Brand Name
Austedo
Generic Name
Deutetrabenazine
View Brand Information FDA approval date: April 12, 2017
Form: Tablet, Kit
What is Austedo (Deutetrabenazine)?
AUSTEDO ® XR and AUSTEDO ® are indicated in adults for the treatment of: chorea associated with Huntington’s disease [see Clinical Studies ( 1.
Approved To Treat
Top Global Experts
Save this treatment for later
Not sure about your diagnosis?
Related Clinical Trials
A Phase 4, Open-Label Study to Evaluate the Efficacy of Valbenazine on Clinician- and Patient-Reported Outcomes in Patients With Tardive Dyskinesia (TD) Who Remain Symptomatic While on Deutetrabenazine or After Discontinuing Prior TD Treatment With a Vesicular Monoamine Transporter 2 (VMAT2) Inhibitor
Summary: This study will evaluate the efficacy of valbenazine on clinician- and patient-reported outcomes in participants with TD while receiving or after stopping a VMAT2 inhibitor.
Related Latest Advances
Brand Information
Austedo (Deutetrabenazine)
WARNING: DEPRESSION AND SUICIDALITY IN PATIENTS WITH HUNTINGTON’S DISEASE
AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO can increase the risk of depression and suicidal thoughts and behavior (suicidality) in patients with Huntington’s disease. Anyone considering the use of AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO must balance the risks of depression and suicidality with the clinical need for treatment of chorea. Closely monitor patients for the emergence or worsening of depression, suicidality, or unusual changes in behavior. Patients, their caregivers, and families should be informed of the risk of depression and suicidality and should be instructed to report behaviors of concern promptly to the treating physician.
Particular caution should be exercised in treating patients with a history of depression or prior suicide attempts or ideation, which are increased in frequency in Huntington’s disease. AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO are contraindicated in patients who are suicidal, and in patients with untreated or inadequately treated depression [see Contraindications ()].
1INDICATIONS AND USAGE
AUSTEDO XR
- chorea associated with Huntington’s disease
- tardive dyskinesia
2DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
AUSTEDO XR extended-release tablets are available in the following strengths:
- The 6 mg extended-release tablets are round, grey-coated tablets, with “Q6” printed in black ink on one side.
- The 12 mg extended-release tablets are round, blue-coated tablets, with “Q12” printed in black ink on one side.
- The 18 mg extended-release tablets are round, light grey-coated tablets, with “Q18” printed in black ink on one side.
- The 24 mg extended-release tablets are round, purple-coated tablets, with “Q24” printed in black ink on one side.
- The 30 mg extended-release tablets are round, light orange-coated tablets, with “Q30” printed in black ink on one side.
- The 36 mg extended-release tablets are round, light purple-coated tablets, with “Q36” printed in black ink on one side.
- The 42 mg extended-release tablets are round, orange-coated tablets, with “Q42” printed in black ink on one side.
- The 48 mg extended-release tablets are round, pink-coated tablets, with “Q48” printed in black ink on one side.
AUSTEDO tablets are available in the following strengths:
- The 6 mg tablets are round, purple-coated tablets, with “SD” over “6” printed in black ink on one side.
- The 9 mg tablets are round, blue-coated tablets, with “SD” over “9” printed in black ink on one side.
- The 12 mg tablets are round, beige-coated tablets, with “SD” over “12” printed in black ink on one side.
3CONTRAINDICATIONS
AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO are contraindicated in patients:
- With Huntington’s disease who are suicidal, or have untreated or inadequately treated depression
- With hepatic impairment
- Taking reserpine. At least 20 days should elapse after stopping reserpine before starting AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO
- Taking monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs). AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO should not be used in combination with an MAOI, or within 14 days of discontinuing therapy with an MAOI
- Taking tetrabenazine or valbenazine
4ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the labeling:
- Depression and Suicidality in Patients with Huntington’s disease
- QTc Prolongation
- Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS)
- Akathisia, Agitation, and Restlessness
- Parkinsonism
- Sedation and Somnolence
- Hyperprolactinemia
- Binding to Melanin-Containing Tissues
4.1Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The studies described below were conducted with AUSTEDO tablets; adverse reactions with AUSTEDO XR extended-release tablets are expected to be similar to AUSTEDO tablets.
Patients with Huntington’s Disease
Study 1
Table 3: Adverse Reactions in Patients with Huntington's Disease (Study 1) Experienced by at Least 4% of Patients on AUSTEDO and with a Greater Incidence than on Placebo
One or more adverse reactions resulted in a reduction of the dose of study medication in 7% of patients in Study 1. The most common adverse reaction resulting in dose reduction in patients receiving AUSTEDO was dizziness (4%).
Agitation led to discontinuation in 2% of patients treated with AUSTEDO in Study 1.
Patients with Tardive Dyskinesia
The data described below reflect 410 tardive dyskinesia patients participating in clinical trials. AUSTEDO was studied primarily in two 12-week, placebo-controlled trials (fixed dose, dose escalation)
The most common adverse reactions occurring in greater than 3% of AUSTEDO-treated patients and greater than placebo were nasopharyngitis and insomnia. The adverse reactions occurring in >2% or more patients treated with AUSTEDO (12-48 mg per day) and greater than in placebo patients in two double-blind, placebo-controlled studies in patients with tardive dyskinesia (Study 1 and Study 2) are summarized in Table 4.
Table 4: Adverse Reactions in 2 Placebo-Controlled Tardive Dyskinesia Studies (Study 1 and Study 2) of 12-week Treatment on AUSTEDO Reported in at Least 2% of Patients and Greater than Placebo
One or more adverse reactions resulted in a reduction of the dose of study medication in 4% of AUSTEDO-treated patients and in 2% of placebo-treated patients.
5OVERDOSAGE
Overdoses ranging from 100 mg to 1 g have been reported in the literature with tetrabenazine, a closely related VMAT2 inhibitor. The following adverse reactions occurred with overdosing: acute dystonia, oculogyric crisis, nausea and vomiting, sweating, sedation, hypotension, confusion, diarrhea, hallucinations, rubor, and tremor.
Treatment should consist of those general measures employed in the management of overdosage with any central nervous system-active drug. General supportive and symptomatic measures are recommended. Cardiac rhythm and vital signs should be monitored. In managing overdosage, the possibility of multiple drug involvement should always be considered. The physician should consider contacting a poison control center on the treatment of any overdose. Telephone numbers for certified poison control centers are listed on the American Association of Poison Control Centers website www.aapcc.org.
6DESCRIPTION
AUSTEDO XR extended-release tablets and AUSTEDO tablets are formulated with deutetrabenazine, a vesicular monoamine transporter 2 (VMAT2) inhibitor for oral administration. The molecular weight of deutetrabenazine is 323.46; the pKa is 6.31. Deutetrabenazine is a hexahydro-dimethoxybenzoquinolizine derivative and has the following chemical name: (
The molecular formula for deutetrabenazine is C
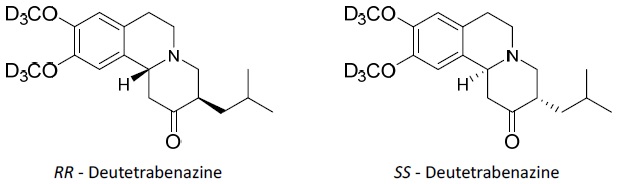
Deutetrabenazine is a white to slightly yellow crystalline powder that is sparingly soluble in water and soluble in ethanol.
AUSTEDO XR extended-release tablets contain 6 mg, 12 mg, 18 mg, 24 mg, 30 mg, 36 mg, 42 mg, or 48 mg deutetrabenazine, and the following inactive ingredients: ammonium hydroxide, black iron oxide, butyl alcohol, butylated hydroxyanisole, butylated hydroxytoluene, cellulose acetate, hydroxypropyl cellulose, hypromellose, isopropyl alcohol, magnesium stearate, polyethylene glycol, polyethylene glycol 3350, polyethylene oxide, polyvinyl alcohol, propylene glycol, shellac, sodium chloride, talc, titanium dioxide, and FD&C red #40 lake. The 6 mg, 12 mg, 18 mg, 30 mg, 36 mg, and 42 mg extended-release tablets also contain FD&C yellow #6 lake. The 6 mg, 12 mg, 24 mg, and 36 mg extended-release tablets also contain FD&C blue #2 lake. The 18 mg extended-release tablets also contain carmine.
AUSTEDO
AUSTEDO tablets contain 6 mg, 9 mg, or 12 mg deutetrabenazine, and the following inactive ingredients: ammonium hydroxide, black iron oxide, butyl alcohol, butylated hydroxyanisole, butylated hydroxytoluene, magnesium stearate, mannitol, microcrystalline cellulose, polyethylene glycol, polyethylene oxide, polysorbate 80, polyvinyl alcohol, povidone, propylene glycol, shellac, talc, titanium dioxide, and FD&C blue #2 lake. The 6 mg tablets also contain FD&C red #40 lake. The 12 mg tablets also contain FD&C yellow #6 lake.
7CLINICAL STUDIES
The studies described below establishing effectiveness for Huntington’s disease and tardive dyskinesia were conducted with AUSTEDO tablets. The efficacy of AUSTEDO XR is based on a relative bioavailability study comparing AUSTEDO XR tablets administered once daily and AUSTEDO tablets administered twice daily
7.1Chorea Associated with Huntington’s Disease
The efficacy of AUSTEDO as a treatment for chorea associated with Huntington's disease was established primarily in Study 1, a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multi-center trial conducted in 90 ambulatory patients with manifest chorea associated with Huntington’s disease. The diagnosis of Huntington’s disease was based on family history, neurological exam, and genetic testing. Treatment duration was 12 weeks, including an 8-week dose titration period and a 4-week maintenance period, followed by a 1-week washout. Patients were not blinded to discontinuation. AUSTEDO was started at 6 mg per day and titrated upward, at weekly intervals, in 6 mg increments until satisfactory treatment of chorea was achieved, intolerable side effects occurred, or until a maximal dose of 48 mg per day was reached. The primary efficacy endpoint was the Total Maximal Chorea Score, an item of the Unified Huntington's Disease Rating Scale (UHDRS). On this scale, chorea is rated from 0 to 4 (with 0 representing no chorea) for 7 different parts of the body. The total score ranges from 0 to 28.
Of the 90 patients enrolled, 87 patients completed the study. The mean age was 54 (range 23 to 74). Patients were 56% male and 92% Caucasian. The mean dose after titration was 40 mg per day. Table 5 and Figure 1 summarize the effects of AUSTEDO on chorea based on the Total Maximal Chorea Score. Total Maximal Chorea Scores for patients receiving AUSTEDO improved by approximately 4.4 units from baseline to the maintenance period (average of Week 9 and Week 12), compared to approximately 1.9 units in the placebo group. The treatment effect of -2.5 units was statistically significant (p<0.0001). The Maintenance Endpoint is the mean of the Total Maximal Chorea Scores for the Week 9 and Week 12 visits. At the Week 13 follow-up visit (1 week after discontinuation of the study medication), the Total Maximal Chorea Scores of patients who had received AUSTEDO returned to baseline (Figure 1).
*TMC is a subscale of the Unified Huntington's Disease Rating Scale (UHDRS)
†Primary efficacy endpoint
†Primary efficacy endpoint
Figure 1: Total Maximal Chorea Score Over Time in Study 1
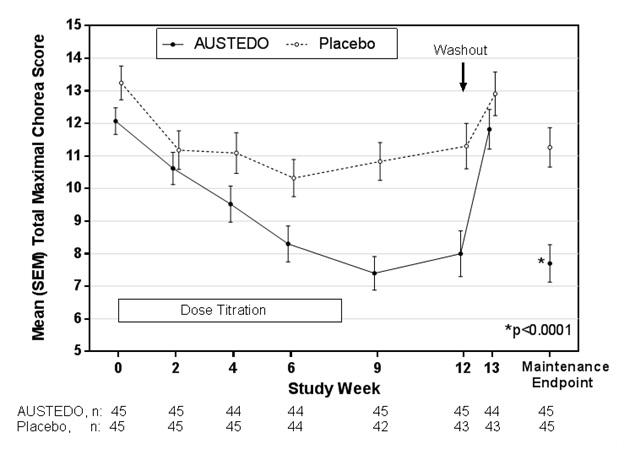
Figure 2: Distribution of the Change in Total Maximal Chorea Scores in Study 1
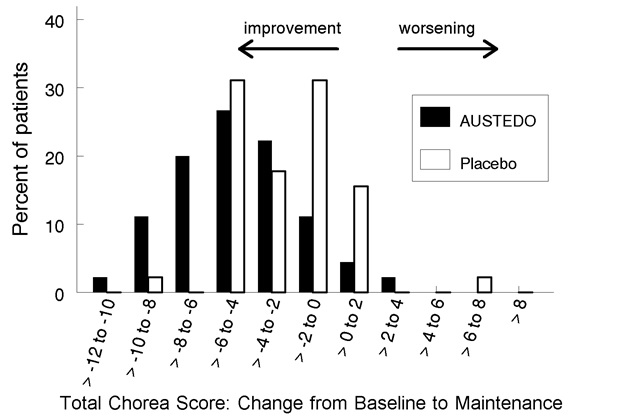
Figure 2 shows the distribution of values for the change in Total Maximal Chorea Score in Study 1. Negative values indicate a reduction in chorea and positive numbers indicate an increase in chorea.
A patient-rated global impression of change assessed how patients rated their overall Huntington’s disease symptoms. Fifty-one percent of patients treated with AUSTEDO rated their symptoms as “Much Improved” or “Very Much Improved” at the end of treatment, compared to 20% of placebo-treated patients.
In a physician-rated clinical global impression of change, physicians rated 42% percent of patients treated with AUSTEDO as “Much Improved” or “Very Much Improved” at the end of treatment compared to 13% of placebo-treated patients.
7.2Tardive Dyskinesia
The efficacy of AUSTEDO in the treatment for tardive dyskinesia was established in two 12‑week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multi-center trials conducted in 335 adult ambulatory patients with tardive dyskinesia caused by use of dopamine receptor antagonists. Patients had a history of using a dopamine receptor antagonist (antipsychotics, metoclopramide) for at least 3 months (or 1 month in patients 60 years of age and older). Concurrent diagnoses included schizophrenia/schizoaffective disorder (62%) and mood disorder (33%). With respect to concurrent antipsychotic use, 64% of patients were receiving atypical antipsychotics, 12% were receiving typical or combination antipsychotics, and 24% were not receiving antipsychotics.
The Abnormal Involuntary Movement Scale (AIMS) was the primary efficacy measure for the assessment of tardive dyskinesia severity. The AIMS is a 12-item scale; items 1 to 7 assess the severity of involuntary movements across body regions and these items were used in this study. Each of the 7 items was scored on a 0 to 4 scale, rated as: 0=not present; 1=minimal, may be extreme normal (abnormal movements occur infrequently and/or are difficult to detect); 2=mild (abnormal movements occur infrequently and are easy to detect); 3=moderate (abnormal movements occur frequently and are easy to detect) or 4 =severe (abnormal movements occur almost continuously and/or of extreme intensity). The AIMS total score (sum of items 1 to 7) could thus range from 0 to 28, with a decrease in score indicating improvement.
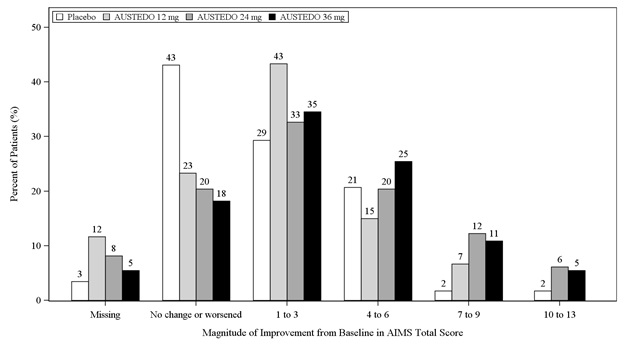
In Study 1, a 12-week, placebo-controlled, fixed-dose trial, adults with tardive dyskinesia were randomized 1:1:1:1 to 12 mg AUSTEDO, 24 mg AUSTEDO, 36 mg AUSTEDO, or placebo. Treatment duration included a 4-week dose escalation period and an 8-week maintenance period followed by a 1-week washout. The dose of AUSTEDO was started at 12 mg per day and increased at weekly intervals in 6 mg/day increments to a dose target of 12 mg, 24 mg or 36 mg per day. The population (n= 222) was 21 to 81 years old (mean 57 years), 48% male, and 79% Caucasian. In Study 1, the AIMS total score for patients receiving AUSTEDO demonstrated statistically significant improvement, from baseline to Week 12, of 3.3 and 3.2 units for the 36 mg and 24 mg arms, respectively, compared with 1.4 units in placebo (Study 1 in Table 6). The improvements on the AIMS total score over the course of the study are displayed in Figure 3. Data did not suggest substantial differences in efficacy across various demographic groups. The treatment response rate distribution, based on magnitude of AIMS total score from baseline to week 12 is displayed in Figure 4.
The mean changes in the AIMS total score by visit are shown in Figure 3.
In Study 2, a 12-week, placebo-controlled, flexible-dose trial, adults with tardive dyskinesia (n=113) received daily doses of placebo or AUSTEDO, starting at 12 mg per day with increases allowed in 6-mg increments at 1-week intervals until satisfactory control of dyskinesia was achieved, until intolerable side effects occurred, or until a maximal dose of 48 mg per day was reached. Treatment duration included a 6-week dose titration period and a 6-week maintenance period followed by a 1-week washout. The population was 25 to 75 years old (mean 55 years), 48% male, and 70% Caucasian. Patients were titrated to an optimal dose over 6 weeks. The average dose of AUSTEDO after treatment was 38.3 mg per day. There was no evidence suggesting substantial differences in efficacy across various demographic groups. In Study 2, AIMS total score for patients receiving AUSTEDO demonstrated statistically significant improvement by 3.0 units from baseline to endpoint (Week 12), compared with 1.6 units in the placebo group with a treatment effect of -1.4 units. Table 6 summarizes the effects of AUSTEDO on tardive dyskinesia based on the AIMS.
*Dose that was statistically significantly different from placebo after adjusting for multiplicity.
LS Mean = Least-squares mean; SD = Standard deviation; SE = Standard error; CI = 2-sided 95% confidence interval
Figure 3: Least Square Means of Change in AIMS Total Score from Baseline for AUSTEDO Compared to Placebo (Study 1)
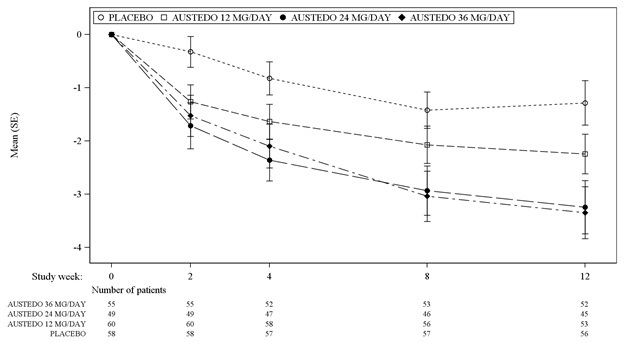
SE = Standard error
Figure 4: Percent of Patients with Specified Magnitude of AIMS Total Score Improvement at the End of Week 12 (Study 1)
8PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient or caregiver to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide).
Administration Instructions
Instruct patients to swallow AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO whole and not to chew, crush, or break AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO
AUSTEDO XR
Advise patients to take AUSTEDO XR with or without food in once-daily doses. Inform patients not to be concerned if they occasionally notice something that looks like a tablet shell in their stool
AUSTEDO
Advise patients to take AUSTEDO with food. Advise patients to take daily dosages of 12 mg or higher in two divided doses (twice daily).
Risk of Depression and Suicide in Patients with Huntington’s Disease
Advise patients, their caregivers, and families that AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO may increase the risk of depression, worsening depression, and suicidality, and to immediately report any symptoms to a healthcare provider
Prolongation of the QTc Interval
Inform patients to consult their physician immediately if they feel faint, lose consciousness, or have heart palpitations
Parkinsonism
Inform patients that AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO may cause Parkinson-like symptoms, which could be severe. Advise patients to consult their healthcare provider if they experience slight shaking, body stiffness, trouble moving, trouble keeping their balance, or falls
Risk of Sedation and Somnolence
Advise patients that AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO may cause sedation and somnolence and may impair the ability to perform tasks that require complex motor and mental skills. Until they learn how they respond to a stable dose of AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO, patients should be careful doing activities that require them to be alert, such as driving a car or operating machinery
Interaction with Alcohol or Other Sedating Drugs
Advise patients that alcohol or other drugs that cause sleepiness will worsen somnolence
Concomitant Medications
Advise patients to notify their physician of all medications they are taking and to consult with their healthcare provider before starting any new medications because of a potential for interactions
Manufactured for:
©2025 Teva Neuroscience, Inc.
AUS-013
AUSTEDO XR U.S. Patent Nos: 8,524,733; 9,550,780; 10,959,996; 11,179,386; 11,357,772; 11,311,488; 11,564,917; 11,446,291; 11,648,244; 11,813,232; 12,016,858
AUSTEDO U.S. Patent Nos: 8,524,733; 9,233,959; 9,296,739; 9,550,780; 9,814,708; 10,959,996; 11,179,386; 11,357,772; 11,564,917; 11,446,291; 11,648,244; 11,666,566; 11,813,232; 12,016,858
9Package/Label Display Panel
NDC 68546-
10Package/Label Display Panel
NDC 68546-

11Package/Label Display Panel
NDC 68546-

12Package/Label Display Panel
NDC 68546-
13Package/Label Display Panel
NDC 68546-

14Package/Label Display Panel
NDC 68546-

15Package/Label Display Panel
NDC 68546-

16Package/Label Display Panel
NDC 68546-

17Package/Label Display Panel
NDC 68546-490-

18Package/Label Display Panel
NDC 68546-

19Package/Label Display Panel
NDC 68546-

20Package/Label Display Panel
NDC 68546-
21Package/Label Display Panel
NDC 68546-

22Package/Label Display Panel
NDC 68546-182-
23Package/Label Display Panel
NDC 68546-181-
SAMPLE – NOT FOR SALEEach time AUSTEDO is dispensed, give the patient the accompanying Medication Guide.
Dispense in this sealed carton.Monthly carton contains 49 tablets in 2 child-resistant packs including, 21 purple tablets, each containing 6 mg of deutetrabenazine, 14 blue tablets, each containing 9 mg of deutetrabenazine, and 14 beige tablets, each containing 12 mg of deutetrabenazine.
teva
Dispense in this sealed carton.Monthly carton contains 49 tablets in 2 child-resistant packs including, 21 purple tablets, each containing 6 mg of deutetrabenazine, 14 blue tablets, each containing 9 mg of deutetrabenazine, and 14 beige tablets, each containing 12 mg of deutetrabenazine.
teva

24Package/Label Display Panel
NDC 68546-176-
- Week 1: 14 purple tablets containing 6 mg deutetrabenazine
- Week 2: 14 blue tablets containing 9 mg deutetrabenazine
2 PULL OUT HERE

25Package/Label Display Panel
NDC 68546-177-
- Week 1: 7 purple tablets containing 6 mg deutetrabenazine
- Week 2: 14 purple tablets containing 6 mg deutetrabenazine
2 PULL OUT HERE




