Brand Name
Bosulif
Generic Name
Bosutinib
View Brand Information FDA approval date: September 04, 2012
Classification: Kinase Inhibitor
Form: Tablet, Capsule
What is Bosulif (Bosutinib)?
BOSULIF is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with chronic, accelerated, or blast phase Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic myelogenous leukemia with resistance or intolerance to prior therapy. BOSULIF is a kinase inhibitor indicated for the treatment of adult patients with chronic, accelerated, or blast phase Ph+ chronic myelogenous leukemia with resistance or intolerance to prior therapy.
Approved To Treat
Top Global Experts
There are no experts for this drug
Save this treatment for later
Not sure about your diagnosis?
Related Clinical Trials
There is no clinical trials being done for this treatment
Related Latest Advances
There is no latest advances for this treatment
Brand Information
BOSULIF (Bosutinib)
1INDICATIONS AND USAGE
BOSULIF is indicated for the treatment of:
- Adult and pediatric patients 1 year of age and older with chronic phase (CP) Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic myelogenous leukemia (Ph+ CML), newly-diagnosed or resistant or intolerant to prior therapy
- Adult patients with accelerated phase (AP), or blast phase (BP) Ph+ CML with resistance or intolerance to prior therapy
2DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Tablets:
- 100 mg: yellow, oval, biconvex, film-coated tablets debossed with "Pfizer" on one side and "100" on the other.
- 400 mg: orange, oval, biconvex, film-coated tablets debossed with "Pfizer" on one side and "400" on the other.
- 500 mg: red, oval, biconvex, film-coated tablets debossed with "Pfizer" on one side and "500" on the other.
Capsules:
- 50 mg: white body/orange cap with “BOS 50” printed on the body and “Pfizer” printed on the cap in black ink.
- 100 mg: white body/brownish-red cap with “BOS 100” printed on the body and “Pfizer” printed on the cap in black ink.
3CONTRAINDICATIONS
BOSULIF is contraindicated in patients with a history of hypersensitivity to BOSULIF. Reactions have included anaphylaxis
4ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the labeling:
- Gastrointestinal toxicity
- Myelosuppression
- Hepatic toxicity
- Cardiovascular toxicity
- Fluid retention
- Renal toxicity
4.1Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The most common adverse reactions, in ≥20% of adults with newly diagnosed CP Ph+ CML or CP, AP, or BP Ph+ CML with resistance or intolerance to prior therapy (N=814) were diarrhea (80%), rash (44%), nausea (44%), abdominal pain (43%), vomiting (33%), fatigue (33%), hepatic dysfunction (33%), respiratory tract infection (25%), pyrexia (24%), and headache (21%).
The most common laboratory abnormalities that worsened from baseline in ≥20% of adults were creatinine increased (93%), hemoglobin decreased (90%), lymphocyte count decreased (72%), platelets decreased (69%), ALT increased (58%), calcium decreased (53%), white blood cell count decreased (52%), absolute neutrophils count decreased (50%), AST increased (50%), glucose increased (46%), phosphorus decreased (44%), urate increased (41%), alkaline phosphatase increased (40%), lipase increased (36%), creatine kinase increased (29%), and amylase increased (24%).
The most common adverse reactions, in ≥20% of pediatric patients (N=49) were diarrhea (82%), abdominal pain (73%), vomiting (55%), nausea (49%), rash (49%), fatigue (37%), hepatic dysfunction (37%), headache (35%), pyrexia (31%), decreased appetite (27%), and constipation (20%).
The most common laboratory abnormalities that worsened from baseline in ≥20% of pediatric patients were creatinine increased (92%), alanine aminotransferase increased (59%), white blood cell count decreased (53%), aspartate aminotransferase increased (51%), platelet count decreased (49%), glucose increased (41%), calcium decreased (31%), hemoglobin decreased (31%), neutrophil count decreased (31%), lymphocyte count decreased (29%), serum amylase increased (27%), and CPK increased (25%).
4.2Postmarketing Experience
The following additional adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of BOSULIF. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Blood and Lymphatic System Disorders: Thrombotic microangiopathy
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders: Stevens-Johnson syndrome
5OVERDOSAGE
Experience with BOSULIF overdose in clinical studies was limited to isolated cases. There were no reports of any serious adverse events associated with the overdoses. Patients who take an overdose of BOSULIF should be observed and given appropriate supportive treatment.
6DESCRIPTION
BOSULIF contains bosutinib, a kinase inhibitor. Bosutinib is present as a monohydrate with a chemical name of 3-Quinolinecarbonitrile, 4-[(2,4-dichloro-5-methoxyphenyl)amino]-6-methoxy-7-[3-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl) propoxy]-, hydrate (1:1). Its chemical formula is C

Bosutinib monohydrate is a white to yellowish-tan powder. Bosutinib monohydrate has a pH dependent solubility across the physiological pH range. At or below pH 5, bosutinib monohydrate behaves as a highly soluble compound. Above pH 5, the solubility of bosutinib monohydrate reduces rapidly.
BOSULIF
BOSULIF
7PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information and Instructions for Use).
8INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
BOSULIF
(bosutinib)
capsules
This Instructions for Use contains information on how to prepare and give a dose of BOSULIF capsules by opening the capsules and mixing the contents with applesauce or yogurt for people who cannot swallow capsules whole. Read this Instructions for Use before you prepare or give the first dose of BOSULIF, and each time you get a refill. Ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist if you have any questions.
Important information you need to know before preparing a dose of BOSULIF capsules:
- BOSULIF capsules can be opened and the capsules contents mixed with room temperature applesauce or yogurt.
- Only use applesauce or yogurt.
- Swallow all of the mixture right away, without chewing.
- If you do not swallow the entire BOSULIF mixture, do not mix another dose. Wait until the next day to take your regularly scheduled dose.
- Take the BOSULIF mixture with a full meal.
Preparing a dose of BOSULIF capsules:
Gather the following supplies:
- BOSULIF capsules
- small, clean container
- yogurt or applesauce
- teaspoon for mixing
- disposable gloves
Giving a dose of BOSULIF capsules:
Step 1: Choose a clean, flat work surface. Place all supplies on the work surface.
Step 2: Wash and dry your hands well.
Step 3: Put on disposable gloves
Step 4: Get the prescribed number of BOSULIF capsule(s) needed to prepare the dose.
Step 5: Add the amount of applesauce or yogurt needed for the prescribed dose to the container.
Step 6: Carefully open each of the BOSULIF capsule(s) needed for the dose and empty the entire contents into the applesauce or yogurt. Mix the entire capsule contents with the applesauce or yogurt in the container.
Step 7: Swallow all of the mixture right away, without chewing.
Step 8: Dispose of (throw away) the empty BOSULIF capsule shell(s) in the household trash.
Step 9: Wash teaspoon and the container with soap and warm water.
Step 10: Remove disposable gloves and throw them away in the household trash.
Step 11: Wash and dry your hands.
How should I store BOSULIF capsules?
- Store BOSULIF at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
- Store the BOSULIF capsules in the original bottle.
- Ask your doctor or pharmacist about the right way to throw away outdated or unused BOSULIF.
Keep BOSULIF and all medicines out of the reach of children.

LAB-0639-13.0
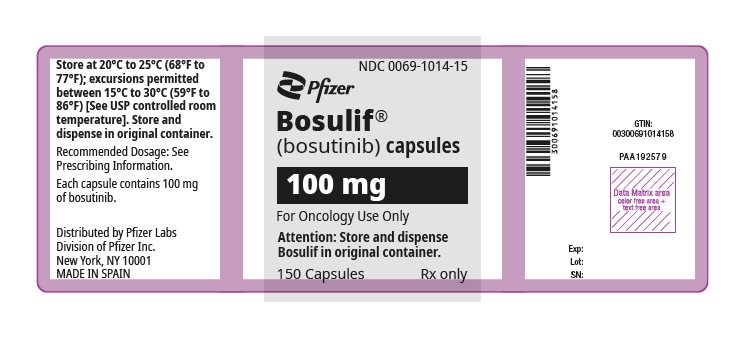
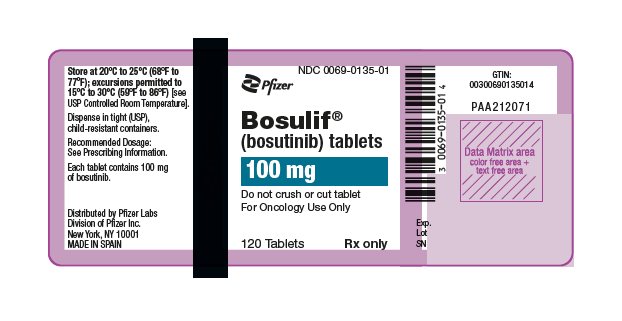
9PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 100 mg Bottle Label
NDC 0069-0135-01
Pfizer
Bosulif
(bosutinib) tablets
(bosutinib) tablets
100 mg
Do not crush or cut tablet
120 Tablets
Rx only
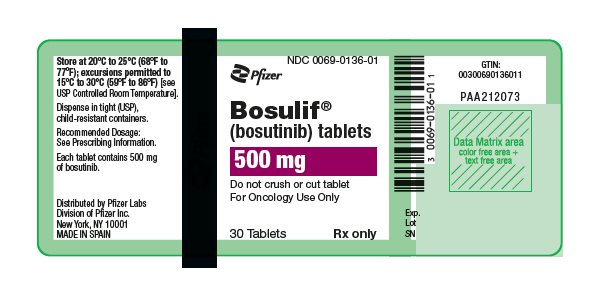
10PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 500 mg Bottle Label
NDC 0069-0136-01
Pfizer
Bosulif
(bosutinib) tablets
(bosutinib) tablets
500 mg
Do not crush or cut tablet
30 Tablets
Rx only
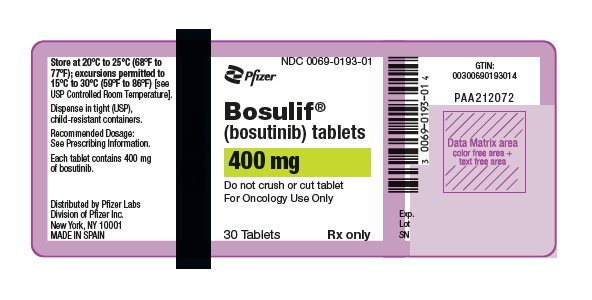
11PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 400 mg Tablet Bottle Label
NDC 0069-0193-01
Pfizer
Bosulif
(bosutinib) tablets
(bosutinib) tablets
400 mg
Do not crush or cut tablet
30 Tablets
Rx only
12PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 50 mg Capsule Bottle Label
NDC 0069-0504-30
Pfizer
Bosulif
(bosutinib) capsules
(bosutinib) capsules
50 mg
For Oncology Use Only
30 Capsules
Rx only
13PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 100 mg Capsule Bottle Label
NDC 0069-1014-15
Pfizer
Bosulif
(bosutinib) capsules
(bosutinib) capsules
100 mg
For Oncology Use Only
150 Capsules
Rx only