Generic Name
Pralidoxime
Brand Names
Protopam, DuoDote
FDA approval date: March 10, 1965
Classification: Cholinesterase Reactivator
Form: Injection, Kit
What is Protopam (Pralidoxime)?
DuoDote is indicated for the treatment of poisoning by organophosphorus nerve agents as well as organophosphorus insecticides in adults and pediatric patients weighing more than 41 kg . DuoDote, a combination of atropine, a cholinergic muscarinic antagonist, and pralidoxime chloride, a cholinesterase reactivator, is indicated for the treatment of poisoning by organophosphorus nerve agents as well as organophosphorus insecticides in adults and pediatric patients weighing more than 41 kg .
Approved To Treat
Top Global Experts
Save this treatment for later
Not sure about your diagnosis?
Related Clinical Trials
There is no clinical trials being done for this treatment
Related Latest Advances
Brand Information
Protopam Chloride (pralidoxime chloride)
1DESCRIPTION
Chemical name: 2-formyl-1-methylpyridinium chloride oxime. Available in the United States as PROTOPAM Chloride for Injection (PROTOPAM Chloride), pralidoxime chloride is frequently referred to as 2-PAM Chloride.
Structural formula:
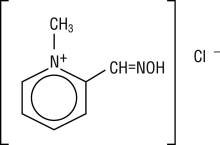
Pralidoxime chloride occurs as an odorless, white, nonhygroscopic, crystalline powder which is soluble in water. Stable in air, it melts between 215º and 225º C, with decomposition.
The specific activity of the drug resides in the 2-formyl-1-methylpyridinium ion and is independent of the particular salt employed. The chloride is preferred because of physiologic compatibility, excellent water solubility at all temperatures, and high potency per gram, due to its low molecular weight.
Pralidoxime chloride is a cholinesterase reactivator.
PROTOPAM Chloride for intravenous injection or infusion is prepared by cryo-desiccation. Each vial contains 1000 mg of sterile pralidoxime chloride, and sodium hydroxide to adjust pH, to be reconstituted with 20 mL of Sterile Water for Injection, USP. The pH of the reconstituted solution is 3.5 to 4.5. Intramuscular or subcutaneous injection may be used when intravenous injection is not feasible.
2CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
The principal action of pralidoxime chloride is to reactivate cholinesterase (mainly outside of the central nervous system) which has been inactivated by phosphorylation due to an organophosphate pesticide or related compound. The destruction of accumulated acetylcholine can then proceed, and neuromuscular junctions will again function normally. Pralidoxime chloride also slows the process of “aging” of phosphorylated cholinesterase to a nonreactivatable form, and detoxifies certain organophosphates by direct chemical reaction. The drug has its most critical effect in relieving paralysis of the muscles of respiration. Because pralidoxime chloride is less effective in relieving depression of the respiratory center, atropine is always required concomitantly to block the effect of accumulated acetylcholine at this site. Pralidoxime chloride relieves muscarinic signs and symptoms, salivation, bronchospasm, etc., but this action is relatively unimportant since atropine is adequate for this purpose.
PROTOPAM Chloride has been studied in animals as an antidote against numerous organophosphate pesticides, chemicals, and drugs (see
3CLINICAL STUDIES
There are no adequate and well controlled clinical studies that establish the effectiveness of pralidoxime chloride as a treatment for poisoning with organophosphates having anticholinesterase activity. However, its use has been considered to be successful against poisoning with numerous pesticides, chemicals, and drugs.
3.1Pharmacokinetics
Animal studies suggest that the minimum therapeutic concentration of pralidoxime in plasma is 4 µg/mL; this level is reached in about 16 minutes after a single injection of 600 mg pralidoxime chloride. In one study of healthy adult volunteers and patients self-poisoned with organophosphate compounds, a single intramuscular injection of 1000 mg of pralidoxime chloride resulted in mean peak plasma levels of 7.5 ± 1.7 µg/mL and 9.9 ± 2.4 µg/mL, respectively. Time to reach the mean peak plasma levels in both groups was similar, 34 minutes in healthy adults and 33 minutes in poisoned patients. Mean half-life was about 3 hours in both groups.
Some evidence suggests that a loading dose followed by continuous intravenous infusion of pralidoxime chloride may maintain therapeutic levels longer than short intermittent infusion therapy. In a cross-over study of seven healthy adults (18 – 50 years) a short intravenous infusion dose of 16 mg/kg over 30 minutes was compared to an intravenous loading dose of 4 mg/kg over 15 minutes, followed by 3.2 mg/kg/hr for 3.75 hours (for a total dose of 16 mg/kg). Results showed that the mean time over which plasma levels were maintained above 4 µg/mL was prolonged in the volunteers who received a loading dose followed by continuous infusion as compared to those who received short infusion therapy (257.5 ± 50.5 min vs. 118.0 ± 52.1 min). Use of continuous intravenous infusion in adult patients with organophosphate poisoning has been described in several case reports, with and without loading doses. Infusion rates ranged from 400 – 600 mg/hr. In one case the blood levels were 11.6 – 13.7 µg /mL when given 400 mg/hr over 5 days (measured at 5, 10 and 18 hours). In another case following an initial loading dose of 1000 mg, blood levels were 11.79 µg/mL when given 500 mg/hr and 17.26 µg/mL when given 600 mg/hr. In the latter case the pralidoxime elimination half-life was 4 hours. In two other cases blood levels were not measured.
Pralidoxime chloride is distributed throughout the extracellular water; its apparent volume of distribution at steady state has been reported to range from 0.60 to 2.7 L/kg. Pralidoxime chloride is not bound to plasma protein.
Pralidoxime chloride is relatively short acting and repeated doses may be needed, unless continuous intravenous infusion is selected. Simulations suggest that after a dose of 1000 mg given intravenously, concentrations fall below 4 µg/mL in about 1.5 hours. The short duration of action of pralidoxime chloride and the necessity for repeated doses should be considered especially where there is any evidence of continuing absorption of the poison. The apparent half-life of pralidoxime chloride is 74 to 77 minutes. The drug is rapidly excreted in the urine by renal tubular secretion, partly unchanged, and partly as a metabolite produced by the liver. After intramuscular administration of 1000 mg of pralidoxime chloride, the renal clearance has been reported to be 7.2 ± 2.9 mL/min/kg in healthy volunteers and 3.6 ± 1.5 mL/min/kg in organophosphate-poisoned patients.
In one study of 11 organophosphate-poisoned pediatric patients (age, 0.8 to 18 years), an intravenous loading dose of 15-50 mg/kg (mean 29 mg/kg) of pralidoxime chloride followed by a continuous infusion of 10-16 mg/kg/hr (mean 14 mg/kg/hr) over 12 to 43 hours (mean 27 ± 8 hours) resulted in an average steady state plasma concentration of 22.2 mg/L (6.9 to 47.4 mg/L) and an average body clearance of 0.88 L/kg/hr (0.28 to 2.20 L/kg/hr). After the continuous infusion was discontinued, determinations of the apparent volume of distribution and half-life ranged from 1.7 to 13.8 L/kg and from 2.4 to 5.3 hours, respectively.
4INDICATIONS AND USAGE
PROTOPAM Chloride is indicated as an antidote:
- In the treatment of poisoning due to those pesticides and chemicals (e.g., nerve agents) of the organophosphate class which have anticholinesterase activity and
- In the control of overdosage by anticholinesterase drugs used in the treatment of myasthenia gravis.
The principal indications for the use of PROTOPAM Chloride are muscle weakness and respiratory depression. In severe poisoning, respiratory depression may be due to muscle weakness.
5CONTRAINDICATIONS
There are no known absolute contraindications for the use of PROTOPAM Chloride (see
6WARNINGS
PROTOPAM Chloride is not effective in the treatment of poisoning due to phosphorus, inorganic phosphates, or organophosphates not having anticholinesterase activity.
PROTOPAM Chloride is
7ADVERSE REACTIONS
Forty to 60 minutes after intramuscular injection, mild to moderate pain may be experienced at the site of injection.
Pralidoxime chloride may cause blurred vision, diplopia and impaired accommodation, dizziness, headache, drowsiness, nausea, tachycardia, increased systolic and diastolic blood pressure, hyperventilation, and muscular weakness when given parenterally to normal volunteers who have not been exposed to anticholinesterase poisons. In patients, it is very difficult to differentiate the toxic effects produced by atropine or the organophosphate compounds from those of the drug.
Elevations in SGOT and/or SGPT enzyme levels were observed in 1 of 6 normal volunteers given 1200 mg of pralidoxime chloride intramuscularly, and in 4 of 6 volunteers given 1800 mg intramuscularly. Levels returned to normal in about 2 weeks. Transient elevations in creatine phosphokinase were observed in all normal volunteers given the drug.
When atropine and pralidoxime chloride are used together, the signs of atropinization may occur earlier than might be expected when atropine is used alone. This is especially true if the total dose of atropine has been large and the administration of pralidoxime chloride has been delayed. Excitement and manic behavior immediately following recovery of consciousness have been reported in several cases. However, similar behavior has occurred in cases of organophosphate poisoning that were not treated with pralidoxime chloride.
8DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
PROTOPAM Chloride is not subject to abuse and possesses no known potential for dependence.
9HOW SUPPLIED
NDC 60977-141-01—Hospital Package: This contains six 20 mL vials of 1 g each of sterile PROTOPAM Chloride (pralidoxime chloride) for Injection white to off-white porous cake*, without diluent or syringe.
*When necessary, sodium hydroxide is added during processing to adjust the pH.
9.1Storage
Store at 20°-25°C (68°-77°F), excursions permitted to 15°-30°C (59°-86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
10ANIMAL PHARMACOLOGY AND TOXICOLOGY
The following table lists chemical and trade or generic names of pesticides, chemicals, and drugs against which PROTOPAM Chloride (usually administered in conjunction with atropine) has been found to have antidotal activity on the basis of animal experiments. All compounds listed are organophosphates having anticholinesterase activity. A great many additional substances are in industrial use but have been omitted because of lack of specific information.
AAT—see PARATHION
PROTOPAM Chloride (pralidoxime chloride) appears to be ineffective, or marginally
CIODRIN (alpha-methylbenzyl-3-[dimethoxyphosphinyloxy]-ciscrotonate)
11PACKAGE LABEL - Principal Display Panel

Container Label
NDC 60977-141-27
Protopam Chloride
(pralidoxime chloride) for injection
1 g Single Dose Vial
Rx only
FOR INTRAVENOUS INJECTION;
may be given subcutaneously or
intramuscularly if this route is not feasible.
Prepare injection by adding
20 mL of Sterile Water for
Injection, USP.
Usual Dosage: 1 g
See accompanying descriptive
literature. Discard unused solution
after a dose have been withdrawn.
Prepared by cryodesiccation.
esi
Mfd. for
Deerfield, IL 60015 USA
by: Baxter Pharmaceutical Solutions, LLC
Bloomington, IN 47403
460-496-01
(01)00360977141275
3-942-233
Lot:
Exp:
Carton Label
NDC 60977-141-01
Protopam Chloride
(pralidoxime chloride) for injection
1 g
Rx only
6 x 1 g Single Dose Vials
FOR INTRAVENOUS INJECION;
may also be given by intramuscular or subcutaneous
injection if the intravenous route is not feasible.
esi
Manufactured for
Baxter Healthcare Corporation
Deerfield, IL 60015 USA
by: Baxter Pharmaceutical Solutions, LLC
Bloomington, IN 47403
Lot:
Exp:
NDC 60977-141-01
Protopam Chloride
(pralidoxime chloride) for injection
1 g
6 x 1 g Single Dose Vials
N3 60977 14101 5
Enclosed in this package are six vials, each containing 1 g of sterile
Protopam Chloride (pralidoxime chloride). When necessary, either 1N
hydrochloric acid or 1N sodium hydroxide may be added during
processing to adjust the pH. Prepare injection by adding 20 mL of
Sterile Water for Injection, USP (not supplied in this package).
Usual Dosage: 1 g
See accompanying descriptive literature.
Discard unused solution after a dose has been withdrawn.
Prepared by cryodesiccation.
Enclosed product circular for human use.
Store at 20°-25°C (68°-77°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Baxter and Protopam are trademarks of Baxter International Inc. or its subsidiaries.
460-497-00
3-809-1808
NDC 60977-141-01
Protopam Chloride
(pralidoxime chloride) for injection
1 g
6 x 1 g Single Dose Vials
FOR INTRAVENOUS INJECTION;
may also be given by intramuscular
or subcutaneous injection
if the intravenous route is not feasible.
esi
Manufactured for
Baxter Healthcare Corporation
Deerfield, IL 60015 USA
by: Baxter Pharmaceutical Solutions LLC
Bloomington, IN 47403