Brand Name
Ridaura
Generic Name
Auranofin
View Brand Information FDA approval date: December 15, 2016
Form: Capsule
What is Ridaura (Auranofin)?
Auranofin Capsules is indicated in the management of adults with active classical or definite rheumatoid arthritis who have had an insufficient therapeutic response to, or are intolerant of, an adequate trial of full doses of one or more nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Auranofin Capsules should be added to a comprehensive baseline program, including non-drug therapies. Unlike anti-inflammatory drugs, Auranofin Capsules does not produce an immediate response. Therapeutic effects may be seen after three to four months of treatment, although improvement has not been seen in some patients before six months. When cartilage and bone damage has already occurred, gold cannot reverse structural damage to joints caused by previous disease. The greatest potential benefit occurs in patients with active synovitis, particularly in its early stage. In controlled clinical trials comparing Auranofin Capsules with injectable gold, Auranofin Capsules was associated with fewer dropouts due to adverse reactions, while injectable gold was associated with fewer dropouts for inadequate or poor therapeutic effect. Physicians should consider these findings when deciding on the use of Auranofin Capsules in patients who are candidates for chrysotherapy.
Approved To Treat
Top Global Experts
There are no experts for this drug
Save this treatment for later
Not sure about your diagnosis?
Related Clinical Trials
There is no clinical trials being done for this treatment
Related Latest Advances
There is no latest advances for this treatment
Brand Information
RIDAURA (auranofin)
1DESCRIPTION
RIDAURA (auranofin) is available in oral form as capsules containing 3 mg auranofin.
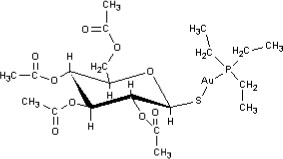
Auranofin is (2,3,4,6-tetra-O-acetyl-1-thio-ß-D-glucopyranosato-S-) (triethyl–phosphine) gold.
Auranofin contains 29% gold and has the following chemical structure:
Each RIDAURA capsule, with opaque brown cap and opaque tan body, contains auranofin, 3 mg, and is imprinted with the product name RIDAURA. Inactive ingredients consist of benzyl alcohol, cellulose, cetylpyridinium chloride, D&C Red No. 33, FD&C Blue No. 1, FD&C Red No. 40, FD&C Yellow No. 6, gelatin, lactose, magnesium stearate, povidone, sodium lauryl sulfate, sodium starch glycolate, starch, titanium dioxide and trace amounts of other inactive ingredients.
2CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
The mechanism of action of RIDAURA (auranofin) is not understood. In patients with adult rheumatoid arthritis, RIDAURA may modify disease activity as manifested by synovitis and associated symptoms, and reflected by laboratory parameters such as ESR. There is no substantial evidence, however, that gold-containing compounds induce remission of rheumatoid arthritis.
3INDICATIONS AND USAGE
RIDAURA (auranofin) is indicated in the management of adults with active classical or definite rheumatoid arthritis (ARA criteria) who have had an insufficient therapeutic response to, or are intolerant of, an adequate trial of full doses of one or more nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. RIDAURA should be added to a comprehensive baseline program, including non-drug therapies.
Unlike anti-inflammatory drugs, RIDAURA does not produce an immediate response. Therapeutic effects may be seen after three to four months of treatment, although improvement has not been seen in some patients before six months.
When cartilage and bone damage has already occurred, gold cannot reverse structural damage to joints caused by previous disease. The greatest potential benefit occurs in patients with active synovitis, particularly in its early stage.
In controlled clinical trials comparing RIDAURA with injectable gold, RIDAURA was associated with fewer dropouts due to adverse reactions, while injectable gold was associated with fewer dropouts for inadequate or poor therapeutic effect. Physicians should consider these findings when deciding on the use of RIDAURA in patients who are candidates for chrysotherapy.
4CONTRAINDICATIONS
RIDAURA (auranofin) is contraindicated in patients with a history of any of the following gold-induced disorders: anaphylactic reactions, necrotizing enterocolitis, pulmonary fibrosis, exfoliative dermatitis, bone marrow aplasia or other severe hematologic disorders.
5WARNINGS
Danger signs of possible gold toxicity include fall in hemoglobin, leukopenia below 4,000 WBC/cu mm, granulocytes below 1,500/cu mm, decrease in platelets below 150,000/cu mm, proteinuria, hematuria, pruritus, rash, stomatitis or persistent diarrhea.
Thrombocytopenia has occurred in 1–3% of patients (See
Proteinuria has developed in 3-9% of patients (See
6ADVERSE REACTIONS
The adverse reactions incidences listed below are based on observations of 1) 4,784 RIDAURA treated patients in clinical trials (2,474 U.S., 2,310 foreign), of whom 2,729 were treated more than one year and 573 for more than three years; and 2) postmarketing experience. The highest incidence is during the first six months of treatment; however, reactions can occur after many months of therapy. With rare exceptions, all patients were on concomitant nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory therapy; some of them were also taking low dosages of corticosteroids.
6.1Reactions occurring in more than 1% of RIDAURA-treated patients
Gastrointestinal: loose stools or diarrhea (47%); abdominal pain (14%); nausea with or without vomiting (10%); constipation; anorexia*; flatulence*; dyspepsia*; dysgeusia.
Dermatological: rash (24%); pruritus (17%); hair loss; urticaria.
Mucous Membrane: stomatitis (13%); conjunctivitis*; glossitis.
Hematological: anemia; leukopenia; thrombocytopenia; eosinophilia.
Renal: proteinuria*; hematuria.
Hepatic: elevated liver enzymes.
*Reactions marked with an asterisk occurred in 3-9% of the patients. The other reactions listed occurred in 1-3%.
6.2Reactions occurring in less than 1% of RIDAURA-treated patients
Gastrointestinal: dysphagia; gastrointestinal bleeding†; melena†; positive stool for occult blood†; ulcerative enterocolitis.
Dermatological: angioedema.
Mucous Membrane: gingivitis†.
Hematological: aplastic anemia; neutropenia†; agranulocytosis; pure red cell aplasia; pancytopenia.
Hepatic: jaundice.
Respiratory: interstitial pneumonitis.
Neurological: peripheral neuropathy.
Ocular: gold deposits in the lens or cornea unassociated clinically with eye disorders or visual impairment.
† Reactions marked with a dagger occurred in 0.1-1% of the patients. The other reactions listed occurred in less than 0.1%.
6.3Reactions reported with injectable gold preparations, but not with RIDAURA (auranofin) (based on clinical trials and on postmarketing experience)
Cutaneous Reactions: generalized exfoliative dermatitis
7OVERDOSAGE
The acute oral LD50 for auranofin is 310 mg/kg in adult mice and 265 mg/ kg in adult rats. The minimum lethal dose in rats is 30 mg/kg.
In case of acute overdosage, immediate induction of emesis or gastric lavage and appropriate supportive therapy are recommended.
RIDAURA overdosage experience is limited. A 50-year-old female, previously on 6 mg RIDAURA daily, took 27 mg (9 capsules) daily for 10 days and developed an encephalopathy and peripheral neuropathy. RIDAURA was discontinued and she eventually recovered.
There has been no experience with treating RIDAURA overdosage with modalities such as chelating agents. However, they have been used with injectable gold and may be considered for RIDAURA overdosage.
8HOW SUPPLIED
Capsules, containing 3 mg auranofin, in bottles of 60.
NDC 54766-093-06
8.1STORAGE AND HANDLING
Store between 15° and 30°C (59° and 86°F). Dispense in a tight, light-resistant container.
©2018 Sebela Pharmaceuticals Inc.
RIDAURA is a registered trademark of Sebela International Limited
Distributed by:
Sebela Pharmaceuticals Inc.
645 Hembree Parkway, Suite I
Roswell, Georgia 30076
www.sebelapharma.com
Toll Free 1-844-732-3521
Revised October 2017
PI 09306001