Kadcyla
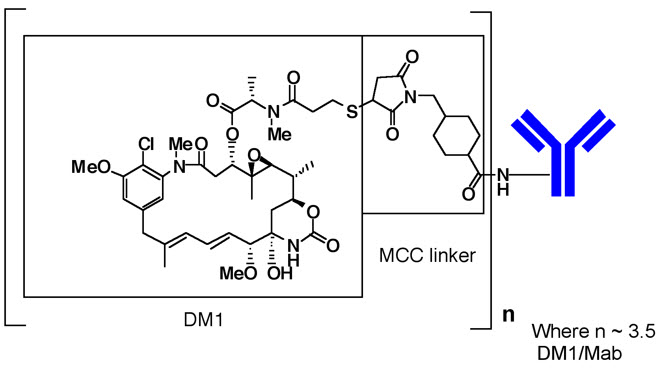
What is Kadcyla (Ado-Trastuzumab Emtansine)?
Approved To Treat
Related Clinical Trials
Summary: This is a Phase Ib/II, open-label, multicenter, randomized umbrella study in participants with breast cancer. The study is designed with the flexibility to open new treatment arms as new treatments become available, close existing treatment arms that demonstrate minimal clinical activity or unacceptable toxicity, or modify the patient population. Cohort 1 will focus on participants with inoperable...
Summary: This research study is studying how well newly diagnosed breast cancer that has tested positive for a protein called HER2 responds using one of two different combination of HER2-directed therapies as a treatment after surgery. The name of the study drugs involved are: * Trastuzumab-emtansine (T-DM1, Kadcyla) * Trastuzumab SC (Herceptin Hylecta) * Paclitaxel
Summary: This is a Phase IB/II multi-cohort study designed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of targeted agents with or without cancer immune checkpoint therapy with atezolizumab in participant with recurrent and/or persistent endometrial cancer. The main protocol provides a platform for genomic screening with homogeneous basic eligibility criteria in order to direct study participants into biomarker-mat...
Related Latest Advances
Brand Information
- Hepatotoxicity: Serious hepatotoxicity has been reported, including liver failure and death in patients treated with KADCYLA. Monitor serum transaminases and bilirubin prior to initiation of KADCYLA treatment and prior to each KADCYLA dose. Reduce dose or discontinue KADCYLA as appropriate in cases of increased serum transaminases or total bilirubin. (
- Cardiac Toxicity: KADCYLA administration may lead to reductions in left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF). Evaluate left ventricular function in all patients prior to and during treatment with KADCYLA. Withhold treatment for clinically significant decrease in left ventricular function. (
- Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: Exposure to KADCYLA during pregnancy can result in embryo-fetal harm. Advise patients of these risks and the need for effective contraception. (
- Hepatotoxicity
- Left Ventricular Dysfunction
- Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
- Pulmonary Toxicity
- Infusion-Related Reactions, Hypersensitivity Reactions
- Hemorrhage
- Thrombocytopenia
- Neurotoxicity