Brand Name
Carnitor
Generic Name
Levocarnitine
View Brand Information FDA approval date: December 27, 1985
Classification: Carnitine Analog
Form: Injection, Tablet, Solution
What is Carnitor (Levocarnitine)?
Levocarnitine Oral Solution USP is indicated in the treatment of primary systemic carnitine deficiency. In the reported cases, the clinical presentation consisted of recurrent episodes of Reye-like encephalopathy, hypoketotic hypoglycemia, and/or cardiomyopathy. Associated symptoms included hypotonia, muscle weakness and failure to thrive. A diagnosis of primary carnitine deficiency requires that serum, red cell and/or tissue carnitine levels be low and that the patient does not have a primary defect in fatty acid or organic acid oxidation. In some patients, particularly those presenting with cardiomyopathy, carnitine supplementation rapidly alleviated signs and symptoms. Treatment should include, in addition to carnitine, supportive and other therapy as indicated by the condition of the patient. Levocarnitine Oral Solution USP is also indicated for acute and chronic treatment of patients with an inborn error of metabolism which results in a secondary carnitine deficiency. CONTRAINDICATIONS None known.
Approved To Treat
Top Global Experts
There are no experts for this drug
Save this treatment for later
Not sure about your diagnosis?
Related Clinical Trials
There is no clinical trials being done for this treatment
Related Latest Advances
There is no latest advances for this treatment
Brand Information
Carnitor (levocarnitine)
1DESCRIPTION
CARNITOR
The chemical name of levocarnitine is 3-carboxy-2(
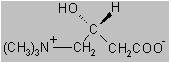
Empirical Formula: C
Molecular Weight: 161.20
Each CARNITOR
Each 118 mL container of CARNITOR
Each 118 mL container of CARNITOR
2CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
CARNITOR
Primary systemic carnitine deficiency is characterized by low concentrations of levocarnitine in plasma, RBC, and/or tissues. It has not been possible to determine which symptoms are due to carnitine deficiency and which are due to an underlying organic acidemia, as symptoms of both abnormalities may be expected to improve with CARNITOR
Secondary carnitine deficiency can be a consequence of inborn errors of metabolism. CARNITOR
3PHARMACOKINETICS
In a relative bioavailability study in 15 healthy adult male volunteers, CARNITOR
The plasma concentration profiles of levocarnitine after a slow 3 minute intravenous bolus dose of 20 mg/kg of CARNITOR
The absolute bioavailability of levocarnitine from the two oral formulations of CARNITOR
Total body clearance of levocarnitine (Dose/AUC including endogenous baseline concentrations) was a mean of 4.00 L/h.
Levocarnitine was not bound to plasma protein or albumin when tested at any concentration or with any species including the human.
4METABOLISM AND EXCRETION
In a pharmacokinetic study where five normal adult male volunteers received an oral dose of [
After attainment of steady state following 4 days of oral administration of CARNITOR
5INDICATIONS AND USAGE
CARNITOR
CARNITOR
6CONTRAINDICATIONS
None known.
7ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions associated with the use of oral formulations of levocarnitine were identified in clinical trials or postmarketing reports. Because these reactions were reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to estimate their frequency, reliability, or to establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Gastrointestinal Reactions: Various mild gastrointestinal complaints have been reported during the long-term administration of oral L- or D,L-carnitine; these include transient nausea and vomiting, abdominal cramps, and diarrhea. Gastrointestinal adverse reactions with CARNITOR® (levocarnitine) Oral Solution or CARNITOR® SF (levocarnitine) Sugar-Free Oral Solution dissolved in liquids might be avoided by a slow consumption of the solution or by a greater dilution. Decreasing the dosage often diminishes or eliminates drug-related patient body odor or gastrointestinal symptoms when present. Tolerance should be monitored very closely during the first week of administration, and after any dosage increases.
Musculoskeletal Reactions: Mild myasthenia has been described only in uremic patients receiving D,L-carnitine.
Neurologic Reactions: Seizures have been reported to occur in patients with or without pre-existing seizure activity receiving either oral or intravenous levocarnitine. In patients with pre-existing seizure activity, an increase in seizure frequency and/or severity has been reported.
Hypersensitivity Reactions: Rash, urticaria, and facial edema have been reported with oral CARNITOR® (see WARNINGS).
8OVERDOSAGE
There have been no reports of toxicity from levocarnitine overdosage. Levocarnitine is easily removed from plasma by dialysis. The intravenous LD
9DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
CARNITOR
Adults: The recommended oral dosage for adults is 990 mg two or three times a day using the 330 mg tablets, depending on clinical response.
Infants and children: The recommended oral dosage for infants and children is between 50 and 100 mg/kg/day in divided doses, with a maximum of 3 g/day. Dosage should begin at 50 mg/kg/day. The exact dosage will depend on clinical response.
Monitoring should include periodic blood chemistries, vital signs, plasma carnitine concentrations and overall clinical condition.
CARNITOR
For oral use only. Not for parenteral use.
Adults: The recommended dosage of levocarnitine is 1 to 3 g/day for a 50 kg subject, which is equivalent to 10 to 30 mL/day of CARNITOR
Infants and children: The recommended dosage of levocarnitine is 50 to 100 mg/kg/day which is equivalent to 0.5 mL/kg/day CARNITOR
CARNITOR
10HOW SUPPLIED
CARNITOR
CARNITOR
CARNITOR
Rx only.
11REFERENCES
- Bohmer, T., Rydning, A. and Solberg, H.E. 1974. Carnitine levels in human serum in health and disease.
- Brooks, H., Goldberg, L., Holland, R.
- Christiansen, R., Bremer, J. 1976. Active transport of butyrobetaine and carnitine into isolated liver cells.
- Lindstedt, S. and Lindstedt, G. 1961. Distribution and excretion of carnitine in the rat.
- Rebouche, C.J. and Engel, A.G. 1983. Carnitine metabolism and deficiency syndromes.
- Rebouche, C.J. and Paulson, D.J. 1986. Carnitine metabolism and function in humans.
- Scriver, C.R., Beaudet, A.L., Sly, W.S. and Valle, D. 1989.
- Schaub, J., Van Hoof, F. and Vis, H.L. 1991.
- Marzo, A., Arrigoni Martelli, E., Mancinelli, A., Cardace, G., Corbelletta, C., Bassani, E. and Solbiati, M. 1991. Protein binding of L-carnitine family components.
- Rebouche, C.J. 1991. Quantitative estimation of absorption and degradation of a carnitine supplement by human adults.

PREVIOUS EDITION IS OBSOLETE
Date of Issue: 07/23 OPI-16
Date of Issue: 07/23 OPI-16
12PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 118 mL Bottle Label
NDC 54482-145-08
CARNITOR
(levocarnitine) Oral Solution
(levocarnitine) Oral Solution
118 mL (4 fl. oz.)
Active ingredient: L-carnitine 1 g/10 mL
Inactive ingredients: Artificial Cherry
Leadiant
Avoid excess heat. Protect from freezing. Store at
Distributed by:
OS(Ha)-2 06/20
1572-01

13PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 118 mL Bottle Label - NDC 54482-145-09
118 mL (4 fl. oz.)
CARNITOR
1 g/10 mL
Rx only.
Active ingredient: L-carnitine 1 g/10 mL
Inactive ingredients: Artificial Cherry
Avoid excess heat. Protect from freezing.
Dosage: See Prescribing Information.
Distributed by: Leadiant Biosciences, Inc.
OS(Ha)-5
1572-03
