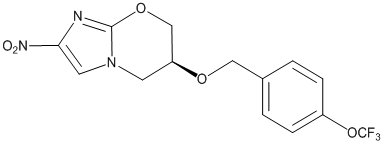
Pretomanid
View Brand InformationWhat is Pretomanid?
Approved To Treat
Top Global Experts
Related Clinical Trials
Summary: This study aims to assess quabodepistat-based treatment regimens for RR/MDR-TB. The study will enroll adults and adolescents with rifampicin-resistant or multidrug-resistant pulmonary TB. The main goal is to see if a new drug called quabodepistat, when combined with other TB drugs, can shorten treatment duration to 4 months and be as effective and safer than current WHO endorsed treatment regimen ...
Summary: A5409/RAD-TB is an adaptive Phase 2 randomized, controlled, open-label, dose-ranging, platform protocol to evaluate the safety and efficacy of multidrug regimens for the treatment of adults with drug-susceptible pulmonary tuberculosis (TB). A5409 hypothesizes that novel regimens for the treatment of pulmonary tuberculosis will result in superior early efficacy, as determined by longitudinal mycoba...
Summary: Tuberculosis (TB) remains a major public health issue and one of the top ten causes of death from a single infectious disease worldwide. China is among the countries with the highest TB burden, ranking third globally for total TB cases and second for drug-resistant TB cases. PAN-TB is an innovative concept in TB treatment, aiming to develop a universal regimen effective for all forms of active TB,...
Related Latest Advances
Brand Information
- Pretomanid Tablets are not indicated in patients with:
- Safety and effectiveness of Pretomanid Tablets have not been established for its use in combination with drugs other than bedaquiline and linezolid as part of the recommended dosing regimen
- Hepatotoxicity
- Myelosuppression
- Peripheral and Optic Neuropathy
- QT Prolongation
- Reproductive Effects
- Lactic Acidosis
- Inform the patient or caregiver that Pretomanid Tablets administered as a combination regimen with bedaquiline and linezolid would be useful only in adult patients with TB resistant to isoniazid, rifamycins, a fluoroquinolone and a second line injectable antibacterial drug or TB resistant to isoniazid and rifampin, who are treatment-intolerant or nonresponsive to standard therapy. This regimen is not indicated for treatment in patients with latent infection or extra-pulmonary infection due to
- Instruct the patient or caregiver that the combination regimen of Pretomanid Tablets, bedaquiline, and linezolid must be administered by directly observed therapy (DOT).
- Inform patients of safety concerns associated with linezolid and bedaquiline and advise the patient or their caregiver to read the Medication Guide for bedaquiline.
- Inform patients to take the regimen with food. Doses of the combination regimen of Pretomanid Tablets, bedaquiline, and linezolid missed for safety reasons can be made up at the end of treatment; doses of linezolid alone missed due to linezolid adverse reactions should not be made up. If bedaquiline and/or Pretomanid Tablets are permanently discontinued, the entire combination regimen of Pretomanid Tablets, bedaquiline, and linezolid should be discontinued.
- Advise patients who have difficulty swallowing tablets that Pretomanid Tablets can be crushed and suspended in water at room temperature. Alternately, the tablet can be soaked for 4 to 5 minutes in room temperature water and then the remaining solid crushed
see Prescribing Information.