Brand Name
Ery-Ped
Generic Name
Ethylsuccinate
View Brand Information FDA approval date: April 18, 2011
Classification: Macrolide
Form: Tablet, Granule, Suspension, For
What is Ery-Ped (Ethylsuccinate)?
To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of Erythromycin Ethylsuccinate and other antibacterial drugs, Erythromycin Ethylsuccinate should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by susceptible bacteria. When culture and susceptibility information are available, they should be considered in selecting or modifying antibacterial therapy. In the absence of such data, local epidemiology and susceptibility patterns may contribute to the empiric selection of therapy. Erythromycin Ethylsuccinate is indicated in the treatment of infections caused by susceptible strains of the designated organisms in the diseases listed below: Upper respiratory tract infections of mild to moderate degree caused by Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus pneumoniae, or Haemophilus influenzae . Lower-respiratory tract infections of mild to moderate severity caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae or Streptococcus pyogenes. Listeriosis caused by Listeria monocytogenes. Pertussis caused by Bordetella pertussis. Erythromycin is effective in eliminating the organism from the nasopharynx of infected individuals rendering them noninfectious. Some clinical studies suggest that erythromycin may be helpful in the prophylaxis of pertussis in exposed susceptible individuals. Respiratory tract infections due to Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Skin and skin structure infections of mild to moderate severity caused by Streptococcus pyogenes or Staphylococcus aureus . Diphtheria Infections due to Corynebacterium diphtheriae, as an adjunct to antitoxin, to prevent establishment of carriers and to eradicate the organism in carriers. Erythrasma In the treatment of infections due to Corynebacterium minutissimum. Intestinal amebiasis caused by Entamoeba histolytica . Extraenteric amebiasis requires treatment with other agents. Acute Pelvic Inflammatory Disease caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae As an alternative drug in treatment of acute pelvic inflammatory disease caused by N. gonorrhoeae in female patients with a history of sensitivity to penicillin. Patients should have a serologic test for syphilis before receiving erythromycin as treatment of gonorrhea and a follow-up serologic test for syphilis after 3 months. Syphilis caused by Treponema pallidum Erythromycin is an alternate choice of treatment for primary syphilis in penicillin-allergic patients. In primary syphilis, spinal fluid examinations should be done before treatment and as part of follow-up after therapy. Erythromycins are indicated for the treatment of the following infections caused by Chlamydia trachomatis Conjunctivitis of the newborn, pneumonia of infancy, and urogenital infections during pregnancy. When tetracyclines are contraindicated or not tolerated, erythromycin is indicated for the treatment of uncomplicated urethral, endocervical, or rectal infections in adults due to Chlamydia trachomatis. When tetracyclines are contraindicated or not tolerated, erythromycin is indicated for the treatment of nongonococcal urethritis caused by Ureaplasma urealyticum. Legionnaires' Disease caused by Legionella pneumophila Although no controlled clinical efficacy studies have been conducted, in vitro and limited preliminary clinical data suggest that erythromycin may be effective in treating Legionnaires' Disease. Prophylaxis Prevention of Initial Attacks of Rheumatic Fever Penicillin is considered by the American Heart Association to be the drug of choice in the prevention of initial attacks of rheumatic fever . Erythromycin is indicated for the treatment of penicillin-allergic patients. 1 The therapeutic dose should be administered for 10 days. Prevention of Recurrent Attacks of Rheumatic Fever Penicillin or sulfonamides are considered by the American Heart Association to be the drugs of choice in the prevention of recurrent attacks of rheumatic fever. In patients who are allergic to penicillin and sulfonamides, oral erythromycin is recommended by the American Heart Association in the long-term prophylaxis of Streptococcal pharyngitis . 1.
Approved To Treat
Save this treatment for later
Not sure about your diagnosis?
Related Clinical Trials
There is no clinical trials being done for this treatment
Related Latest Advances
Brand Information
Ery-Ped (Erythromycin Ethylsuccinate)
1DESCRIPTION
Erythromycin is produced by a strain of
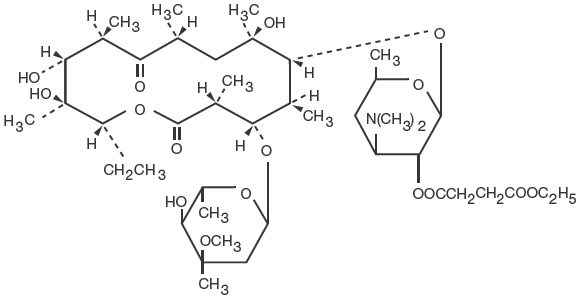
Ery-Ped 200 (erythromycin ethylsuccinate for oral suspension) when reconstituted with water, forms a suspension containing erythromycin ethylsuccinate equivalent to 200 mg erythromycin per 5 mL (teaspoonful) or 100 mg per 2.5 mL (dropperful) with an appealing fruit flavor. Ery-Ped 400 when reconstituted with water, forms a suspension containing erythromycin ethylsuccinate equivalent to 400 mg of erythromycin per 5 mL (teaspoonful) with an appealing banana flavor.
These products are intended primarily for pediatric use but can also be used in adults.
1.1Inactive Ingredients
Ery-Ped 200, Ery-Ped 400:
Caramel, polysorbate, sodium citrate, sucrose, xanthan gum and artificial flavors.
2CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Orally administered erythromycin ethylsuccinate suspension is readily and reliably absorbed under both fasting and nonfasting conditions.
Erythromycin diffuses readily into most body fluids. Only low concentrations are normally achieved in the spinal fluid, but passage of the drug across the blood-brain barrier increases in meningitis. In the presence of normal hepatic function, erythromycin is concentrated in the liver and excreted in the bile; the effect of hepatic dysfunction on excretion of erythromycin by the liver into the bile is not known. Less than 5 percent of the orally administered dose of erythromycin is excreted in active form in the urine.
Erythromycin crosses the placental barrier, but fetal plasma levels are low. The drug is excreted in human milk.
3INDICATIONS AND USAGE
To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of Ery-Ped and other antibacterial drugs, Ery-Ped should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by susceptible bacteria. When culture and susceptibility information are available, they should be considered in selecting or modifying antibacterial therapy. In the absence of such data, local epidemiology and susceptibility patterns may contribute to the empiric selection of therapy.
Ery-Ped is indicated in the treatment of infections caused by susceptible strains of the designated organisms in the diseases listed below:
Upper respiratory tract infections of mild to moderate degree caused by
Lower-respiratory tract infections of mild to moderate severity caused by
Listeriosis caused by
Pertussis (whooping cough) caused by
Respiratory tract infections due to
Skin and skin structure infections of mild to moderate severity caused by
3.1Diphtheria
Infections due to
3.2Erythrasma
In the treatment of infections due to
3.3Acute Pelvic Inflammatory Disease Caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae
As an alternative drug in treatment of acute pelvic inflammatory disease caused by
3.4Syphilis Caused by Treponema pallidum
Erythromycin is an alternate choice of treatment for primary syphilis in penicillin-allergic patients. In primary syphilis, spinal fluid examinations should be done before treatment and as part of follow-up after therapy.
3.5Erythromycins are indicated for the treatment of the following infections caused by Chlamydia trachomatis
Conjunctivitis of the newborn, pneumonia of infancy, and urogenital infections during pregnancy. When tetracyclines are contraindicated or not tolerated, erythromycin is indicated for the treatment of uncomplicated urethral, endocervical, or rectal infections in adults due to
4CONTRAINDICATIONS
Erythromycin is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to this antibiotic.
Erythromycin is contraindicated in patients taking terfenadine, astemizole, pimozide, or cisapride. (See
Do not use erythromycin concomitantly with HMG CoA reductase inhibitors (statins) that are extensively metabolized by CYP 3A4 (lovastatin or simvastatin), due to the increased risk of myopathy, including rhabdomyolysis.
5ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most frequent side effects of oral erythromycin preparations are gastrointestinal and are dose-related. They include nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea and anorexia. Symptoms of hepatitis, hepatic dysfunction and/or abnormal liver function test results may occur. (See
Onset of pseudomembranous colitis symptoms may occur during or after antibacterial treatment. (See
Erythromycin has been associated with QT prolongation and ventricular arrhythmias, including ventricular tachycardia and torsades de pointes. (See
Allergic reactions ranging from urticaria to anaphylaxis have occurred. Skin reactions ranging from mild eruptions to erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, and toxic epidermal necrolysis have been reported rarely.
There have been reports of interstitial nephritis coincident with erythromycin use.
There have been rare reports of pancreatitis and convulsions.
There have been isolated reports of reversible hearing loss occurring chiefly in patients with renal insufficiency and in patients receiving high doses of erythromycin.
6OVERDOSAGE
In case of overdosage, erythromycin should be discontinued. Overdosage should be handled with the prompt elimination of unabsorbed drug and all other appropriate measures should be instituted.
Erythromycin is not removed by peritoneal dialysis or hemodialysis.
7DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Ery-Ped (erythromycin ethylsuccinate) oral suspensions may be administered without regard to meals.
7.1Children
Age, weight, and severity of the infection are important factors in determining the proper dosage. In mild to moderate infections, the usual dosage of erythromycin ethylsuccinate for children is 30 to 50 mg/kg/day in equally divided doses every 6 hours. For more severe infections this dosage may be doubled. If twice-a-day dosage is desired, one-half of the total daily dose may be given every 12 hours. Doses may also be given three times daily by administering one-third of the total daily dose every 8 hours.
The following dosage schedule is suggested for mild to moderate infections:
7.2Adults
400 mg erythromycin ethylsuccinate every 6 hours is the usual dose. Dosage may be increased up to 4 g per day according to the severity of the infection. If twice-a-day dosage is desired, one-half of the total daily dose may be given every 12 hours. Doses may also be given three times daily by administering one-third of the total daily dose every 8 hours.
For adult dosage calculation, use a ratio of 400 mg of erythromycin activity as the ethylsuccinate to 250 mg of erythromycin activity as the stearate, base or estolate.
In the treatment of streptococcal infections, a therapeutic dosage of erythromycin ethylsuccinate should be administered for at least 10 days. In continuous prophylaxis against recurrences of streptococcal infections in persons with a history of rheumatic heart disease, the usual dosage is 400 mg twice a day.
8HOW SUPPLIED
Ery-Ped 200 (erythromycin ethylsuccinate for oral suspension, USP) is supplied in bottles of 100 mL (
Ery-Ped 400 (erythromycin ethylsuccinate for oral suspension, USP) is supplied in bottles of 100 mL (
8.1Recommended Storage
Store Ery-Ped 200 and Ery-Ped 400, prior to mixing, below 86°F (30°C). After reconstitution, Ery-Ped 200 and Ery-Ped 400 must be stored at or below 77°F (25°C) and used within 35 days; refrigeration is not required.
9REFERENCES
- Committee on Rheumatic Fever, Endocarditis, and Kawasaki Disease of the Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young, the American Heart Association: Prevention of Rheumatic Fever. Circulation. 78(4):1082-1086, October 1988.
- Honein, M.A., et al.: Infantile hypertrophic pyloric stenosis after pertussis prophylaxis with erythromycin: a case review and cohort study. The Lancet 1999;354 (9196): 2101-5
10PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 200 mg per 5 mL Bottle Label
NDC24338-132-13
100 mL For Oral Suspension
(when mixed)
100 mL For Oral Suspension
(when mixed)
EryPed®200
ERYTHROMYCIN
Erythromycin activity
200 mg per 5 mL
when reconstituted
when reconstituted
Rx only
arbor®
PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.

11PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 400 mg per 5 mL Bottle Label
NDC24338-130-13
100 mL For Oral Suspension
(when mixed)
100 mL For Oral Suspension
(when mixed)
EryPed®400
ERYTHROMYCIN
Erythromycin activity
400 mg per 5 mL
when reconstituted
when reconstituted
Rx only
arbor®
PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.

