Menopur
What is Menopur (Menotropins)?
Approved To Treat
Top Global Experts
Related Clinical Trials
Summary: The goal of this clinical trial is to evaluate the safety and effectiveness of a personalized ovarian stimulation regimen in women aged 18 to 40 undergoing in vitro fertilization (IVF). The main question it aims to answer is: \- Does personalizing the starting doses of follitropin delta (REKOVELLE) and HP-hMG (MENOPUR) based on both age and body lead to similar results as anti-Müllerian hormone (A...
Summary: Gonal-F® (follitropin alfa) is a recombinant FSH without LH activity, while Menopur® contains both LH and hCG. The MEGASET trial compared Menopur® and Gonal-F® in GnRH antagonist cycles with SET, showing similar efficacy. A subsequent study (MEGASET-HR) in high responders found ongoing pregnancy rates of 35.5% for Menopur® and 30.7% for Gonal-F®, with a lower early pregnancy loss for Menopur® (14....
Summary: Both controlled ovarian stimulation (COS) and frozen embryo transfer has become an integral part of in vitro fertilization (IVF) treatment. Fresh embryo transfer is usually performed by providing Luteal Phase Support (LPS) with progesterone after COS. Frozen embryo transfer (FET) is usually performed in artificial cycles with hormone replacement treatment (HRT), in which exogenous progesterone is ...
Related Latest Advances
Brand Information
- Prior hypersensitivity to MENOPUR or menotropins products or one of their excipients
- High levels of FSH indicating primary ovarian failure
- Pregnancy
- Presence of uncontrolled non-gonadal endocrinopathies (e.g., thyroid, adrenal, or pituitary disorders)
- Sex hormone dependent tumors of the reproductive tract and accessory organs
- Tumors of pituitary gland or hypothalamus
- Abnormal uterine bleeding of undetermined origin
- Ovarian cyst or enlargement of undetermined origin, not due to polycystic ovary syndrome
- Acute Phase:
- Chronic Phase:
- Resolution Phase:
- Urinary or serum luteinizing hormone (LH) rise
- A rise in basal body temperature
- Increase in serum progesterone
- Menstruation following the shift in basal body temperature
- Collapsed follicle
- Fluid in the cul-de-sac
- Features consistent with corpus luteum formation
- Secretory endometrium
- Abnormal Ovarian Enlargement
- Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome
- Atelectasis, acute respiratory distress syndrome and exacerbation of asthma
- Thromboembolic events
- Ovarian Torsion
- Multi-fetal Gestation and Birth
- Congenital Malformations
- Ectopic Pregnancy
- Spontaneous Abortion
- Ovarian Neoplasms
- are allergic to menotropins or any of the ingredients in MENOPUR. See the end of this leaflet for a complete list of ingredients in MENOPUR.
- have ovaries that no longer make eggs (primary ovarian failure)
- are pregnant or think you may be pregnant. If MENOPUR is taken while you are pregnant, it may harm your baby.
- have problems with your thyroid gland, adrenal gland or pituitary gland that are not controlled by taking medicine.
- have a tumor in your female organs, including your ovaries, breast, or uterus that may get worse with high levels of estrogen
- have a tumor of your pituitary gland or hypothalamus
- have abnormal bleeding from your uterus or vagina and the cause is not known
- have ovarian cysts or enlarged ovaries, not due to a problem called polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
- have been told by a healthcare provider that you are at an increased risk for blood clots (thrombosis)
- have ever had a blood clot (thrombosis), or anyone in your family has ever had a blood clot
- had twisting of your ovary (ovarian torsion)
- had or have a cyst in your ovary
- have any other medical conditions
- are breast feeding or plan to breast feed. It is not known if MENOPUR passes into your breast milk. You and your healthcare provider should decide if you will use MENOPUR or breastfeed. You should not do both.
- Read the
- Use MENOPUR exactly as your healthcare provider tells you to use it.
- Your healthcare provider will tell you how much MENOPUR to use and when to use it.
- Your healthcare provider may change your dose of MENOPUR if needed.
- If you miss a dose of MENOPUR, call your healthcare provider right away.
- You may need more than 1 vial of MENOPUR for your dose.
- MENOPUR may be mixed with BRAVELLE in the same syringe.
- ovaries that are too large. MENOPUR may cause your ovaries to be abnormally large. Symptoms of large ovaries include bloating or pain in your lower stomach (pelvic) area. If your ovaries become too large your healthcare provider may tell you that you should not have intercourse (sex) so you do not rupture an ovarian cyst.
- ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS). Using MENOPUR may cause OHSS. OHSS is a serious medical condition that can happen when your ovaries produce too many eggs (overstimulated). OHSS can cause fluid to suddenly build up in the area of your stomach, chest, heart, and cause blood clots to form. OHSS may also happen after you stop using MENOPUR. Stop using MENOPUR and call your healthcare provider or go to the nearest hospital emergency room right away if you have any of the following symptoms of OHSS:
- lung problems. MENOPUR may cause serious lung problems that can sometimes lead to death including fluid in the lungs, trouble breathing, and worsening of asthma.
- blood clots. MENOPUR may increase your chance of having blood clots in your blood vessels. Blood clots can cause:
- blood vessel problems (thrombophlebitis)
- stroke
- loss of your arm or leg
- blood clot in your lung (pulmonary embolus)
- twisting (torsion) of your ovary. MENOPUR may increase the chance of your ovary twisting, if you already have certain conditions such as OHSS, pregnancy, and previous abdominal surgery. Twisting of your ovary may lead to blood flow being cut off to your ovary.
- pregnancy with and birth of multiple babies. MENOPUR may increase your chance of having a pregnancy with more than 1 baby. Having a pregnancy and giving birth to more than 1 baby at a time increases the health risk for you and your babies. Your healthcare provider should talk to you about your chances of multiple births before you start using MENOPUR.
- birth defects. Babies born after ART may have an increased chance of birth defects. Your age, certain sperm problems, your genetic background, and that of your partner, and a pregnancy with more than 1 baby at a time may increase the chance that your baby may have birth defects.
- ectopic pregnancy (pregnancy outside your womb). MENOPUR may increase your chance of having a pregnancy that is abnormally outside of your womb. Your chance of having a pregnancy outside of your womb is increased if you also have fallopian tube problems.
- miscarriage. Your chance of loss of an early pregnancy may be increased if you had difficulty becoming pregnant.
- tumors of the ovary. If you have used medicines like MENOPUR more than 1 time to get pregnant, you may have an increased chance of having tumors in your ovaries, including cancer.
- stomach cramps, fullness or pain
- headache
- injection site swelling, heat, redness and pain
- Before mixing, store MENOPUR powder in the refrigerator or at room temperature between 37°F to 77°F (3°C to 25°C).
- Protect MENOPUR from light.
- MENOPUR should be used right after mixing.
- Throw away any unused MENOPUR.
- a clean, flat surface to work on, like a table
- vials of MENOPUR powder (and BRAVELLE powder if you are going to mix the 2 medicines)
- 1 vial of 0.9% Sodium Chloride, USP used for mixing the medicine
- alcohol pads
- rubbing alcohol
- gauze pads
- 1 sterile syringe and 1 sterile needle with cap. Your healthcare provider should tell you which syringe and needle to use.
- the Q•Cap
- a sharps disposal container for throwing away your used needles and syringes. See "

- Wash your hands well with soap and water and dry them with a clean towel.
- Place all the supplies you need on the clean surface you already prepared.
- Check the vial(s) of MENOPUR (and BRAVELLE if needed) to make sure there is powder or a pellet in the vial(s). If you do not see any powder in the vial(s) do not use the vial and call your pharmacist or healthcare provider.
- Check the 0.9% Sodium Chloride, USP vial to make sure that the liquid is clear and does not contain any particles. If you see any particles in the liquid or the liquid is discolored, do not use the vial and call your pharmacist or healthcare provider.
- Check the Q•Cap blister pack package to make sure it is intact. Do not use if the package is damaged.
- Remove the plastic cap(s) from the vial(s) of MENOPUR (and BRAVELLE if needed) and 0.9% Sodium Chloride, USP vial(s).
- Wipe the tops of the vials with alcohol and allow them to dry. Do not touch the tops of the vials after you have wiped them.
- Place the vial of 0.9% Sodium Chloride, USP on the table.
- Open the Q•Cap blister pack by peeling back the lidding
- Hold the 0.9% Sodium Chloride, USP vial in 1 hand. With your other hand, hold the sides of the Q•Cap blister pack, turn the Q•Cap blister pack over, and place it on top of the vial. Push the Q•Cap straight down into the rubber stopper of the vial until the Q•Cap spike pierces the top of the vial and snaps into place.
- Remove the blister pack and throw it away in your household trash. Do not touch the connector end (luer) of the Q•Cap.
- Take the syringe and pull down on the syringe plunger rod until you have reached the line that corresponds with the amount of 0.9% Sodium Chloride, USP that your healthcare provider told you to use (typically 1 mL). Air is just being drawn into the syringe at this step.
- Place the tip of the syringe into the connector end (luer) of the Q•Cap then twist the syringe clockwise until it is tight. Be careful not to overtighten the syringe.
- Slowly push down on the syringe plunger to push the air from the syringe into the vial.
- Keeping the syringe and Q•Cap together, turn the vial upside down and pull down on the syringe plunger to withdraw the right amount of 0.9% Sodium Chloride, USP from the vial. Your healthcare provider should tell you the right amount of 0.9% Sodium Chloride, USP to use.
- Separate the Q•Cap and syringe from the vial by pulling up on the syringe barrel. Do not pull the plunger to remove the Q•Cap. Throw away 0.9% Sodium Chloride, USP vial in your household trash.
- Hold the vial of MENOPUR powder in 1 hand. With your other hand, hold the sides of the syringe with the Q•Cap attached and place the tip of the Q•Cap over the top of the vial. Push the tip of the Q•Cap into the rubber stopper on the top of the vial until it stops and snaps into place. Be careful not to push down on the syringe plunger during this step.
- Slowly push down on the syringe plunger to push the 0.9% Sodium Chloride, USP into the vial with the MENOPUR powder in it. The entire amount of the 0.9% Sodium Chloride, USP in the syringe should be added
- As soon as the powdered medicine has completely dissolved, push the plunger down to empty any remaining air from the syringe, then turn the vial upside down and slowly pull down on the plunger to withdraw all of the MENOPUR into the syringe.
- Mix your first vial of MENOPUR powder or BRAVELLE powder with 0.9% Sodium Chloride, USP.
- Use the liquid in the syringe you have just mixed to mix the next vial of MENOPUR or BRAVELLE.
- You can use the liquid in the syringe to mix up to 5 more vials of medicine.
- Your healthcare provider will tell you how many vials of MENOPUR and BRAVELLE to use.
- When you have finished mixing the last vial needed for your injection and have withdrawn all the medicine into the syringe, remove the syringe from the Q•Cap by twisting the syringe counter-clockwise while holding the Q•Cap steady.
- You are now ready to attach the needle to the syringe for your injection.
- While holding the syringe with the syringe tip pointing up, place the needle on the top of the syringe. Gently push down on the needle and twist the needle onto the syringe in a clockwise direction until it is tight.
- Do not remove the needle cap until you are ready for your injection.(See Step 4)
- Carefully set the syringe with the needle down on the table.
- Select a site to inject MENOPUR or MENOPUR mixed with BRAVELLE on your stomach area (abdomen).
- Clean your injection site with an alcohol pad. Let the alcohol dry.
- Carefully remove the needle cap from the syringe.
- Hold the syringe with the needle pointing straight up. Pull down slightly on the plunger and tap the barrel of the syringe so that any air bubbles rise to the top. Slowly press the plunger up until all the air is out of the syringe and a small drop of liquid is seen at the tip of the needle.
- Tap the syringe to remove the small drop of liquid at the tip of the needle.
- The medicine is now ready for you to inject.
- Hold the syringe in 1 hand. Use your other hand to gently pinch a fold of cleaned skin where you will insert your needle. Hold the skin between your thumb and index finger.
- Hold your syringe at a right angle to your skin. Quickly insert the needle all the way into your skin fold.
- Push down the plunger of the syringe with a steady motion. Keep pushing until all the fluid is injected into your skin.
- Let go of your skin fold and pull the needle straight out of your skin.
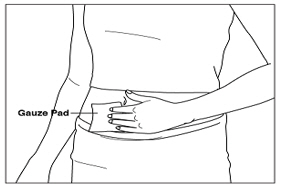
- If there is any bleeding at your injection site, place a gauze pad over your injection site. Apply gentle pressure to stop the bleeding. Do not rub the site.
- If your injection site becomes sore or red, you may put ice on your injection site for 1 minute and then take it off for 3 minutes. If needed, you may repeat this 3 or 4 times.
- Put your used needles and syringes in a FDA-cleared sharps disposal container right away after use.
- If you do not have a FDA-cleared sharps disposal container, you may use a household container that:
- When your sharps disposal container is almost full, you will need to follow your community guidelines for the right way to dispose of your sharps disposal container. There may be state or local laws about how you should throw away used needles and syringes. For more information about safe sharps disposal, and for specific information about sharps disposal in the state that you live in, go to the FDA's website at: http://www.fda.gov/safesharpsdisposal.