibitors like azole antifungals (for example, ketoconazole, itraconazole, voriconazole, fluconazole), verapamil, macrolides (for example, clarithromycin, erythromycin), diltiazem, and grapefruit increase the serum concentrations of both estradiol and dienogest.
In a multiple dose study investigating the effect of CYP3A4 inhibitors (ketoconazole and erythromycin) on Natazia, steady state estradiol and dienogest exposures were increased when co-administered with ketoconazole or erythromycin
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)/Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) Protease Inhibitors and Non-Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors: Significant changes (increase and decrease) in plasma concentrations of estrogen and progestin have been noted in some cases of co-administration of HIV/HCV protease inhibitors or with non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors.
Antibiotics: There have been reports of pregnancy while taking hormonal contraceptives and antibiotics, but clinical pharmacokinetic studies have not shown consistent effects of antibiotics on plasma concentrations of synthetic steroids.
4.2Effects of Combined Oral Contraceptives on Other Drugs
COCs containing ethinyl estradiol may inhibit the metabolism of other compounds. COCs have been shown to significantly decrease plasma concentrations of lamotrigine, likely due to induction of lamotrigine glucuronidation. This may reduce seizure control; therefore, dosage adjustments of lamotrigine may be necessary. Consult the labeling of the concurrently-used drug to obtain further information about interactions with COCs or the potential for enzyme alterations.
Women on thyroid hormone replacement therapy may need increased doses of thyroid hormone because serum concentrations of thyroid-binding globulin increase with use of COCs.
4.3Interference with Laboratory Tests
The use of contraceptive steroids may influence the results of certain laboratory tests, such as coagulation factors, lipids, glucose tolerance, and binding proteins
5OVERDOSAGE
There have been no reports of serious ill effects from overdose, including ingestion by children. Overdosage may cause withdrawal bleeding in females and nausea.
6DESCRIPTION
Natazia (estradiol valerate and estradiol valerate/dienogest) tablets provide an oral contraceptive regimen consisting of 26 active film-coated tablets that contain the active ingredients specified for each tablet below, followed by two inert film-coated tablets:
- 2 dark yellow tablets each containing 3 mg estradiol valerate
- 5 medium red tablets each containing 2 mg estradiol valerate and 2 mg dienogest
- 17 light yellow tablets each containing 2 mg estradiol valerate and 3 mg dienogest
- 2 dark red tablets each containing 1 mg estradiol valerate
- 2 white tablets (inert)
Natazia also contains the excipients lactose monohydrate, maize starch, maize starch pre-gelatinized, povidone 25, magnesium stearate, hypromellose, macrogol 6000, talc, titanium dioxide, and ferric oxide pigment, yellow, or ferric oxide pigment, red.
The empirical formula of estradiol valerate is C
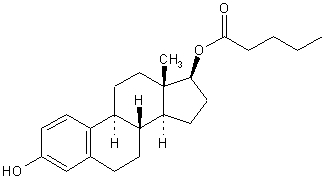
The chemical name of estradiol valerate is Estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,17-diol(17ß)-,17-pentanoate.
The empirical formula of dienogest is C
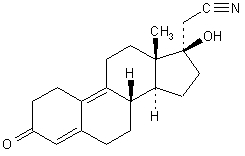
The chemical name of dienogest is (17α)-17-Hydroxy-3-oxo-19-norpregna-4,9-diene-21-nitrile.
7PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
See “FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information).”
- Counsel patients that cigarette smoking increases the risk of serious cardiovascular events from COC use, and that women who are over 35 years old and smoke should not use COCs.
- Counsel patients that the increased risk of VTE compared to non-users of COCs is greatest after initially starting a COC or restarting (following a 4 week or greater pill-free interval) the same or a different COC.
- Counsel patients that Natazia does not protect against HIV infection (AIDS) and other sexually transmitted diseases.
- Counsel patients on Warnings and Precautions associated with COCs.
- Inform patients that Natazia is not indicated during pregnancy. If pregnancy occurs during treatment with Natazia, instruct the patient to stop further intake.
- Counsel patients to take one tablet daily by mouth at the same time every day in the exact order noted on the blister. Instruct patients what to do in the event pills are missed. See
- Counsel women who are taking strong CYP3A4 inducers (for example, carbamazepine, phenytoin, rifampicin, and St. John’s wort) not to choose Natazia as their oral contraceptive due to the possibility of decreased contraceptive efficacy.
- Counsel patients to use a back-up or alternative method of contraception when weak or moderate enzyme inducers are used with Natazia.
- Counsel patients who are breastfeeding or who desire to breastfeed that COCs may reduce breast milk production. This is less likely to occur if breastfeeding is well established.
- Counsel any patient who starts COCs postpartum, and who has not yet had a period, to use an additional method of contraception until she has taken Natazia for 9 consecutive days.
- Counsel patients that amenorrhea may occur. Rule out pregnancy in the event of amenorrhea in two or more consecutive cycles.
8FDA-Approved Patient Labeling
Guide for Using Natazia
Birth control pills help to lower the chances of becoming pregnant when taken as directed. They do not protect against HIV infection (AIDS) and other sexually transmitted diseases.
What Is Natazia?
Natazia is a birth control pill. It contains two female hormones, an estrogen called estradiol valerate and a progestin called dienogest. Estradiol valerate is a synthetic estrogen that is converted to estradiol in your body.
Natazia is used to treat heavy menstruation (your monthly period) that is not caused by any diagnosed conditions of the uterus (womb) in women who decide to use an oral contraceptive for birth control. Talk to your healthcare provider to determine if your bleeding is heavier than normal.
How Does Natazia Work?
Birth control pills prevent your ovaries from producing and releasing mature eggs. Natazia decreases menstrual bleeding by thinning the lining of the uterus.
How Well Does Natazia Work For Contraception?
Your chance of getting pregnant depends on how well you follow the directions for taking your birth control pills. The better you follow the directions, the less chance you have of getting pregnant.
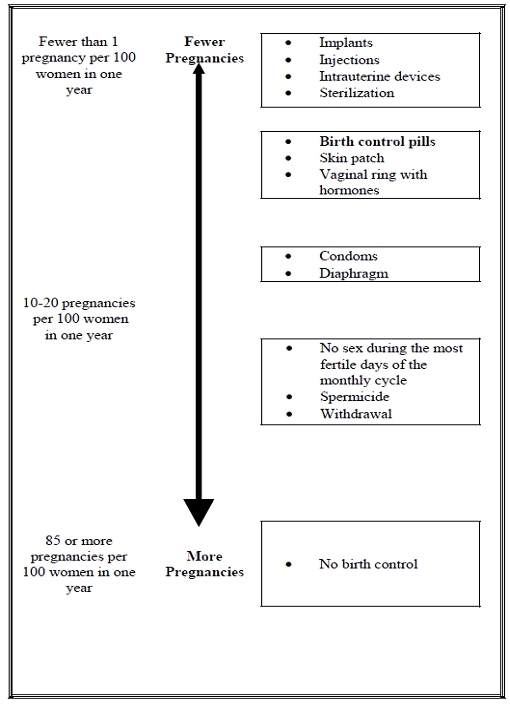
Based on the results of two clinical studies, 1 to 2 women out of 100 women may get pregnant during the first year they use Natazia.
The following chart shows the chance of getting pregnant for women who use different methods of birth control. Each box on the chart contains a list of birth control methods that are similar in effectiveness. The most effective methods are at the top of the chart. The box on the bottom of the chart shows the chance of getting pregnant for women who do not use birth control and are trying to get pregnant.
How Well Does Natazia Work For Heavy Menstrual Bleeding?
In two clinical trials in women with heavy menstrual bleeding who were treated with Natazia, their menstrual bleeding was reduced by an average of 90% in one trial and 87% in the other. For women treated with placebo, their menstrual bleeding was reduced by an average of 14% and 32% in the two trials, respectively.
How Do I Take Natazia?
- Take one pill every day at the same time. Take the pills in the order directed on the blister pack.
- Do not skip pills or delay taking your pill by more than 12 hours. If you miss pills (including starting the pack late), you could get pregnant. The more pills you miss, the more likely you are to get pregnant.
- If you have trouble remembering to take Natazia, talk to your healthcare provider about how to make pill-taking easier, or about using another method of birth control.
- You may have spotting or light bleeding when you first take Natazia. Spotting or light bleeding is normal at first.
- You may feel sick to your stomach (nauseous), especially during the first few months that you take Natazia. If you feel sick to your stomach, do not stop taking the pill. The problem will usually go away. If your nausea doesn't go away, call your healthcare provider.
- If you vomit or have diarrhea within 4 hours of taking your pill, follow the instructions for “What Should I Do if I Miss any Pills.”
- Missing pills can also cause spotting or light bleeding, even when you take the missed pills later. On the days you take 2 pills to make up for missed pills, you could also feel a little sick to your stomach.
Before you start taking Natazia
- Decide what time of day you want to take your pill. It is important to take it at the same time every day and in the order as directed on the blister pack.
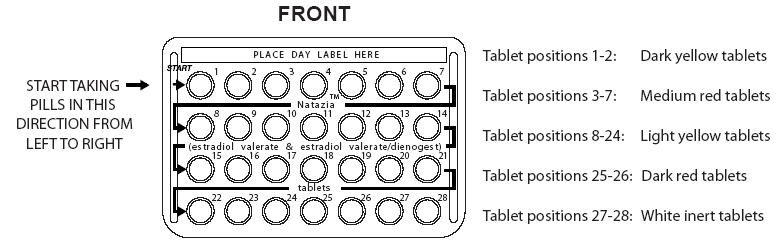
- Look at your Natazia blister pack. The blister pack has 4 rows of 7 pills each, for a total of 28 pills. Find:
- where on the pack to start taking your pills
- in what order to take the pills
Each NATAZIA blister pack has 28 pills
- 2 dark yellow pills with hormones, for Days 1 and 2
- 5 medium red pills with hormones for Days 3–7
- 17 light yellow pills with hormones for Days 8–24
- 2 dark red pills with hormones for Days 25 and 26
- 2 white pills without hormones for Days 27 and 28
- After taking the last white pill (day 28) of the blister pack, start taking the first dark yellow pill from a new blister pack the very next day whether or not you are having your period.
- Be sure to have ready at all times another kind of birth control (such as condoms and spermicides) to use as a back-up in case you miss pills.
- It is not uncommon to miss a period. However, if you miss 2 periods in a row or feel like you may be pregnant, call your healthcare provider. If you are pregnant, you should stop taking Natazia.
- When to Start Natazia
If you start taking Natazia and you did not use a hormonal birth control method before:
- Take the first dark yellow pill on the first day (Day 1) of your natural menstrual cycle. The first day of your menstrual cycle is the first day you start spotting or bleeding.
- Use non-hormonal back-up contraception such as a condom and spermicide for the first 9 days that you take Natazia.
If you start taking Natazia and you are switching from a combination hormonal method such as:
- another pill
- vaginal ring
- patch
- Take the first dark yellow pill on the first day of your period. Do not continue taking the pills from your previous birth control pack. If you do not have a period, contact your healthcare provider before you start Natazia.
- If you previously used a vaginal ring or transdermal patch, you should start using Natazia on the day the ring or patch is removed.
- Use a non-hormonal back-up method such as a condom and spermicide for the first 9 days you take Natazia.
If you start taking Natazia and you are switching from a progestin-only method such as a:
- progestin-only pill
- implant
- intrauterine system
- injection
- Take the first dark yellow pill on the day you would have taken your next progestin-only pill or on the day of removal of your implant or intrauterine system or on the day when you would have had your next injection.
- Use a non-hormonal back-up method such as a condom and spermicide for the first 9 days you take Natazia.
What Should I Do if I Miss any Pills
If you forgot to start a new blister pack,
- Do not take more than 2 pills in one day. On the days you take 2 pills to make up for missed pills, you may feel a little sick to your stomach (nauseous).
- If you start vomiting or have diarrhea within 4 hours of taking your pill, take another pill of the same color from your extra blister pack.
If you are less than 12 hours late taking your pill
- Take your pill as soon as you remember.
- Take the next pill at the usual time.
- You do not need to use back-up contraception.
If you miss ONE PILL for more than 12 hours
Days 1–17
- Take your missed pill immediately.
- Take your next pill at the usual time (you may have to take two pills that day).
- Use back-up contraception for the next 9 days.
- Continue taking one pill each day at the same time for the rest of your cycle.
Days 18–24
- Do not take any pills from your current blister pack and throw the pack away.
- Take Day 1 pill from a new blister pack.
- Use back-up contraception for the next 9 days.
- Continue taking one pill from the new blister pack at the same time each day.
Days 25–28
- Take your missed pill immediately.
- Take your next pill at the usual time (you may have to take two pills that day).
- No back-up contraception is needed.
- Continue taking one pill each day at the same time for the rest of your cycle.
If you miss TWO PILLS in a row
Days 1–17
(if you miss the pills for Days 17 and 18, follow the instructions for Days 17–25 instead)
(if you miss the pills for Days 17 and 18, follow the instructions for Days 17–25 instead)
- Do not take the missed pills. Instead, take the pill for the day on which you first noticed you had missed pills.
- Use back-up contraception for the next 9 days.
- Continue taking one pill each day at the same time for the rest of your cycle.
Days 17–25
(if you miss the pills for Days 25 and 26, follow the instructions for Days 25–28 instead)
(if you miss the pills for Days 25 and 26, follow the instructions for Days 25–28 instead)
- Do not take any pills from your current blister pack and throw the pack away.
- Take Day 3 pill from a new blister pack.
- Use back-up contraception for the next 9 days.
- Continue taking one pill from the new blister pack at the same time each day.
Days 25–28
- Do not take any pills from your current blister pack and throw the pack away.
- Start a new pack on the same day or start a new pack on the day you usually start a new pack.
- No back-up contraception is needed.
- Continue taking one pill from the new pack at the same time each day, for the rest of your cycle.
If you are still not sure of what to do about the pills you have missed:
- Call your healthcare provider
- Use back-up contraception (such as condoms and spermicides) anytime you have sex and keep taking 1 pill each day
Who Should Not Take Natazia?
Your healthcare provider will not give you Natazia if you have:
- Ever had breast cancer which may be sensitive to female hormones
- Liver disease, including liver tumors
- Ever had blood clots in your arms, legs, or lungs
- Ever had a stroke
- Ever had a heart attack
- Certain heart valve problems or heart rhythm abnormalities that can cause blood clots to form in the heart
- An inherited problem with your blood that makes it clot more than normal
- High blood pressure that medicine can't control
- Diabetes with kidney, eye, or blood vessel damage
- Certain kinds of severe migraine headaches with aura, numbness, weakness or changes in vision
If any of these conditions happen for the first time while using Natazia, stop taking Natazia right away and talk to your healthcare provider. You should use non-hormonal contraceptive measures when you stop using Natazia.
Also, do not take birth control pills if you:
- Smoke and are over 35 years old
- Are pregnant
- Have any unexplained bleeding from the vagina
Birth control pills may not be a good choice for you if you have ever had jaundice (yellowing of the skin or eyes) caused by pregnancy (also called cholestasis of pregnancy).
What Else Should I Know about Taking Natazia?
Birth control pills do not protect you against any sexually transmitted disease, including HIV, the virus that causes AIDS.
Do not skip any pills, even if you do not have sex often.
If you miss a period, you could be pregnant. However, some women miss periods or have light periods on birth control pills, even when they are not pregnant. Contact your healthcare provider for advice if you:
- Think you are pregnant
- Miss one period and have not taken your birth control pills according to directions
- Miss two periods in a row
Birth control pills should not be taken during pregnancy. However, birth control pills taken by accident during pregnancy are not known to cause birth defects.
If you are breastfeeding, consider another birth control method until you are ready to stop breastfeeding. Birth control pills that contain estrogen, like Natazia, may decrease the amount of milk you make. A small amount of the pill's hormones pass into breast milk.
If you have vomiting or diarrhea, your birth control pills may not work as well. Use another birth control method, like condoms and a spermicide, until you check with your healthcare provider.
If you are scheduled for any laboratory tests, tell your healthcare provider you are taking birth-control pills. Certain blood tests may be affected by birth-control pills.
Tell your healthcare provider about all medicines and herbal products that you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins and herbal supplements.
Natazia may affect the way other medicines work, and other medicines may affect how well Natazia works. Know the medicines you take.
Keep a list of them to show your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get a new medicine. You should not choose Natazia as your birth control pill if you take carbamazepine, phenytoin, rifampicin or St. John's wort, because these medicines may make Natazia ineffective.
What are the Most Serious Risks of Taking Birth Control Pills?
Like pregnancy, birth control pills increase the risk of serious blood clots, especially in women who have other risk factors, such as smoking, obesity, or age greater than 35. This increased risk is highest when you first start taking birth control pills and when you restart the same or different birth control pills after not using them for a month or more.
It is possible to die from a problem caused by a blood clot, such as a heart attack or a stroke. Some examples of serious blood clots are blood clots in the:
- Legs (deep vein thrombosis)
- Lungs (pulmonary embolus)
- Eyes (loss of eyesight)
- Heart (heart attack)
- Brain (stroke)
A few women who take birth control pills may get:
- High blood pressure
- Gallbladder problems
- Rare cancerous or noncancerous liver tumors
- All of these events are uncommon in healthy women.
Call your healthcare provider right away if you have:
- Persistent leg pain
- Sudden shortness of breath
- Sudden blindness, partial or complete
- Severe pain in your chest
- Sudden, severe headache unlike your usual headaches
- Weakness or numbness in an arm or leg, or trouble speaking
- Yellowing of the skin or eyeballs
- What are the Common Side Effects of Birth Control Pills?
The most common side effects of birth control pills are:
- Spotting or bleeding between menstrual periods
- Nausea
- Breast tenderness
- Headache
These side effects are usually mild and usually disappear with time.
Less common side effects are:
- Acne
- Less sexual desire
- Bloating or fluid retention
- Blotchy darkening of the skin, especially on the face
- High blood sugar, especially in women who already have diabetes
- High fat levels in the blood
- Depression, especially if you have had depression in the past.
Call your healthcare provider immediately if you have any thoughts of harming yourself.
- Problems tolerating contact lenses
- Weight changes
This is not a complete list of possible side effects. Talk to your healthcare provider if you develop any side effects that concern you. You may report side effects to the FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
No serious problems have been reported from a birth control pill overdose, even when accidentally taken by children.
Do Birth Control Pills Cause Cancer?
It is not known if hormonal birth control pills causes breast cancer. Some studies, but not all, suggest that there could be a slight increase in the risk of breast cancer among current users with longer duration of use.
If you have breast cancer now, or have had it in the past, do not use hormonal birth control because some breast cancers are sensitive to hormones.
Women who use birth control pills may have a slightly higher chance of getting cervical cancer. However, this may be due to other reasons such as having more sexual partners.
What Should I Know about My Period when Taking Natazia?
Irregular vaginal bleeding or spotting may occur while you are taking Natazia. Irregular bleeding may vary from slight staining between menstrual periods to breakthrough bleeding, which is a flow much like a regular period. Irregular bleeding occurs most often during the first few months of oral contraceptive use, but may also occur after you have been taking the pill for some time. Such bleeding may be temporary and usually does not indicate any serious problems. It is important to continue taking your pills on schedule. If the bleeding occurs in more than one cycle, is unusually heavy, or lasts for more than a few days, call your healthcare provider.
Also, your menstrual period while using oral contraceptives may be shorter and lighter than usual. Some women may not have a menstrual period but this should not be cause for alarm as long has you have taken the pills according to direction.
What if I Miss My Scheduled Period when Taking Natazia?
It is not uncommon to miss your period. However, if you miss more than two periods in a row or miss one period when you have not taken your birth control pills according to directions, call your healthcare provider. Also notify your healthcare provider if you have symptoms of pregnancy such as morning sickness or unusual breast tenderness. It is important that your healthcare provider checks you to find out if you are pregnant. Stop taking Natazia if you are pregnant.
What If I Want to Become Pregnant?
You may stop taking the pill whenever you wish. Consider a visit with your healthcare provider for a pre-pregnancy checkup before you stop taking the pill.
General Advice about Natazia
Your healthcare provider prescribed Natazia for you. Please do not share Natazia with anyone else. Keep Natazia out of the reach of children.
If you have concerns or questions, ask your healthcare provider. You may also ask your healthcare provider for a more detailed label written for medical professionals.
Revised 6/2024
Manufactured for:
Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals Inc.
Manufactured in Germany
© 2023, Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals Inc.
Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals Inc.