Brand Name
ZYFLO
Generic Name
Zileuton
View Brand Information FDA approval date: December 06, 1996
Classification: 5-Lipoxygenase Inhibitor
Form: Tablet
What is ZYFLO (Zileuton)?
Zileuton extended-release tablets are indicated for the prophylaxis and chronic treatment of asthma in adults and children 12 years of age and older. Zileuton extended-release tablets are not indicated for use in the reversal of bronchospasm in acute asthma attacks. Therapy with zileuton extended-release tablets can be continued during acute exacerbations of asthma. Zileuton extended-release tablets are a leukotriene synthesis inhibitor indicated for the prophylaxis and chronic treatment of asthma in adults and children 12 years of age and older. Do not use zileuton extended-release tablets to treat an acute asthma attack.
Approved To Treat
Top Global Experts
There are no experts for this drug
Save this treatment for later
Not sure about your diagnosis?
Related Clinical Trials
There is no clinical trials being done for this treatment
Related Latest Advances
There is no latest advances for this treatment
Brand Information
ZYFLO (zileuton)
1DESCRIPTION
Zileuton is an orally active inhibitor of 5-lipoxygenase, the enzyme that catalyzes the formation of leukotrienes from arachidonic acid. Zileuton has the chemical name (±)-1-(1-Benzo[b]thien-2-ylethyl)-1-hydroxyurea and the following chemical structure:
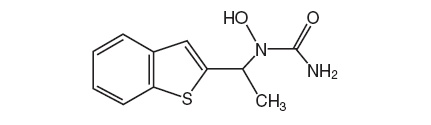
Zileuton has the molecular formula C
Inactive Ingredients: crospovidone, hydroxypropyl cellulose, hypromellose, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, pregelatinized starch, propylene glycol, sodium starch glycolate, talc, and titanium dioxide.
2CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action:
Zileuton is a specific inhibitor of 5-lipoxygenase and thus inhibits leukotriene (LTB
Zileuton is an orally active inhibitor of
Zileuton inhibits leukotriene-dependent smooth muscle contractions
3PHARMACOKINETICS
Zileuton is rapidly absorbed upon oral administration with a mean time to peak plasma concentration (T
The apparent volume of distribution (V/F) of zileuton is approximately 1.2 L/kg. Zileuton is 93% bound to plasma proteins, primarily to albumin, with minor binding to αl-acid glycoprotein.
Elimination of zileuton is predominantly via metabolism with a mean terminal half-life of 2.5 hours. Apparent oral clearance of zileuton is 7.0 mL/min/kg. ZYFLO activity is primarily due to the parent drug. Studies with radiolabeled drug demonstrated that orally administered zileuton is well absorbed into the systemic circulation with 94.5% and 2.2% of the radiolabeled dose recovered in urine and feces, respectively. Several zileuton metabolites have been identified in human plasma and urine. These include two diastereomeric O-glucuronide conjugates (major metabolites) and an N-dehydroxylated metabolite of zileuton. The urinary excretion of the inactive N-dehydroxylated metabolite and unchanged zileuton each accounted for less than 0.5% of the dose.
Special populations:
Effect of age: The pharmacokinetics of zileuton were investigated in healthy elderly volunteers (ages 65 to 81 years, 9 males, 9 females) and healthy young volunteers (ages 20 to 40 years, 5 males and 4 females) after single and multiple oral doses of 600 mg every 6 hours of zileuton. Zileuton pharmacokinetics were similar in healthy elderly subjects (≥65 years) compared to healthy younger adults (18 to 40 years).
Effect of gender: Across several studies, no significant gender effects were observed on the pharmacokinetics of zileuton.
Renal insufficiency: The pharmacokinetics of zileuton were similar in healthy subjects and in subjects with mild, moderate, and severe renal insufficiency. In subjects with renal failure requiring hemodialysis, zileuton pharmacokinetics were not altered by hemodialysis and a very small percentage of the administered zileuton dose (<0.5%) was removed by hemodialysis. Hence, dosing adjustment in patients with renal dysfunction or undergoing hemodialysis is not necessary.
Hepatic insufficiency: ZYFLO is contraindicated in patients with active liver disease (see CONTRAINDICATIONS and PRECAUTIONS, Hepatic).
4CLINICAL STUDIES
Two double-blind, parallel, placebo-controlled, multi-center studies have established the efficacy of ZYFLO in the treatment of asthma. Three hundred seventy-three (373) patients were enrolled in the 6-month, double-blind phase of Study 1, and 401 patients were enrolled in the 3-month double-blind phase of Study 2. In these studies, the patients were mild-to-moderate asthmatics who had a mean baseline FEV
Efficacy endpoints measured in Study 1 are shown in Table 1 below as mean change from baseline to the end of the study (six months). Statistically significant differences from placebo at the p<0.05 level are indicated by an asterisk(*). Similar results were observed after three months in Study 2.
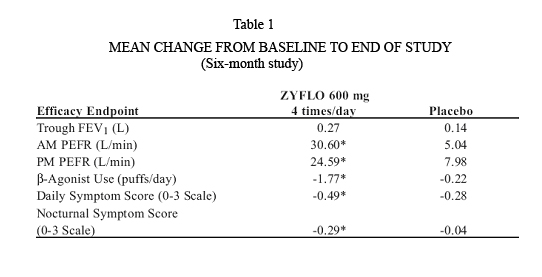
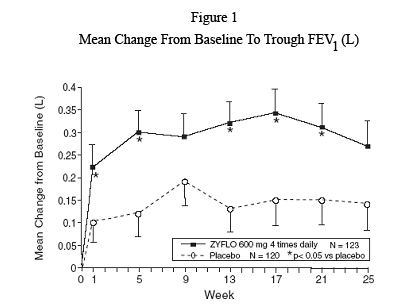
Figure 1 shows the mean effect of ZYFLO versus placebo for the primary efficacy variable, trough FEV
Of all the patients in Study 1 and Study 2, 7.0% of those administered ZYFLO 600 mg four times daily required systemic corticosteroid therapy for exacerbation of asthma, whereas 18.7% of the placebo group required corticosteroid treatment. This difference was statistically significant.
In these trials, there was a statistically significant improvement from baseline in FEV
These studies evaluated patients receiving as-needed inhaled beta-agonist as their only asthma therapy. In this patient population, post-hoc analyses suggested that individuals with lower FEV
The role of ZYFLO in the management of patients with more severe asthma, patients receiving anti-asthma therapy other than as-needed, inhaled beta-agonists, or patients receiving it as an oral or inhaled corticosteroid-sparing agent remains to be fully characterized.
5INDICATIONS AND USAGE
ZYFLO is indicated for the prophylaxis and chronic treatment of asthma in adults and children 12 years of age and older.
6CONTRAINDICATIONS
ZYFLO tablets are contraindicated in patients with:
- Active liver disease or transaminase elevations greater than or equal to three times the upper limit of normal (≥3xULN) (see
- Hypersensitivity to zileuton or any of its inactive ingredients.
7WARNINGS
ZYFLO is not indicated for use in the reversal of bronchospasm in acute asthma attacks, including status asthmaticus. Therapy with ZYFLO can be continued during acute exacerbations of asthma.
Co-administration of ZYFLO and theophylline results in, on average, an approximate doubling of serum theophylline concentrations. Theophylline dosage in these patients should be reduced and serum theophylline concentrations monitored closely (see
Co-administration of ZYFLO and warfarin results in a clinically significant increase in prothrombin time (PT). Patients on oral warfarin therapy and ZYFLO should have their prothrombin times monitored closely and anticoagulant dose adjusted accordingly (see
Co-administration of ZYFLO and propranolol results in doubling of propranolol AUC and consequent increased beta-blocker activity. Patients on ZYFLO and propranolol should be closely monitored and the dose of the propranolol reduced as necessary (see
8PRECAUTIONS
Hepatic:
Elevations of one or more liver function tests may occur during ZYFLO therapy. These laboratory abnormalities may progress, remain unchanged, or resolve with continued therapy. In a few cases, initial transaminase elevations were first noted after discontinuing treatment, usually within 2 weeks. The ALT (SGPT) test is considered the most sensitive indicator of liver injury. In placebo-controlled clinical trials, the frequency of ALT elevations greater than or equal to three times the upper limit of normal (3xULN) was 1.9% for ZYFLO-treated patients, compared with 0.2% for placebo-treated patients.
In a long-term safety surveillance study, 2458 patients received ZYFLO in addition to their usual asthma care and 489 received their usual asthma care. In patients treated for up to 12 months with ZYFLO in addition to their usual asthma care, 4.6% developed an ALT of at least 3xULN, compared with 1.1% of patients receiving only their usual asthma care. Sixty-one percent of these elevations occurred during the first two months of ZYFLO therapy. After two months of treatment, the rate of new ALT elevations ≥3xULN stabilized at a mean of 0.30% per month for patients receiving ZYFLO-plus-usual-asthma care compared with 0.11% per month for patients receiving usual asthma care alone. Of the 61 ZYFLO plus-usual-asthma-care patients with ALT elevations between 3 to 5xULN, 32 patients (52%) had ALT values decrease to below 2xULN while continuing ZYFLO therapy. Twenty-one of the 61 patients (34%) had further increases in ALT levels to ≥5xULN and were withdrawn from the study in accordance with the study protocol. In patients who discontinued ZYFLO, elevated ALT levels returned to <2xULN in an average of 32 days (range 1-111 days).
In controlled and uncontrolled clinical trials involving more than 5000 patients treated with ZYFLO, the overall rate of ALT elevation ≥3xULN was 3.2%. In these trials, one patient developed symptomatic hepatitis with jaundice, which resolved upon discontinuation of therapy. An additional 3 patients with transaminase elevations developed mild hyperbilirubinemia that was less than three times the upper limit of normal. There was no evidence of hypersensitivity or other alternative etiologies for these findings. In subset analyses, females over the age of 65 appeared to be at an increased risk for ALT elevations. Patients with pre-existing transaminase elevations may also be at an increased risk for ALT elevations (see
It is recommended that hepatic transaminases be evaluated at initiation of, and during therapy with, ZYFLO. Serum ALT should be monitored before treatment begins, once-a-month for the first 3 months, every two to three months for the remainder of the first year, and periodically thereafter for patients receiving long-term ZYFLO therapy. If clinical signs and/or symptoms of liver dysfunction (e.g., right upper quadrant pain, nausea, fatigue, lethargy, pruritus, jaundice, or “flu-like” symptoms) develop or transaminase elevations greater than 5 times the ULN occur, ZYFLO should be discontinued and transaminase levels followed until normal.
Since treatment with ZYFLO may result in increased hepatic transaminases, ZYFLO should be used with caution in patients who consume substantial quantities of alcohol and/or have a past history of liver disease.
Neuropsychiatric Events:
Neuropsychiatric events have been reported in adult and adolescent patients taking zileuton, the active ingredient in ZYFLO and zileuton extended-release tablets. Post-marketing reports with zileuton include sleep disorders and behavior changes. The clinical details of some post-marketing reports involving ZYFLO appear consistent with a drug-induced effect. Patients and prescribers should be alert for neuropsychiatric events. Patients should be instructed to notify their prescriber if these changes occur. Prescribers should carefully evaluate the risks and benefits of continuing treatment with ZYFLO if such events occur (see
Information for Patients:
Patients should be told that:
- ZYFLO is indicated for the chronic treatment of asthma and should be taken regularly as prescribed, even during symptom-free periods.
- ZYFLO is not a bronchodilator and should not be used to treat acute episodes of asthma.
- When taking ZYFLO, they should not decrease the dose or stop taking any other antiasthma medications unless instructed by a physician.
- While using ZYFLO, medical attention should be sought if short-acting bronchodilators are needed more often than usual, or if more than the maximum number of inhalations of short-acting bronchodilator treatment prescribed for a 24-hour period are needed.
- The most serious side effect of ZYFLO is elevation of liver enzyme tests and that, while taking ZYFLO, they must return for liver enzyme test monitoring on a regular basis.
- If they experience signs and/or symptoms of liver dysfunction (e.g., right upper quadrant pain, nausea, fatigue, lethargy, pruritus, jaundice, or “flu-like” symptoms), they should contact their physician immediately.
- Patients should be instructed to notify their healthcare provider if neuropsychiatric events occur while using ZYFLO.
- ZYFLO can interact with other drugs and that, while taking ZYFLO, they should consult their doctor before starting or stopping any prescription or non-prescription medicines.
A patient leaflet is included with the tablets.
Drug Interactions:
In a drug-interaction study in 16 healthy volunteers, co-administration of multiple doses of zileuton (800 mg every 12 hours) and theophylline (200 mg every 6 hours) for 5 days resulted in a significant decrease (approximately 50%) in steady-state clearance of theophylline, an approximate doubling of theophylline AUC, and an increase in theophylline C
Concomitant administration of multiple doses of ZYFLO (600 mg every 6 hours) and warfarin (fixed daily dose obtained by titration in each subject) to 30 healthy male volunteers resulted in a 15% decrease in R-warfarin clearance and an increase in AUC of 22%. The pharmacokinetics of S-warfarin were not affected. These pharmacokinetic changes were accompanied by a clinically significant increase in prothrombin times. Monitoring of prothrombin time, or other suitable coagulation tests, with the appropriate dose titration of warfarin is recommended in patients receiving concomitant ZYFLO and warfarin therapy (see
Co-administration of ZYFLO and propranolol results in a significant increase in propranolol concentrations. Administration of a single 80-mg dose of propranolol in 16 healthy male volunteers who received ZYFLO 600 mg every 6 hours for 5 days resulted in a 42% decrease in propranolol clearance. This resulted in an increase in propranolol C
In a drug interaction study in 16 healthy volunteers, co-administration of multiple doses of terfenadine (60 mg every 12 hours) and ZYFLO (600 mg every 6 hours) for 7 days resulted in a decrease in clearance of terfenadine by 22% leading to a statistically significant increase in mean AUC and C
Drug-drug interaction studies conducted in healthy volunteers between ZYFLO and prednisone and ethinyl estradiol (oral contraceptive), drugs known to be metabolized by the P450 3A4 (CYP3A4) isoenzyme, have shown no significant interaction. However, no formal drug-drug interaction studies between ZYFLO and dihydropyridine, calcium channel blockers, cyclosporine, cisapride, and astemizole, also metabolized by CYP3A4, have been conducted. It is reasonable to employ appropriate clinical monitoring when these drugs are co-administered with ZYFLO.
Drug-drug interaction studies in healthy volunteers have been conducted with ZYFLO and digoxin, phenytoin, sulfasalazine, and naproxen. There was no significant interaction between ZYFLO and any of these drugs.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility:
In 2-year carcinogenicity studies, increases in the incidence of liver, kidney, and vascular tumors in female mice and a trend towards an increase in the incidence of liver tumors in male mice were observed at 450 mg/kg/day (providing approximately 4 times [females] or 7 times [males] the systemic exposure [AUC] achieved at the maximum recommended human daily oral dose). No increase in the incidence of tumors was observed at 150 mg/kg/day (providing approximately 2 times the systemic exposure [AUC] achieved at the maximum recommended human daily oral dose). In rats, an increase in the incidence of kidney tumors was observed in both sexes at 170 mg/kg/day (providing approximately 6 times [males] or 14 times [females] the systemic exposure [AUC] achieved at the maximum recommended human daily oral dose). No increased incidence of kidney tumors was seen at 80 mg/kg/day (providing approximately 4 times [males] or 6 times [females] the systemic exposure [AUC] achieved at the maximum recommended human daily oral dose). Although a dose-related increased incidence of benign Leydig cell tumors was observed, Leydig cell tumorigenesis was prevented by supplementing male rats with testosterone.
Zileuton was negative in genotoxicity studies including bacterial reverse mutation (Ames) using
In reproductive performance/fertility studies, zileuton produced no effects on fertility in rats at oral doses up to 300 mg/kg/day (providing approximately 8 times [male rats] and 18 times [female rats] the systemic exposure [AUC] achieved at the maximum recommended human daily oral dose). Comparative systemic exposure (AUC) is based on measurements in male rats or nonpregnant female rats at similar dosages. However, reduction in fetal implants was observed at oral doses of 150 mg/kg/day and higher (providing approximately 9 times the systemic exposure [AUC] achieved at the maximum recommended human daily oral dose). Increases in gestation length, prolongation of estrous cycle, and increases in stillbirths were observed at oral doses of 70 mg/kg/day and higher (providing approximately 4 times the systemic exposure (AUC) achieved at the maximum recommended human daily oral dose). In a perinatal/postnatal study in rats, reduced pup survival and growth were noted at an oral dose of 300 mg/kg/day (providing approximately 18 times the systemic exposure [AUC] achieved at the maximum recommended human daily oral dose).
Pregnancy: Pregnancy Category C: Developmental studies indicated adverse effects (reduced body weight and increased skeletal variations) in rats at an oral dose of 300 mg/kg/day (providing approximately 18 times the systemic exposure [AUC] achieved at the maximum recommended human daily oral dose). Comparative systemic exposure [AUC] is based on measurements in nonpregnant female rats at a similar dosage. Zileuton and/or its metabolites cross the placental barrier of rats. Three of 118 (2.5%) rabbit fetuses had cleft palates at an oral dose of 150 mg/kg/day (equivalent to the maximum recommended human daily oral dose on a mg/m2 basis). There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. ZYFLO should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Nursing Mothers: Zileuton and/or its metabolites are excreted in rat milk. It is not known if zileuton is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, and because of the potential for tumorigenicity shown for ZYFLO in animal studies, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
Pediatric Use: The safety and effectiveness of ZYFLO in pediatric patients under 12 years of age have not been established. Due to the risk of hepatoxicity, use of ZYFLO in pediatric patients under 12 years of age is not recommended.
Geriatric Use: In subset analyses, females over the age of 65 appeared to be at an increased risk for ALT elevations. Zileuton pharmacokinetics were similar in healthy elderly subjects (≥65 years) compared to healthy younger adults (18 to 40 years) (see PHARMACOKINETICS-- Special populations: Effect of age).
9ADVERSE REACTIONS
Clinical Studies:
A total of 5542 patients have been exposed to zileuton in clinical trials, 2252 of them for greater than 6 months and 742 for greater than 1 year.
Adverse events most frequently occurring (frequency ≥3%) in ZYFLO-treated patients and at a frequency greater than placebo-treated patients are summarized in Table 2.
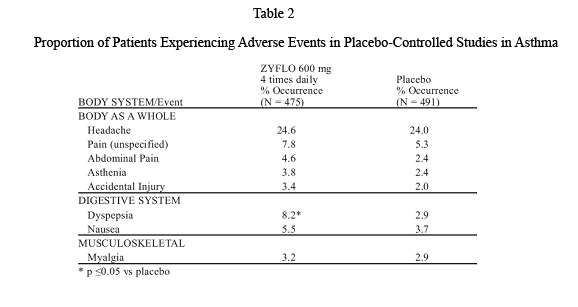
Less common adverse events occurring at a frequency of greater than 1% and more commonly in ZYFLO-treated patients included: arthralgia, chest pain, conjunctivitis, constipation, dizziness, fever, flatulence, hypertonia, insomnia, lymphadenopathy, malaise, neck pain/rigidity, nervousness, pruritus, somnolence, urinary tract infection, vaginitis, and vomiting.
The frequency of discontinuation from the asthma clinical studies due to any adverse event was comparable between ZYFLO (9.7%) and placebo-treated (8.4%) groups.
In placebo-controlled clinical trials, the frequency of ALT elevations ≥3xULN was 1.9% for ZYFLO-treated patients, compared with 0.2% for placebo-treated patients. In controlled and uncontrolled trials, one patient developed symptomatic hepatitis with jaundice, which resolved upon discontinuation of therapy. An additional 3 patients with transaminase elevations developed mild hyperbilirubinemia that was less than three times the upper limit of normal. There was no evidence of hypersensitivity or other alternative etiologies for these findings. ZYFLO is contraindicated in patients with active liver disease or transaminase elevations greater than or equal to 3xULN (see
Occurrences of low white blood cell count (≤2.8 x 10
In the long-term safety surveillance trial of ZYFLO plus usual asthma care versus usual asthma care alone, a similar adverse event profile was seen as in other clinical trials.
Post-Marketing Experience: Cases of sleep disorders and behavior changes have been reported (see PRECAUTIONS, Neuropsychiatric Events). Rash and urticaria have been also reported with ZYFLO.
10OVERDOSAGE
Human experience of acute overdose with zileuton is limited. A patient in a clinical trial took between 6.6 and 9.0 grams of zileuton in a single dose. Vomiting was induced and the patient recovered without sequelae. Zileuton is not removed by dialysis. Should an overdose occur, the patient should be treated symptomatically and supportive measures instituted as required. If indicated, elimination of unabsorbed drug should be achieved by emesis or gastric lavage; usual precautions should be observed to maintain the airway. A Certified Poison Control Center should be consulted for up-to-date information on management of overdose with ZYFLO.
The oral minimum lethal doses in mice and rats were 500-4000 and 300-1000 mg/kg in various preparations, respectively (providing greater than 3 and 9 times the systemic exposure [AUC] achieved at the maximum recommended human daily oral dose, respectively). No deaths occurred, but nephritis was reported in dogs at an oral dose of 1000 mg/kg (providing in excess of 12 times the systemic exposure [AUC] achieved at the maximum recommended human daily oral dose).
11DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
The recommended dosage of ZYFLO for the symptomatic treatment of patients with asthma is one 600-mg tablet four times a day for a total daily dose of 2400 mg. For ease of administration, ZYFLO may be taken with meals and at bedtime. Hepatic transaminases should be evaluated prior to initiation of ZYFLO and periodically during treatment (see
12HOW SUPPLIED
ZYFLO Tablets are available as 1 dosage strength: 600-mg white to off white, ovaloid, film coated tablets debossed “CT 1” on one side and bisect on the other side.
High-density polyethylene bottles of: 120 Tablets.....................................................................................NDC 10122-901-12
Recommended storage: Store tablets at controlled room temperature between 20˚-25˚C, (68˚-77˚F). See USP. Protect from light.
CTZI-003-0314-01-SPL-3
Manufactured for:
Chiesi USA, Inc.
Cary, NC 27518
13Patient Information Leaflet
ZYFLO
(zileuton tablets)
Patient Information Leaflet
ZYFLO
Generic Name: zileuton
Please read this leaflet carefully before you start taking ZYFLO
This leaflet provides important information about taking ZYFLO. It is not meant to take the place of your doctor’s specific instructions. Talk to your doctor if you have any questions about ZYFLO. Your doctor or pharmacist can also provide you with additional information about ZYFLO.
What is the most important information I should know about ZYFLO?
The most important things to remember are to take all your doses of ZYFLO every day and to make sure that you return to your doctor’s office for scheduled liver enzyme tests.
You should also know that you should seek medical help immediately if you need more “puffs” of your bronchodilator inhaler than normal or if you use the maximum number of “puffs” prescribed for one 24-hour period. These could be a sign of worsening asthma which means that your asthma therapy may need to be changed.
What is ZYFLO?
ZYFLO, which contains the active ingredient zileuton, blocks the formation of certain chemicals (leukotrienes) that may contribute to your asthma symptoms.
Who should not take ZYFLO?
You should not take ZYFLO if you:
- have active liver disease or have liver enzymes that are elevated.
- have ever had an allergic reaction to this medicine.
Your doctor will determine if it is safe for you to take ZYFLO.
What should I tell my doctor before I take the first dose of ZYFLO?
You should tell your doctor if you:
- have ever had liver disease, hepatitis, jaundice (yellow eyes or skin), or dark urine.
- drink alcohol.
- are taking any prescription or nonprescription medicines. Your doctor may adjust the doses of some of your other medicines while you are taking ZYFLO.
- if you are taking theophylline for your asthma, the blood-thinning medication warfarin, or the blood-pressure medication propranolol, your doctor may need to change the doses of these drugs.
- are pregnant, planning to become pregnant, or are breast-feeding.
How should I take ZYFLO?
- ZYFLO is taken four times a day with or without food. It may be easier to remember to take ZYFLO if you make it part of your daily routine such as with meals and at bedtime.
- For ZYFLO to help control your asthma symptoms, it must be taken everyday as prescribed by your doctor. ZYFLO WILL NOT relieve an asthma attack that has already started. While taking ZYFLO, it is important to keep taking your other asthma medicines as directed and to follow all of your doctor’s instructions.
- Even if you have no asthma symptoms, do not decrease the dose of ZYFLO or stop taking the medicine without talking to your doctor first. Feeling good is a sign that the medicine is working.
- When you take your dose of ZYFLO, the tablets may be swallowed whole or split in half to make them easier to swallow.
What should I avoid while taking ZYFLO?
- Because ZYFLO may affect how other medications work, always talk to your doctor before you start or stop taking any medicines while taking ZYFLO. This includes all prescription and nonprescription medicines.
- Never take a larger dose of ZYFLO or take it more often than your doctor has prescribed.
- It is also important for you to know that it may take several days or a few weeks to get the full benefit from ZYFLO and that you should not stop taking it if you do not feel better right away.
What are the possible side effects of ZYFLO?
All medicines, including ZYFLO, cause side effects in some people. Some of the most common side effects are abdominal pain, upset stomach, and nausea. You should tell your doctor if you experience any new or unusual symptoms while taking ZYFLO.
One side effect that occurs in a small number of patients is an increased release of substances from the liver called “enzymes.” Liver enzymes can be measured by a simple blood test. It is important that your doctor makes sure that your liver enzymes do not become too high and that it is safe for you to continue taking ZYFLO. To insure your safety, your doctor will do this blood test before you first start taking ZYFLO and repeat it on a regular basis while you are taking the medicine.
Usually, even if your liver enzymes are increased, you will not notice any symptoms. However, some symptoms of increased liver enzymes are feeling more tired than normal, “flu-like” symptoms, itching, yellow skin, and/or yellow color in the whites of the eyes, or urine that is darker than normal.
Sleep problems and changes in your behavior can happen while you take ZYFLO. Tell your healthcare provider if you have any sleep problems or changes in behavior.
If you notice these or any other symptoms that you think may be caused by ZYFLO, call your doctor immediately. Once the medicine is stopped, these symptoms usually go away.
Even if you do not have any of these symptoms, you should continue to see your doctor for regular check-ups and liver enzyme tests.
Where should I keep my supply of ZYLFO?
Keep ZYFLO and all medicines out of the reach of children. In case of an accidental overdose, call your doctor or a Poison Control Center immediately.
Protect ZYFLO from light and replace the child-resistant cap each time after use. Store ZYFLO between 68
If you would like more information about ZYFLO, ask your doctor or pharmacist. If you have any questions or concerns about taking ZYFLO, discuss them with your doctor.
Revised: January 2017