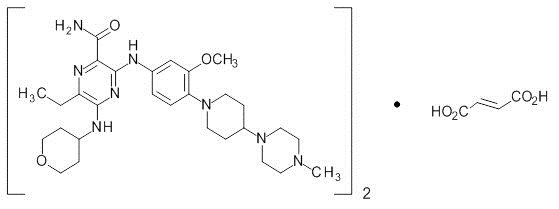
Xospata
What is Xospata (Gilteritinib)?
Approved To Treat
Related Clinical Trials
Summary: This screening and multi-sub-study Phase 1b/2 trial will establish a method for genomic screening followed by assigning and accruing simultaneously to a multi-study Master Protocol (BAML-16-001-M1). The specific subtype of acute myeloid leukemia will determine which sub-study, within this protocol, a participant will be assigned to evaluate investigational therapies or combinations with the ultima...
Summary: People with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) are usually treated with chemotherapy. Some people with AML have a changed FLT3 gene which causes leukemia cells to grow faster. Therefore, chemotherapy is less suitable to treat AML in people with the changed FLT3 gene. Gilteritinib, given with venetoclax and azacitidine, is a potential new treatment for people with AML with the changed FLT3 gene. They can...
Summary: This MyeloMATCH Master Screening and Reassessment Protocol (MSRP) evaluates the use of a screening tool and specific laboratory tests to help improve participants' ability to register to clinical trials throughout the course of their myeloid cancer (acute myeloid leukemia or myelodysplastic syndrome) treatment. This study involves testing patients' bone marrow and blood for certain biomarkers. A b...
Related Latest Advances
Brand Information
- Differentiation syndrome
- Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome
- Prolonged QT interval
- Pancreatitis
- Bottles of 90 tablets with Child Resistant Closure (NDC 0469-1425-90)
- Advise female patients with reproductive potential to use effective contraceptive methods while receiving XOSPATA and for 6 months after completion of treatment.
- Advise patients to notify their healthcare provider immediately in the event of a pregnancy or if pregnancy is suspected during XOSPATA treatment.
- Advise males with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with XOSPATA and for 4 months after the last dose of XOSPATA
- Advise patients not to break, crush or chew the tablets but to swallow them whole with a cup of water.
- Instruct patients that, if they miss a dose of XOSPATA, to take it as soon as possible on the same day, and at least 12 hours prior to the next scheduled dose, and return to the normal schedule the following day. Instruct patients to not take 2 doses within 12 hours

