Generic Name
Alprazolam
Brand Names
Xanax, Alprazolam C-IV, Alprazolam ODT C-IV
FDA approval date: October 16, 1981
Classification: Benzodiazepine
Form: Tablet, Solution
What is Xanax (Alprazolam)?
Alprazolam tablets are indicated for the: acute treatment of generalized anxiety disorder in adults. treatment of panic disorder , with or without agoraphobia in adults.
Approved To Treat
Top Global Experts
There are no experts for this drug
Save this treatment for later
Not sure about your diagnosis?
Related Clinical Trials
There is no clinical trials being done for this treatment
Related Latest Advances
There is no latest advances for this treatment
Brand Information
Xanax (alprazolam)
WARNING: RISKS FROM CONCOMITANT USE WITH OPIOIDS; ABUSE, MISUSE, AND ADDICTION; and DEPENDENCE AND WITHDRAWAL REACTIONS
- Concomitant use of benzodiazepines and opioids may result in profound sedation, respiratory depression, coma, and death. Reserve concomitant prescribing of these drugs for patients for whom alternative treatment options are inadequate. Limit dosages and durations to the minimum required. Follow patients for signs and symptoms of respiratory depression and sedation
- The use of benzodiazepines, including XANAX, exposes users to risks of abuse, misuse, and addiction, which can lead to overdose or death. Abuse and misuse of benzodiazepines commonly involve concomitant use of other medications, alcohol, and/or illicit substances, which is associated with an increased frequency of serious adverse outcomes. Before prescribing XANAX and throughout treatment, assess each patient’s risk for abuse, misuse, and addiction
- The continued use of benzodiazepines, including XANAX, may lead to clinically significant physical dependence. The risks of dependence and withdrawal increase with longer treatment duration and higher daily dose. Abrupt discontinuation or rapid dosage reduction of XANAX after continued use may precipitate acute withdrawal reactions, which can be life-threatening. To reduce the risk of withdrawal reactions, use a gradual taper to discontinue XANAX or reduce the dosage
1INDICATIONS AND USAGE
XANAX is indicated for the:
- acute treatment of generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) in adults.
- treatment of panic disorder (PD), with or without agoraphobia in adults.
2DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
XANAX tablets are available as:
- 0.25 mg: white, oval, scored, imprinted “XANAX 0.25”
- 0.5 mg: peach, oval, scored, imprinted “XANAX 0.5”
- 1 mg: blue, oval, scored, imprinted “XANAX 1.0”
- 2 mg: white, oblong, multi-scored, imprinted “XANAX ” on one side and “2” on the reverse side
3CONTRAINDICATIONS
XANAX is contraindicated in patients:
- with known hypersensitivity to alprazolam or other benzodiazepines. Angioedema has been reported
- taking strong cytochrome P450 3A (CYP3A) inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole, itraconazole), except ritonavir
4ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Risks from Concomitant Use with Opioids
- Abuse, Misuse, and Addiction
- Dependence and Withdrawal Reactions
- Effects on Driving and Operating Machinery
- Patients with Depression
- Neonatal Sedation and Withdrawal Syndrome
- Risks in Patients with Impaired Respiratory Function
4.1Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The data in the two tables below are estimates of adverse reaction incidence among adult patients who participated in:
- 4-week placebo-controlled clinical studies with XANAX dosages up to 4 mg per day for the acute treatment of generalized anxiety disorder (Table 1)
- Short-term (up to 10 weeks) placebo-controlled clinical studies with XANAX dosages up to 10 mg per day for panic disorder, with or without agoraphobia (Table 2).
In addition to the adverse reactions (i.e., greater than 1%) enumerated in the table above for patients with generalized anxiety disorder, the following adverse reactions have been reported in association with the use of benzodiazepines: dystonia, irritability, concentration difficulties, anorexia, transient amnesia or memory impairment, loss of coordination, fatigue, seizures, sedation, slurred speech, jaundice, musculoskeletal weakness, pruritus, diplopia, dysarthria, changes in libido, menstrual irregularities, incontinence and urinary retention.
In addition to the reactions (i.e., greater than 1%) enumerated in the table above for patients with panic disorder, the following adverse reactions have been reported in association with the use of XANAX: seizures, hallucinations, depersonalization, taste alterations, diplopia, elevated bilirubin, elevated hepatic enzymes, and jaundice.
Adverse Reactions Reported as Reasons for Discontinuation in Treatment of Panic Disorder in Placebo-Controlled Trials
In a larger database comprised of both controlled and uncontrolled studies in which 641 patients received XANAX, discontinuation-emergent symptoms which occurred at a rate of over 5% in patients treated with XANAX and at a greater rate than the placebo-treated group are shown in Table 3.
There have also been reports of withdrawal seizures upon rapid decrease or abrupt discontinuation of XANAX
Paradoxical reactions such as stimulation, increased muscle spasticity, sleep disturbances, hallucinations, and other adverse behavioral effects such as agitation, rage, irritability, and aggressive or hostile behavior have been reported rarely. In many of the spontaneous case reports of adverse behavioral effects, patients were receiving other CNS drugs concomitantly and/or were described as having underlying psychiatric conditions. Should any of the above events occur, alprazolam should be discontinued. Isolated published reports involving small numbers of patients have suggested that patients who have borderline personality disorder, a prior history of violent or aggressive behavior, or alcohol or substance abuse may be at risk for such events. Instances of irritability, hostility, and intrusive thoughts have been reported during discontinuation of alprazolam in patients with posttraumatic stress disorder.
4.2Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during postapproval use of XANAX. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Endocrine disorders: Hyperprolactinemia
General disorders and administration site conditions: Edema peripheral
Hepatobiliary disorders: Hepatitis, hepatic failure
Investigations: Liver enzyme elevations
Psychiatric disorders: Hypomania, mania
Reproductive system and breast disorders: Gynecomastia, galactorrhea
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: Photosensitivity reaction, angioedema, Stevens-Johnson syndrome
5OVERDOSAGE
Overdosage of benzodiazepines is characterized by central nervous system depression ranging from drowsiness to coma. In mild to moderate cases, symptoms can include drowsiness, confusion, dysarthria, lethargy, hypnotic state, diminished reflexes, ataxia, and hypotonia. Rarely, paradoxical or disinhibitory reactions (including agitation, irritability, impulsivity, violent behavior, confusion, restlessness, excitement, and talkativeness) may occur. In severe overdosage cases, patients may develop respiratory depression and coma. Overdosage of benzodiazepines in combination with other CNS depressants (including alcohol and opioids) may be fatal
In managing benzodiazepine overdosage, employ general supportive measures, including intravenous fluids and airway management. Flumazenil, a specific benzodiazepine receptor antagonist indicated for the complete or partial reversal of the sedative effects of benzodiazepines in the management of benzodiazepine overdosage, can lead to withdrawal and adverse reactions, including seizures, particularly in the context of mixed overdosage with drugs that increase seizure risk (e.g., tricyclic and tetracyclic antidepressants) and in patients with long-term benzodiazepine use and physical dependency. The risk of withdrawal seizures with flumazenil use may be increased in patients with epilepsy. Flumazenil is contraindicated in patients who have received a benzodiazepine for control of a potentially life-threatening condition (e.g., status epilepticus). If the decision is made to use flumazenil, it should be used as an adjunct to, not as a substitute for, supportive management of benzodiazepine overdosage. See the flumazenil injection Prescribing Information.
Consider contacting the Poison Help Line (1-800-222-1222), or a medical toxicologist for additional overdosage management recommendations.
6DESCRIPTION
XANAX contains alprazolam which is a triazolo analog of the 1,4 benzodiazepine class of central nervous system-active compounds.
The chemical name of alprazolam is 8-Chloro-1-methyl-6-phenyl-4H-s-triazolo [4,3-α] [1,4] benzodiazepine.
The structural formula is:
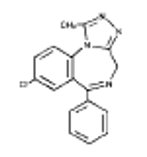
Alprazolam is a white crystalline powder, which is soluble in methanol or ethanol but which has no appreciable solubility in water at physiological pH.
Each XANAX tablet, for oral administration, contains 0.25 mg, 0.5 mg, 1 mg, or 2 mg of alprazolam.
Inactive ingredients: cellulose, corn starch, docusate sodium, lactose, magnesium stearate, silicon dioxide and sodium benzoate. In addition, the 0.5 mg tablet contains FD&C Yellow No. 6 and the 1 mg tablet contains FD&C Blue No. 2.
7HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
XANAX is supplied in the following strengths and package configurations:
Store at controlled room temperature 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
8PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (
Risks from Concomitant Use with Opioids
Advise both patients and caregivers about the risks of potentially fatal respiratory depression and sedation when XANAX is used with opioids and not to use such drugs concomitantly unless supervised by a healthcare provider. Advise patients not to drive or operate heavy machinery until the effects of concomitant use with the opioid have been determined
Abuse, Misuse, and Addiction
Inform patients that the use of XANAX, even at recommended dosages, exposes users to risks of abuse, misuse, and addiction, which can lead to overdose and death, especially when used in combination with other medications (e.g., opioid analgesics), alcohol, and/or illicit substances. Inform patients about the signs and symptoms of benzodiazepine abuse, misuse, and addiction; to seek medical help if they develop these signs and/or symptoms; and on the proper disposal of unused drug
Withdrawal Reactions
Inform patients that the continued use of XANAX may lead to clinically significant physical dependence and that abrupt discontinuation or rapid dosage reduction of XANAX may precipitate acute withdrawal reactions, which can be life-threatening. Inform patients that in some cases, patients taking benzodiazepines have developed a protracted withdrawal syndrome with withdrawal symptoms lasting weeks to more than 12 months. Instruct patients that discontinuation or dosage reduction of XANAX may require a slow taper
Effects on Driving and Operating Machinery
Advise patients not to drive a motor vehicle or operate heavy machinery while taking XANAX due to its CNS depressant effects. Also advise patients to avoid use of alcohol or other CNS depressants while taking XANAX
Patients with Depression
Advise patients, their families, and caregivers to look for signs of suicidality or worsening depression, and to inform the patient’s healthcare provider immediately
Concomitant Medications
Advise patients to inform their healthcare provider of all medicines they take, including prescription and nonprescription medications, vitamins and herbal supplements
Pregnancy
Advise pregnant females that use of XANAX late in pregnancy can result in sedation (respiratory depression, lethargy, hypotonia) and/or withdrawal symptoms (hyperreflexia, irritability, restlessness, tremors, inconsolable crying, and feeding difficulties) in newborns
Advise patients that there is a pregnancy exposure registry that monitors pregnancy outcomes in women exposed to XANAX during pregnancy
Lactation
Advise patients that breastfeeding is not recommended during treatment with XANAX
Distributed by:
UPJ:XNXT:RX2
9Medication Guide
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Revised: 1/2023
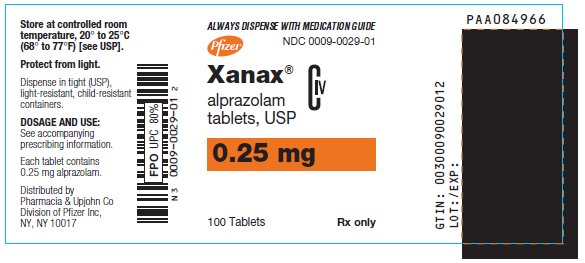
10PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 0.25 mg
ALWAYS DISPENSE WITH MEDICATION GUIDE
NDC 0009-0029-01
Pfizer
Xanax
alprazolam
CIV
0.25 mg
100 Tablets
Store at controlled room
Protect from light.
Dispense in tight (USP),
DOSAGE AND USE:
See accompanying
prescribing information.
See accompanying
prescribing information.
Each tablet contains
Distributed by
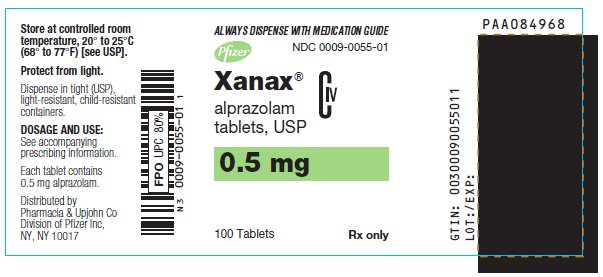
11PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 0.5 mg
ALWAYS DISPENSE WITH MEDICATION GUIDE
NDC 0009-0055-01
Pfizer
Xanax
alprazolam
CIV
0.5 mg
100 Tablets
Store at controlled room
Protect from light.
Dispense in tight (USP),
DOSAGE AND USE:
See accompanying
prescribing information.
See accompanying
prescribing information.
Each tablet contains
Distributed by
12PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 1 mg
ALWAYS DISPENSE WITH MEDICATION GUIDE
NDC 0009-0090-01
Pfizer
Xanax
alprazolam
CIV
1 mg
100 Tablets
Store at controlled room
Protect from light.
Dispense in tight (USP),
DOSAGE AND USE:
See accompanying
prescribing information.
See accompanying
prescribing information.
Each tablet contains
Distributed by

13PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 2 mg
ALWAYS DISPENSE WITH MEDICATION GUIDE
NDC 0009-0094-01
Pfizer
Xanax
alprazolam
CIV
2 mg
100 Tablets
Store at controlled room
Protect from light.
Dispense in tight (USP),
DOSAGE AND USE:
See accompanying
prescribing information.
See accompanying
prescribing information.
Each tablet contains
Distributed by
