DOXOrubicin
What is Adriamycin (DOXOrubicin)?
Receiving a cancer diagnosis can be one of the most challenging moments in life. Treatment often involves a combination of surgery, radiation, and powerful medicines designed to target and destroy cancer cells. Adriamycin (doxorubicin) is one of the most widely used and effective chemotherapy drugs, known for its ability to treat a broad range of cancers.
Adriamycin belongs to a class of medications called anthracycline antibiotics. Despite its name, it is not an antibiotic used for infections; instead, it’s a chemotherapy agent that interferes with cancer cell growth and reproduction. This drug has been a cornerstone in cancer treatment for decades and is often part of combination chemotherapy regimens. Doctors use it to treat cancers such as breast cancer, lymphomas, leukemias, sarcomas, and ovarian cancer, among others.
Although Adriamycin is a strong and potent medication, it plays a vital role in improving survival rates and helping patients achieve remission when carefully managed by an oncology team.
What does Adriamycin do?
Adriamycin is used to treat various types of cancer by slowing or stopping the growth of malignant cells. It is often included in combination chemotherapy protocols where multiple drugs are used together to improve effectiveness and reduce the likelihood of resistance.
Some of the most common cancers treated with Adriamycin include:
- Breast cancer (often part of the “AC” regimen with cyclophosphamide)
- Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphoma
- Leukemias (such as acute lymphoblastic leukemia)
- Sarcomas (cancers of connective tissues like bone or muscle)
- Bladder, ovarian, and thyroid cancers
In these settings, Adriamycin helps shrink tumors, control disease spread, and enhance the effectiveness of other cancer treatments. Clinical studies have shown that doxorubicin remains one of the most active drugs against solid and blood cancers, significantly improving long-term outcomes when used appropriately (NIH, 2024).
How does Adriamycin work?
Adriamycin works by interfering with the DNA inside cancer cells, preventing them from dividing and multiplying. In simple terms, it disrupts the “instructions” that cancer cells need to grow.
Doxorubicin acts through several mechanisms:
- DNA intercalation: The drug slips between DNA strands, blocking the enzymes responsible for replication.
- Topoisomerase II inhibition: This enzyme helps unwind DNA during cell division; Adriamycin blocks it, halting the process.
- Free radical generation: The drug produces reactive oxygen species that damage cell membranes, proteins, and DNA, leading to cancer cell death.
This multi-targeted approach makes Adriamycin one of the most effective chemotherapy drugs in oncology. However, because it affects rapidly dividing cells, it can also impact healthy tissues like hair follicles, bone marrow, and the lining of the digestive tract leading to some of its side effects.
Clinically, its mechanism is powerful because it helps kill cancer cells at multiple stages of their growth cycle, reducing the risk of recurrence and improving treatment success.
Adriamycin side effects
Like most chemotherapy medications, Adriamycin can cause side effects, some of which are temporary and manageable with supportive care. Oncologists closely monitor patients to balance treatment effectiveness with safety.
Common side effects may include:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Hair loss (usually temporary)
- Fatigue and weakness
- Mouth sores
- Changes in urine color (reddish tint for a day or two after treatment)
Serious side effects, though managed, include heart damage (monitored via echocardiograms), bone marrow suppression (reducing white/red blood cells and platelets), and liver toxicity (checked with blood tests). Infusion must be intravenous to prevent tissue damage.
Patients should immediately contact their doctor if they experience chest pain, shortness of breath, fever, unexplained bruising, or swelling.
Who should avoid Adriamycin:
Individuals with severe heart disease, prior high-dose anthracycline exposure, or doxorubicin allergies should avoid this drug or seek alternatives. Pregnant patients are generally advised against Adriamycin unless benefits clearly outweigh risks.
However, oncologists have extensive experience safely using Adriamycin with modern protocols, including dose adjustments, protective agents, and regular monitoring, to minimize risks.
Adriamycin dosage
Adriamycin is given intravenously in a hospital by an oncology nurse or doctor as part of a chemotherapy cycle, typically every few weeks. Dosage and frequency depend on cancer type and stage, patient’s body surface area, heart and liver function, and whether other chemotherapy drugs are used.
Due to Adriamycin’s potency, close monitoring of blood counts, heart function, and liver enzyme levels is essential. Dosing may be adjusted for older adults or those with existing heart or liver disease, with alternatives like liposomal doxorubicin (Doxil) considered to reduce side effects.
Does Adriamycin have a generic version?
Yes. Doxorubicin, the active ingredient in Adriamycin, is available as a generic medication approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Generic versions have the same active ingredient, strength, safety, and effectiveness as the brand-name drug but are typically more affordable.
Doxorubicin comes in conventional and liposomal (encapsulated) forms. Liposomal doxorubicin (Doxil, Caelyx) reduces heart-related side effects and may be used when the standard version isn’t tolerated. Adriamycin is another brand. Your oncologist will choose the best version based on your cancer, prior treatments, and health.
Conclusion
Adriamycin (doxorubicin) remains one of the most trusted and effective chemotherapy drugs in modern oncology. By targeting cancer cells at the DNA level, it helps slow tumor growth, improve remission rates, and extend survival in many types of cancer.
Adriamycin can cause heart and bone marrow side effects, but careful monitoring and supportive care improve safety and tolerability. Most side effects are temporary. Discuss concerns with your oncology team and follow monitoring. Adriamycin, when used responsibly, remains a key cancer therapy that has helped millions.
References
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). (2024). Doxorubicin hydrochloride: Prescribing information. Retrieved from https://www.accessdata.fda.gov
- Mayo Clinic. (2024). Doxorubicin (injection route) drug information. Retrieved from https://www.mayoclinic.org
- MedlinePlus. (2024). Doxorubicin injection: Uses, side effects, and precautions. National Library of Medicine. Retrieved from https://medlineplus.gov
- National Cancer Institute (NCI). (2024). Doxorubicin and anthracycline chemotherapy agents. Retrieved from https://www.cancer.gov
Approved To Treat
Top Global Experts
There are no experts for this drug
Related Clinical Trials
There is no clinical trials being done for this treatment
Related Latest Advances
There is no latest advances for this treatment
Brand Information
- Severe myocardial insufficiency
- Recent (occurring within the past 4 to 6 weeks) myocardial infarction
- Severe persistent drug-induced myelosuppression
- Severe hypersensitivity reaction to doxorubicin including anaphylaxis
- Cardiomyopathy and Arrhythmias
- Secondary Malignancies
- Extravasation and Tissue Necrosis
- Severe Myelosuppression
- Tumor Lysis Syndrome
- Radiation Sensitization and Radiation Recall
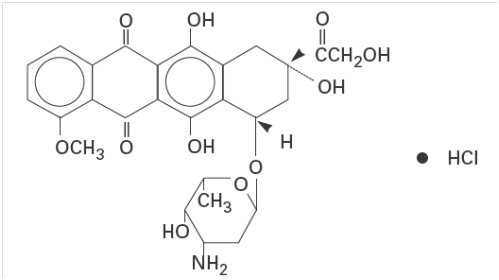

- Doxorubicin can cause irreversible myocardial damage. Advise patients to contact a healthcare provider for symptoms of heart failure during or after treatment with doxorubicin HCl
- There is an increased risk of treatment-related leukemia from doxorubicin HCl
- Doxorubicin can reduce the absolute neutrophil count resulting in an increased risk of infection. Advise patients to contact a healthcare provider for new onset fever or symptoms of infection
- Doxorubicin can cause fetal harm when administered during pregnancy. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with doxorubicin HCl and for 6 months after treatment, and to contact their healthcare provider if they become pregnant, or if pregnancy is suspected, during treatment with doxorubicin HCl
- Doxorubicin may induce chromosomal damage in sperm, which may lead to loss of fertility and offspring with birth defects. Advise patients to use effective contraception during and for 6 months after treatment
- Doxorubicin can cause premature menopause in females and loss of fertility in males
- Discontinue nursing while receiving doxorubicin HCl
- Doxorubicin can cause nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, mouth/oral pain and sores. Advise patients to contact a healthcare provider should they develop any severe symptoms that prevent them from eating and drinking
- Doxorubicin causes alopecia
- Doxorubicin can cause their urine to appear red for 1 to 2 days after administration.
- Heart failure. Doxorubicin may cause heart muscle damage that may lead to heart failure, which is a condition in which the heart does not pump well. Heart failure is irreversible in some cases and can lead to death. Heart failure can happen during your treatment with Doxorubicin or months to years after stopping treatment. Your risk of heart muscle damage increases with higher total amounts of doxorubicin hydrochloride that you receive in your lifetime. Your risk of heart failure is higher if you:
- already have other heart problems
- have had or are currently receiving radiation therapy to your chest
- have had treatment with certain other anti-cancer medicines
- take other medicines that can have severe side effects on your heart
- Tell your doctor if you get any of these symptoms of heart failure during or after treatment with Doxorubicin:
- extreme tiredness or
- fast heartbeat weakness
- swelling of your feet and ankles
- shortness of breath
- Your doctor will do tests to check the strength of your heart muscle before,
- during, and after your treatment with Doxorubicin.
- Risk of new cancers. You may have an increased risk of developing certain blood cancers called acute myelogenous leukemia (AML) or myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) after treatment with doxorubicin. Talk with your doctor about your risk of developing new cancers if you take Doxorubicin.
- Skin damage near the vein where Doxorubicin is given (Injection site reaction). Doxorubicin can damage the skin if it leaks out of the vein. Symptoms of infusion reaction include blisters and skin sores at injection site which may require skin grafts.
- Decreased blood cell counts. Doxorubicin can cause a decrease in neutrophils (a type of white blood cells important in fighting bacterial infections) and platelets (important for clotting and to control bleeding). This may lead to a serious infection, the need for blood transfusions, treatment in a hospital and death. Your doctor will check your blood cell count during your treatment with Doxorubicin and after you have stopped your treatment. Call your doctor right away if you get a fever (temperature of 100.4°F or greater) or chills with shivering.
- you have had a recent heart attack or have severe heart problems
- your blood cell counts (platelets, red blood cells, and white blood cells) are
- very low because of prior chemotherapy
- you have a severe liver problem
- you have had a serious allergic reaction to doxorubicin hydrochloride
- have heart problems including heart failure
- are currently receiving radiation therapy or plan to receive radiation to the chest
- have severe liver problems
- have had an allergic reaction to doxorubicin
- have any other medical conditions
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. Doxorubicin can harm your unborn baby. Women who are able to become pregnant and men who take Doxorubicin should use effective birth control (contraception) during treatment and for 6 months after treatment. Talk to your doctor about birth control methods. If you or your partner becomes pregnant, tell your doctor right away.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breast feed. Doxorubicin can pass into your breast milk and harm your baby. You and your doctor should decide if you will receive Doxorubicin or breastfeed. You should not do both.
- Doxorubicin will be given to you into your vein.
- See
- Total hair loss (alopecia). Your hair may re-grow after your treatment
- nausea
- vomiting
- Red colored urine. You may have red colored urine for 1 to 2 days after your infusion of Doxorubicin. This is normal. Tell your doctor if it does not stop in a few days, or if you see what looks like blood or blood clots in your urine.
- Darkening of your nails or separation of your nails from your nail bed.
- Easy bruising or bleeding.
- Call your doctor if you have severe symptoms that prevent you from eating or drinking, such as:
- nausea
- vomiting
- diarrhea
- mouth sores

FOR INTRAVENOUS USE ONLY

FOR INTRAVENOUS USE ONLY