Brand Name
Sular
Generic Name
Nisoldipine
View Brand Information FDA approval date: July 25, 2008
Classification: Dihydropyridine Calcium Channel Blocker
Form: Tablet
What is Sular (Nisoldipine)?
Nisoldipine is indicated for the treatment of hypertension. It may be used alone or in combination with other antihypertensive agents.
Approved To Treat
Save this treatment for later
Not sure about your diagnosis?
Related Clinical Trials
There is no clinical trials being done for this treatment
Related Latest Advances
Brand Information
Sular (nisoldipine)
1DESCRIPTION
SULAR
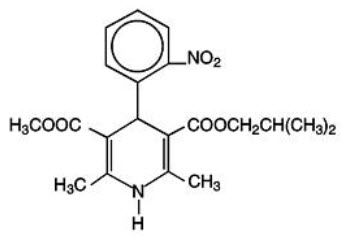
Nisoldipine is a yellow crystalline substance, practically insoluble in water but soluble in ethanol. It has a molecular weight of 388.4. SULAR tablets comprise three layers: a top barrier layer, a middle layer containing nisoldipine, and a bottom barrier layer. The erodible barrier layers and the hydrogel middle layer provide for the controlled release of the drug. SULAR tablets contain either 8.5, 17, or 34 mg of nisoldipine for once-a-day oral administration.
Inactive ingredients in the formulation include: Hypromellose, hypromellose phthalate, lactose, glyceryl behenate, povidone, magnesium stearate, silicon dioxide, methacrylic acid copolymer, and sodium lauryl sulfate. Inactive ingredients in the film coating include: polydextrose, titanium dioxide, hypromellose, polyethylene glycol, iron oxide, and carnauba wax. Additionally, the 17 mg formulation contains FD&C Yellow #5.
2INDICATIONS AND USAGE
SULAR is indicated for the treatment of hypertension. It may be used alone or in combination with other antihypertensive agents.
3CONTRAINDICATIONS
SULAR is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to dihydropyridine calcium channel blockers.
4WARNINGS
Increased angina and/or myocardial infarction in patients with coronary artery disease:
Rarely, patients, particularly those with severe obstructive coronary artery disease, have developed increased frequency, duration and/or severity of angina, or acute myocardial infarction on starting calcium channel blocker therapy or at the time of dosage increase. The mechanism of this effect has not been established. In controlled studies of SULAR in patients with angina this was seen about 1.5% of the time in patients given nisoldipine, compared with 0.9% in patients given placebo.
5ADVERSE EXPERIENCES
More than 6000 patients world-wide have received nisoldipine in clinical trials for the treatment of hypertension, either as the immediate release or the SULAR extended release formulation. Of about 1,500 patients who received SULAR in hypertension studies, about 55% were exposed for at least 2 months and about one third were exposed for over 6 months, the great majority at doses equivalent to 17 mg and above.
SULAR is generally well-tolerated. In the U.S. clinical trials of SULAR in hypertension, 10.9% of the 921 SULAR patients discontinued treatment due to adverse events compared with 2.9% of 280 placebo patients. The frequency of discontinuations due to adverse experiences was related to dose, with a 5.4% and 10.9% discontinuation rate at the lowest and highest daily dose, respectively.
The most frequently occurring adverse experiences with SULAR are those related to its vasodilator properties; these are generally mild and only occasionally lead to patient withdrawal from treatment. The table below, from U.S. placebo-controlled parallel dose response trials of SULAR using doses across the clinical dosage range in patients with hypertension, lists all of the adverse events, regardless of the causal relationship to SULAR, for which the overall incidence on SULAR was both >1% and greater with SULAR than with placebo.
The common adverse events occurred at about the same rate in men as in women, and at a similar rate in patients over age 65 as in those under that age, except that headache was much less common in older patients. Except for peripheral edema and vasodilation, which were more common in whites, adverse event rates were similar in blacks and whites.
The following adverse events occurred in ≤1% of all patients treated for hypertension in U.S. and foreign clinical trials, or with unspecified incidence in other studies. Although a causal relationship of SULAR to these events cannot be established, they are listed to alert the physician to a possible relationship with SULAR treatment.
Body As A Whole: cellulitis, chills, facial edema, fever, flu syndrome, malaise
Cardiovascular: atrial fibrillation, cerebrovascular accident, congestive heart failure, first degree AV block, hypertension, hypotension, jugular venous distension, migraine, myocardial infarction, postural hypotension, ventricular extrasystoles, supraventricular tachycardia, syncope, systolic ejection murmur, T wave abnormalities on ECG (flattening, inversion, nonspecific changes), venous insufficiency
Digestive: abnormal liver function tests, anorexia, colitis, diarrhea, dry mouth, dyspepsia, dysphagia, flatulence, gastritis, gastrointestinal hemorrhage, gingival hyperplasia, glossitis, hepatomegaly, increased appetite, melena, mouth ulceration
Endocrine: diabetes mellitus, thyroiditis
Hemic and Lymphatic: anemia, ecchymoses, leukopenia, petechiae
Metabolic and Nutritional: gout, hypokalemia, increased serum creatine kinase, increased nonprotein nitrogen, weight gain, weight loss
Musculoskeletal: arthralgia, arthritis, leg cramps, myalgia, myasthenia, myositis, tenosynovitis
Nervous: abnormal dreams, abnormal thinking and confusion, amnesia, anxiety, ataxia, cerebral ischemia, decreased libido, depression, hypesthesia, hypertonia, insomnia, nervousness, paresthesia, somnolence, tremor, vertigo
Respiratory: asthma, dyspnea, end inspiratory wheeze and fine rales, epistaxis, increased cough, laryngitis, pharyngitis, pleural effusion, rhinitis, sinusitis
Skin and Appendages: acne, alopecia, dry skin, exfoliative dermatitis, fungal dermatitis, herpes simplex, herpes zoster, maculopapular rash, pruritus, pustular rash, skin discoloration, skin ulcer, sweating, urticaria
Special Senses: abnormal vision, amblyopia, blepharitis, conjunctivitis, ear pain, glaucoma, itchy eyes, keratoconjunctivitis, otitis media, retinal detachment, tinnitus, watery eyes, taste disturbance, temporary unilateral loss of vision, vitreous floater
Urogenital: dysuria, hematuria, impotence, nocturia, urinary frequency, increased BUN and serum creatinine, vaginal hemorrhage, vaginitis
The following postmarketing event has been reported very rarely in patients receiving SULAR: systemic hypersensitivity reaction which may include one or more of the following; angioedema, shortness of breath, tachycardia, chest tightness, hypotension, and rash. A definite causal relationship with SULAR has not been established. An unusual event observed with immediate release nisoldipine but not observed with SULAR was one case of photosensitivity. Gynecomastia has been associated with the use of calcium channel blockers.
6OVERDOSAGE
There is no experience with nisoldipine overdosage. Generally, overdosage with other dihydropyridines leading to pronounced hypotension calls for active cardiovascular support including monitoring of cardiovascular and respiratory function, elevation of extremities, judicious use of calcium infusion, pressor agents and fluids. Clearance of nisoldipine would be expected to be slowed in patients with impaired liver function. Since nisoldipine is highly protein bound, dialysis is not likely to be of any benefit; however, plasmapheresis may be beneficial.
7DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
The dosage of SULAR must be adjusted to each patient's needs. Therapy usually should be initiated with 17 mg orally once daily, then increased by 8.5 mg per week or longer intervals, to attain adequate control of blood pressure. Usual maintenance dosage is 17 to 34 mg once daily. Blood pressure response increases over the 8.5 - 34 mg daily dose range but adverse event rates also increase. Doses beyond 34 mg once daily are not recommended. SULAR has been used safely with diuretics, ACE inhibitors, and beta-blocking agents. Patients over age 65, or patients with impaired liver function, are expected to develop higher plasma concentrations of nisoldipine. Their blood pressure should be monitored closely during any dosage adjustment. A starting dose not exceeding 8.5 mg daily is recommended in these patient groups. SULAR tablets should be administered orally once daily. SULAR should be taken on an empty stomach (1 hour before or 2 hours after a meal). Grapefruit products should be avoided before and after dosing. SULAR is an extended release dosage form and tablets should be swallowed whole, not bitten, divided or crushed.
8HOW SUPPLIED
SULAR extended release tablets are supplied as 8.5 mg and 17 mg round film coated tablets and 34 mg elliptic film coated tablets. The different strengths can be identified as follows:
SULAR Tablets are supplied in bottles of 100:
Protect from light and moisture. Store at 20°-25°C (68°-77°F); excursions permitted to 15°-30°C (59°-86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Dispense in tight, light-resistant containers.
Rx only
Sular is a trademark of Covis Pharma
Manufactured for:
Made in Germany
Rev 07/17
9PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 8.5 mg Carton

NDC 70515-500-10
100 Tablets
Sular
8.5 mg
Rx only
See package insert for full prescribing
COVIS
Store at 20°-25°C (68°-77°F); excursions
See package insert for full prescribing
Manufactured for:
Made in Germany
GTIN: XXXXXXXXXXXXXX
10PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 17 mg Carton
NDC 70515-501-10
100 Tablets
Sular
17 mg
Rx only
See package insert for full prescribing
COVIS
Store at 20°-25°C (68°-77°F); excursions
See package insert for full prescribing
Manufactured for:
Made in Germany
GTIN: XXXXXXXXXXXXXX
11PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 34 mg Carton
NDC 70515-503-10
100 Tablets
Sular
34 mg
Rx only
See package insert for full prescribing
COVIS
Store at 20°-25°C (68°-77°F); excursions
See package insert for full prescribing
Manufactured for:
Made in Germany
GTIN: XXXXXXXXXXXXXX