Natazia
What is Natazia (Dienogest)?
Approved To Treat
Related Clinical Trials
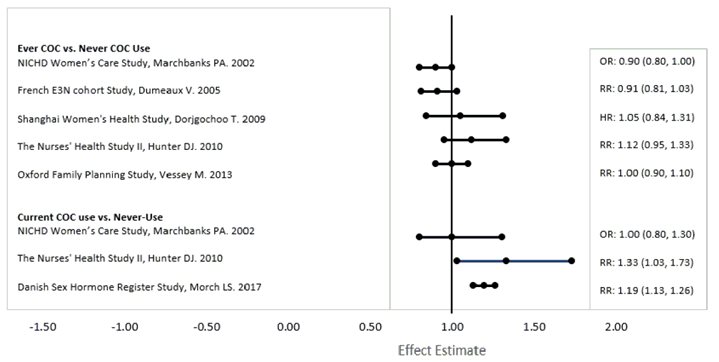
Summary: Prospective open-label randomized parallel groups study to compare efficacy and safety of Indinol Forto® 200 mg capsules and Visanne 2 mg tablets in treatment of endometriosis. This is phase 3 study, based on hypothesis of non-inferiority.
Summary: This study aims to analyze the salivary miRNA specific for patients diagnosed with endometriosis, specifically evaluating the miRNA profile of patients who respond versus those who do not respond to progestin therapy. Ninety patients attending the Chronic Pelvic Pain Clinic will be recruited, and they will be asked to provide a saliva sample before starting medical therapy. The response to the the...
Summary: This study aims to evaluate the effects of therapy with implantable Gestrinone compared to oral Dienogest in relieving complaints related to endometriosis.
Related Latest Advances
Brand Information
- 2 dark yellow tablets, with an embossed “DD” in a regular hexagon on one side, each containing 3 mg estradiol valerate
- 5 medium red tablets, with an embossed “DJ” in a regular hexagon on one side, each containing 2 mg estradiol valerate and 2 mg dienogest
- 17 light yellow tablets, with an embossed “DH” in a regular hexagon on one side, each containing 2 mg estradiol valerate and 3 mg dienogest
- 2 dark red tablets, with an embossed “DN” in a regular hexagon on one side, each containing 1 mg estradiol valerate
- 2 white tablets (inert), with an embossed “DT” in a regular hexagon on one side
- A high risk of arterial or venous thrombotic diseases. Examples include women who are known to:
- Undiagnosed abnormal uterine bleeding
- Current diagnosis of, or history of, breast cancer, which may be hormone sensitive
- Liver tumors, benign or malignant, or liver disease
- Serious cardiovascular events and stroke
- Vascular events
- Liver disease
- Irregular uterine bleeding
- Nausea
- Breast tenderness
- Headache
- 2 dark yellow tablets each containing 3 mg estradiol valerate
- 5 medium red tablets each containing 2 mg estradiol valerate and 2 mg dienogest
- 17 light yellow tablets each containing 2 mg estradiol valerate and 3 mg dienogest
- 2 dark red tablets each containing 1 mg estradiol valerate
- 2 white tablets (inert)
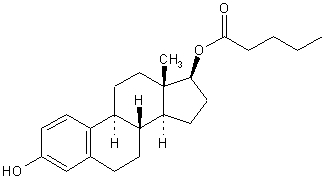
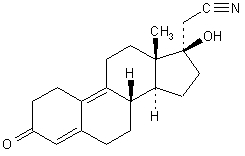
- Counsel patients that cigarette smoking increases the risk of serious cardiovascular events from COC use, and that women who are over 35 years old and smoke should not use COCs.
- Counsel patients that the increased risk of VTE compared to non-users of COCs is greatest after initially starting a COC or restarting (following a 4 week or greater pill-free interval) the same or a different COC.
- Counsel patients that Natazia does not protect against HIV infection (AIDS) and other sexually transmitted diseases.
- Counsel patients on Warnings and Precautions associated with COCs.
- Inform patients that Natazia is not indicated during pregnancy. If pregnancy occurs during treatment with Natazia, instruct the patient to stop further intake.
- Counsel patients to take one tablet daily by mouth at the same time every day in the exact order noted on the blister. Instruct patients what to do in the event pills are missed. See
- Counsel women who are taking strong CYP3A4 inducers (for example, carbamazepine, phenytoin, rifampicin, and St. John’s wort) not to choose Natazia as their oral contraceptive due to the possibility of decreased contraceptive efficacy.
- Counsel patients to use a back-up or alternative method of contraception when weak or moderate enzyme inducers are used with Natazia.
- Counsel patients who are breastfeeding or who desire to breastfeed that COCs may reduce breast milk production. This is less likely to occur if breastfeeding is well established.
- Counsel any patient who starts COCs postpartum, and who has not yet had a period, to use an additional method of contraception until she has taken Natazia for 9 consecutive days.
- Counsel patients that amenorrhea may occur. Rule out pregnancy in the event of amenorrhea in two or more consecutive cycles.
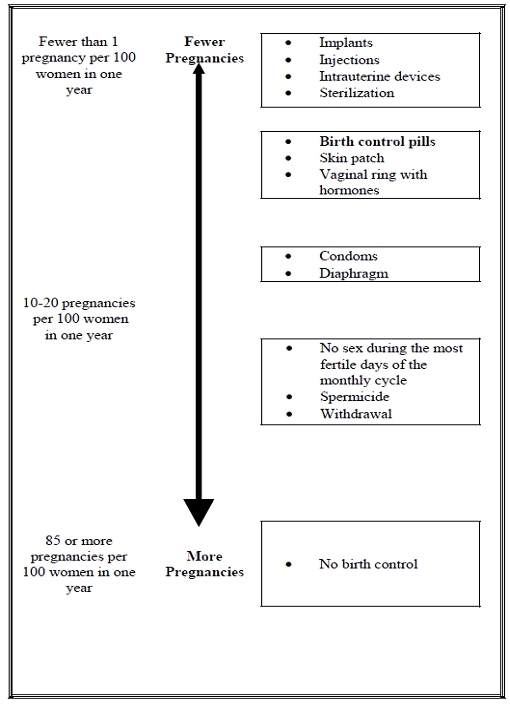
- Take one pill every day at the same time. Take the pills in the order directed on the blister pack.
- Do not skip pills or delay taking your pill by more than 12 hours. If you miss pills (including starting the pack late), you could get pregnant. The more pills you miss, the more likely you are to get pregnant.
- If you have trouble remembering to take Natazia, talk to your healthcare provider about how to make pill-taking easier, or about using another method of birth control.
- You may have spotting or light bleeding when you first take Natazia. Spotting or light bleeding is normal at first.
- You may feel sick to your stomach (nauseous), especially during the first few months that you take Natazia. If you feel sick to your stomach, do not stop taking the pill. The problem will usually go away. If your nausea doesn't go away, call your healthcare provider.
- If you vomit or have diarrhea within 4 hours of taking your pill, follow the instructions for “What Should I Do if I Miss any Pills.”
- Missing pills can also cause spotting or light bleeding, even when you take the missed pills later. On the days you take 2 pills to make up for missed pills, you could also feel a little sick to your stomach.
- Decide what time of day you want to take your pill. It is important to take it at the same time every day and in the order as directed on the blister pack.
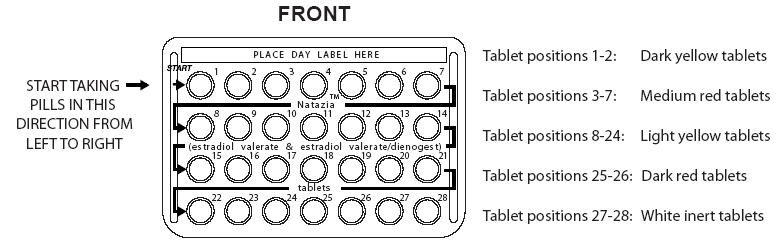
- Look at your Natazia blister pack. The blister pack has 4 rows of 7 pills each, for a total of 28 pills. Find:
- where on the pack to start taking your pills
- in what order to take the pills
- 2 dark yellow pills with hormones, for Days 1 and 2
- 5 medium red pills with hormones for Days 3–7
- 17 light yellow pills with hormones for Days 8–24
- 2 dark red pills with hormones for Days 25 and 26
- 2 white pills without hormones for Days 27 and 28
- After taking the last white pill (day 28) of the blister pack, start taking the first dark yellow pill from a new blister pack the very next day whether or not you are having your period.
- Be sure to have ready at all times another kind of birth control (such as condoms and spermicides) to use as a back-up in case you miss pills.
- It is not uncommon to miss a period. However, if you miss 2 periods in a row or feel like you may be pregnant, call your healthcare provider. If you are pregnant, you should stop taking Natazia.
- When to Start Natazia
- Take the first dark yellow pill on the first day (Day 1) of your natural menstrual cycle. The first day of your menstrual cycle is the first day you start spotting or bleeding.
- Use non-hormonal back-up contraception such as a condom and spermicide for the first 9 days that you take Natazia.
- another pill
- vaginal ring
- patch
- Take the first dark yellow pill on the first day of your period. Do not continue taking the pills from your previous birth control pack. If you do not have a period, contact your healthcare provider before you start Natazia.
- If you previously used a vaginal ring or transdermal patch, you should start using Natazia on the day the ring or patch is removed.
- Use a non-hormonal back-up method such as a condom and spermicide for the first 9 days you take Natazia.
- progestin-only pill
- implant
- intrauterine system
- injection
- Take the first dark yellow pill on the day you would have taken your next progestin-only pill or on the day of removal of your implant or intrauterine system or on the day when you would have had your next injection.
- Use a non-hormonal back-up method such as a condom and spermicide for the first 9 days you take Natazia.
- Do not take more than 2 pills in one day. On the days you take 2 pills to make up for missed pills, you may feel a little sick to your stomach (nauseous).
- If you start vomiting or have diarrhea within 4 hours of taking your pill, take another pill of the same color from your extra blister pack.
- Take your pill as soon as you remember.
- Take the next pill at the usual time.
- You do not need to use back-up contraception.
- Take your missed pill immediately.
- Take your next pill at the usual time (you may have to take two pills that day).
- Use back-up contraception for the next 9 days.
- Continue taking one pill each day at the same time for the rest of your cycle.
- Do not take any pills from your current blister pack and throw the pack away.
- Take Day 1 pill from a new blister pack.
- Use back-up contraception for the next 9 days.
- Continue taking one pill from the new blister pack at the same time each day.
- Take your missed pill immediately.
- Take your next pill at the usual time (you may have to take two pills that day).
- No back-up contraception is needed.
- Continue taking one pill each day at the same time for the rest of your cycle.
(if you miss the pills for Days 17 and 18, follow the instructions for Days 17–25 instead)
- Do not take the missed pills. Instead, take the pill for the day on which you first noticed you had missed pills.
- Use back-up contraception for the next 9 days.
- Continue taking one pill each day at the same time for the rest of your cycle.
(if you miss the pills for Days 25 and 26, follow the instructions for Days 25–28 instead)
- Do not take any pills from your current blister pack and throw the pack away.
- Take Day 3 pill from a new blister pack.
- Use back-up contraception for the next 9 days.
- Continue taking one pill from the new blister pack at the same time each day.
- Do not take any pills from your current blister pack and throw the pack away.
- Start a new pack on the same day or start a new pack on the day you usually start a new pack.
- No back-up contraception is needed.
- Continue taking one pill from the new pack at the same time each day, for the rest of your cycle.
- Call your healthcare provider
- Use back-up contraception (such as condoms and spermicides) anytime you have sex and keep taking 1 pill each day
- Ever had breast cancer which may be sensitive to female hormones
- Liver disease, including liver tumors
- Ever had blood clots in your arms, legs, or lungs
- Ever had a stroke
- Ever had a heart attack
- Certain heart valve problems or heart rhythm abnormalities that can cause blood clots to form in the heart
- An inherited problem with your blood that makes it clot more than normal
- High blood pressure that medicine can't control
- Diabetes with kidney, eye, or blood vessel damage
- Certain kinds of severe migraine headaches with aura, numbness, weakness or changes in vision
- Smoke and are over 35 years old
- Are pregnant
- Have any unexplained bleeding from the vagina
- Think you are pregnant
- Miss one period and have not taken your birth control pills according to directions
- Miss two periods in a row
- Legs (deep vein thrombosis)
- Lungs (pulmonary embolus)
- Eyes (loss of eyesight)
- Heart (heart attack)
- Brain (stroke)
- High blood pressure
- Gallbladder problems
- Rare cancerous or noncancerous liver tumors
- All of these events are uncommon in healthy women.
- Persistent leg pain
- Sudden shortness of breath
- Sudden blindness, partial or complete
- Severe pain in your chest
- Sudden, severe headache unlike your usual headaches
- Weakness or numbness in an arm or leg, or trouble speaking
- Yellowing of the skin or eyeballs
- What are the Common Side Effects of Birth Control Pills?
- Spotting or bleeding between menstrual periods
- Nausea
- Breast tenderness
- Headache
- Acne
- Less sexual desire
- Bloating or fluid retention
- Blotchy darkening of the skin, especially on the face
- High blood sugar, especially in women who already have diabetes
- High fat levels in the blood
- Depression, especially if you have had depression in the past.
- Problems tolerating contact lenses
- Weight changes




