Generic Name
Deferasirox
Brand Names
Deferasorox, Exjade, Jadenu
FDA approval date: November 30, 2005
Classification: Iron Chelator
Form: Tablet, Granule
What is Deferasorox (Deferasirox)?
Deferasirox granule is an iron chelator indicated for the treatment of chronic iron overload due to blood transfusions in patients 2 years of age and older.
Top Global Experts
There are no experts for this drug
Save this treatment for later
Not sure about your diagnosis?
Related Clinical Trials
There is no clinical trials being done for this treatment
Related Latest Advances
There is no latest advances for this treatment
Brand Information
Deferasorox (Deferasirox)
WARNING: RENAL FAILURE, HEPATIC FAILURE, and GASTROINTESTINAL HEMORRHAGE
Renal Failure
- Deferasirox can cause acute renal failure and death, particularly in patients with comorbidities and those who are in the advanced stages of their hematologic disorders.
- Evaluate baseline renal function prior to starting or increasing deferasirox dosing in all patients. Deferasirox is contraindicated in adult and pediatric patients with eGFR less than 40 mL/min/1.73 m
Hepatic Failure
- Deferasirox can cause hepatic injury including hepatic failure and death.
- Measure serum transaminases and bilirubin in all patients prior to initiating treatment, every 2 weeks during the first month, and at least monthly thereafter.
- Avoid use of deferasirox in patients with severe (Child-Pugh C) hepatic impairment and reduce the dose in patients with moderate (Child-Pugh B) hepatic impairment
Gastrointestinal Hemorrhage
- Deferasirox can cause gastrointestinal (GI) hemorrhages, which may be fatal, especially in elderly patients who have advanced hematologic malignancies and/or low platelet counts.
- Monitor patients and discontinue deferasirox for suspected GI ulceration or hemorrhage
1DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 90 mg deferasirox oral granules
Supplied in cartons containing 30 child resistant foil sachets. Each sachet contains 162.5 mg of white to almost white granules, equivalent to 90 mg deferasirox.
- 180 mg deferasirox oral granules
Supplied in cartons containing 30 child resistant foil sachets. Each sachet contains 325 mg of white to almost white granules, equivalent to 180 mg deferasirox.
- 360 mg deferasirox oral granules
Supplied in cartons containing 30 child resistant foil sachets. Each sachet contains 650 mg of white to almost white granules, equivalent to 360 mg deferasirox.
2CONTRAINDICATIONS
Deferasirox is contraindicated in patients with:
- Estimated GFR less than 40 mL/min/1.73 m
- Poor performance status
- High-risk myelodysplastic syndromes
- Advanced malignancies
- Platelet counts less than 50 x 10
- Known hypersensitivity to deferasirox or any component of deferasirox
3ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are also discussed in other sections of the labeling:
- Acute Kidney Injury, Including Acute Renal Failure Requiring Dialysis, and Renal Tubular Toxicity Including Fanconi Syndrome
- Hepatic Toxicity and Failure
- GI Hemorrhage
- Bone Marrow Suppression
- Hypersensitivity
- Severe Skin Reactions
- Skin Rash
- Auditory and Ocular Abnormalities
3.1Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice. Deferasirox was evaluated in healthy volunteer trials. Currently, there are no clinical data in patients with deferasirox oral granules. Deferasirox contains the same active ingredient as deferasirox tablets for oral suspension. The following adverse reactions have been reported with deferasirox tablets for oral suspension.
Table 1. Adverse Reactions
In Study 1, a total of 113 (38%) patients treated with deferasirox had increases in serum creatinine greater than 33% above baseline on 2 separate occasions (Table 2) and 25 (8%) patients required dose reductions. Increases in serum creatinine appeared to be dose related
3.2Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been spontaneously reported during post-approval use of deferasirox in the transfusional iron overload setting. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, in which patients may have received concomitant medication, it is not always possible to reliably estimate frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
4OVERDOSAGE
Cases of overdose (2 to 3 times the prescribed dose for several weeks) have been reported. In one case, this resulted in hepatitis which resolved without long-term consequences after a dose interruption. In one pediatric case, a dose of 2-3 times the prescribed dose for 6 days resulted in acute renal failure requiring hemofiltration and acute liver injury/failure, which were reversible with intensive care support. Single doses of deferasirox up to 80 mg per kg per day with the tablet for oral suspension formulation in iron-overloaded beta-thalassemic patients have been tolerated with nausea and diarrhea noted. In healthy subjects, single doses of up to 40 mg per kg per day with the tablet for oral suspension formulation were tolerated.
Early signs of acute overdose are digestive effects such as abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting. Hepatic and renal disorders have been reported, including cases of liver enzyme and creatinine increased with recovery after treatment discontinuation. An erroneously administered single dose of 90 mg/kg led to Fanconi syndrome which resolved after treatment.
5DESCRIPTION
Deferasirox is an iron-chelating agent provided as a granules for oral use. Deferasirox is designated chemically as 4-[3,5-bis(2-hydroxyphenyl)-1
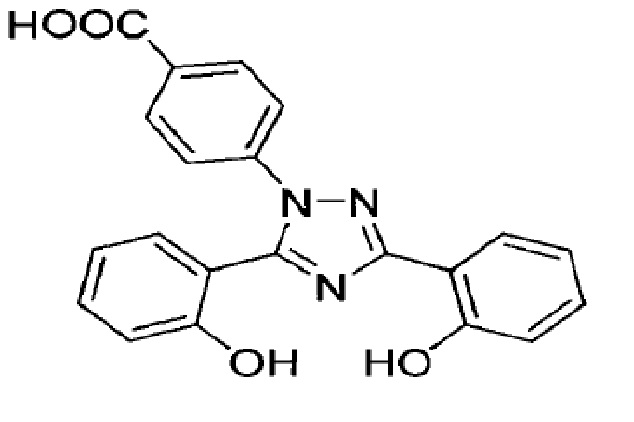
Deferasirox is a white to slightly yellow powder. It has a molecular formula C
6CLINICAL STUDIES
Deferasirox was evaluated in healthy subjects. There are no clinical data in patients with deferasirox. Deferasirox contains the same active ingredient as deferasirox tablets for oral suspension. The following information is based on clinical trials conducted with deferasirox tablets for oral suspension.
Study 6 (NCT00873041) was an open-label trial of deferasirox tablets for oral suspension for the treatment of patients previously enrolled on Study 5, including cross-over to active treatment for those previously treated with placebo. The starting dose of deferasirox tablets for oral suspension in Study 6 was assigned based on the patient’s LIC at completion of Study 5, being 20 mg/kg/day for an LIC exceeding 15 mg Fe/g dw, 10 mg/kg/day for LIC 3 to 15 mg Fe/g dw, and observation if the LIC was less than 3 mg Fe/g dw. Patients could continue on 5 mg/kg/day if they had previously exhibited at least a 30% reduction in LIC. Doses could be increased to a maximum of 20 mg/kg/day after 6 months if the LIC was more than 7 mg Fe/g dw and the LIC reduction from baseline was less than 15%. The primary efficacy endpoint in Study 6 was the proportion of patients achieving an LIC less than 5 mg Fe/g dw. A total of 133 patients were enrolled. Twenty patients began Study 6 with an LIC less than 5 mg Fe/g dw. Of the 113 patients with a baseline LIC of at least 5 mg Fe/g dw in Study 6, the target LIC (less than 5 mg Fe/g dw) was reached by 39 patients (35%). The responders included 4 (10%) of 39 patients treated at 20 mg/kg/day for a baseline LIC exceeding 15 mg Fe/g dw, and 31 (51%) of 61 patients treated at 10 mg/kg/day for a baseline LIC between 5 and 15 mg Fe/g dw. The absolute change in LIC at Week 52 by starting dose is shown in Table 5 below.
7HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Deferasirox oral granules 90 mg are white to almost white granules in sachet. They are available in cartons of 30 sachets………………………………………………..(NDC 72205-176-30).
Deferasirox oral granules 180 mg are white to almost white granules in sachet.They are available in cartons of 30 sachets………………………………………………..(NDC 72205-075-30).
Deferasirox oral granules 360 mg are white to almost white granules in sachet. They are available in cartons of 30 sachets………………………………………………..(NDC 72205-076-30).
Store deferasirox oral granules at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted between 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Protect from moisture.
8PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide).
Dosing Instructions
Advise patients to take deferasirox oral granules by sprinkling the full dose on soft food (e.g., yogurt or applesauce) immediately prior to use and administered orally. Advise patients to take deferasirox oral granules once a day, preferably at the same time each day. Deferasirox oral granules may be taken on an empty stomach or with a light meal (contains less than 7% fat content and approximately 250 calories). Examples of light meals include 1 whole wheat English muffin, 1 packet jelly (0.5 ounces), and skim milk (8 fluid ounces) or a turkey sandwich (2 oz. turkey on whole wheat bread w/lettuce, tomato, and 1 packet mustard).
Blood Testing
Advise patients that blood tests will be performed frequently to check for damage to kidneys, liver, or blood cells [see .
Acute Kidney Injury, Including Acute Renal Failure
Caution patients about the potential for kidney toxicity when taking deferasirox oral granules. Inform patients of the signs and symptoms of kidney injury. Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider immediately if they experience any of these symptoms [see .
Hepatic Toxicity and Failure
Caution patients about the potential for hepatic toxicity when taking deferasirox oral granules. Inform patients of the signs and symptoms of hepatic toxicity. Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider immediately if they experience any of these symptoms [see .
GI Ulceration and Hemorrhage
Caution patients about the potential for the development of GI ulcers or bleeding when taking deferasirox in combination with drugs that have ulcerogenic or hemorrhagic potential, such as NSAIDs, corticosteroids, oral bisphosphonates, or anticoagulants. Inform patients of the signs and symptoms of GI ulcers or bleeding. Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider for symptoms of heartburn but to seek immediate medical attention for symptoms of GI hemorrhage [see
Advise patients to take deferasirox oral granules by sprinkling the full dose on soft food (e.g., yogurt or applesauce) immediately prior to use and administered orally. Advise patients to take deferasirox oral granules once a day, preferably at the same time each day. Deferasirox oral granules may be taken on an empty stomach or with a light meal (contains less than 7% fat content and approximately 250 calories). Examples of light meals include 1 whole wheat English muffin, 1 packet jelly (0.5 ounces), and skim milk (8 fluid ounces) or a turkey sandwich (2 oz. turkey on whole wheat bread w/lettuce, tomato, and 1 packet mustard).
Blood Testing
Advise patients that blood tests will be performed frequently to check for damage to kidneys, liver, or blood cells [see .
Acute Kidney Injury, Including Acute Renal Failure
Caution patients about the potential for kidney toxicity when taking deferasirox oral granules. Inform patients of the signs and symptoms of kidney injury. Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider immediately if they experience any of these symptoms [see .
Hepatic Toxicity and Failure
Caution patients about the potential for hepatic toxicity when taking deferasirox oral granules. Inform patients of the signs and symptoms of hepatic toxicity. Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider immediately if they experience any of these symptoms [see .
GI Ulceration and Hemorrhage
Caution patients about the potential for the development of GI ulcers or bleeding when taking deferasirox in combination with drugs that have ulcerogenic or hemorrhagic potential, such as NSAIDs, corticosteroids, oral bisphosphonates, or anticoagulants. Inform patients of the signs and symptoms of GI ulcers or bleeding. Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider for symptoms of heartburn but to seek immediate medical attention for symptoms of GI hemorrhage [see
Allergic Reactions
Serious allergic reactions (which include swelling of the throat) have been reported in patients taking deferasirox, usually within the first month of treatment. If reactions are severe, advise patients to stop taking deferasirox immediately and seek immediate medical attention [see .
Severe Skin Reactions
Severe skin reactions have been reported in patients taking deferasirox oral granules. Inform patients of the signs and symptoms of severe skin reactions. If reactions are severe, advise patients to stop taking deferasirox oral granules immediately and seek immediate medical attention [see .
Skin Rash
Skin rashes may occur during deferasirox treatment. If the skin rash is severe, advise patients to stop taking deferasirox and seek medical attention [see .
Pediatric Patients with Acute Illness
Instruct pediatric patients and their caregivers to contact their healthcare provider during episodes of acute illness, especially if the patient has not been drinking fluids or the patient has volume depletion due to fever, vomiting, or diarrhea [see .
Auditory and Ocular Testing
Because auditory and ocular disturbances have been reported with deferasirox, conduct auditory testing and ophthalmic testing before starting deferasirox treatment and thereafter at regular intervals. Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider if they develop visual or auditory changes during treatment [see .
Drug Interactions
Caution patients not to take aluminum containing antacids and deferasirox granules simultaneously [.
Caution patients about potential loss of effectiveness of drugs metabolized by CYP3A4 (e.g., cyclosporine, simvastatin, hormonal contraceptive agents) when deferasirox is administered with these drugs [see .
Caution patients about potential loss of effectiveness of deferasirox when administered with drugs that are potent UGT inducers (e.g., rifampicin, phenytoin, phenobarbital, ritonavir). Based on serum ferritin levels and clinical response, consider increases in the dose of deferasirox when concomitantly used with potent UGT inducers [see .
Caution patients about potential loss of effectiveness of deferasirox when administered with drugs that are bile acid sequestrants (e.g., cholestyramine, colesevelam, colestipol). Based on serum ferritin levels and clinical response, consider increases in the dose of deferasirox when concomitantly used with bile acid sequestrants [see .
Caution patients with diabetes to monitor their glucose levels more frequently when repaglinide is used concomitantly with deferasirox [see .
Handling Instructions
Advise patients to store deferasirox in a dry, room-temperature environment [see .
Driving and Using Machines
Caution patients experiencing dizziness to avoid driving or operating machinery [see .
Manufactured by:
MSN Laboratories Private Limited
Telangana – 509 228,
INDIA
Distributed by:Piscataway, NJ 08854-3714
Issued on:
March 2022
Serious allergic reactions (which include swelling of the throat) have been reported in patients taking deferasirox, usually within the first month of treatment. If reactions are severe, advise patients to stop taking deferasirox immediately and seek immediate medical attention [see .
Severe Skin Reactions
Severe skin reactions have been reported in patients taking deferasirox oral granules. Inform patients of the signs and symptoms of severe skin reactions. If reactions are severe, advise patients to stop taking deferasirox oral granules immediately and seek immediate medical attention [see .
Skin Rash
Skin rashes may occur during deferasirox treatment. If the skin rash is severe, advise patients to stop taking deferasirox and seek medical attention [see .
Pediatric Patients with Acute Illness
Instruct pediatric patients and their caregivers to contact their healthcare provider during episodes of acute illness, especially if the patient has not been drinking fluids or the patient has volume depletion due to fever, vomiting, or diarrhea [see .
Auditory and Ocular Testing
Because auditory and ocular disturbances have been reported with deferasirox, conduct auditory testing and ophthalmic testing before starting deferasirox treatment and thereafter at regular intervals. Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider if they develop visual or auditory changes during treatment [see .
Drug Interactions
Caution patients not to take aluminum containing antacids and deferasirox granules simultaneously [.
Caution patients about potential loss of effectiveness of drugs metabolized by CYP3A4 (e.g., cyclosporine, simvastatin, hormonal contraceptive agents) when deferasirox is administered with these drugs [see .
Caution patients about potential loss of effectiveness of deferasirox when administered with drugs that are potent UGT inducers (e.g., rifampicin, phenytoin, phenobarbital, ritonavir). Based on serum ferritin levels and clinical response, consider increases in the dose of deferasirox when concomitantly used with potent UGT inducers [see .
Caution patients about potential loss of effectiveness of deferasirox when administered with drugs that are bile acid sequestrants (e.g., cholestyramine, colesevelam, colestipol). Based on serum ferritin levels and clinical response, consider increases in the dose of deferasirox when concomitantly used with bile acid sequestrants [see .
Caution patients with diabetes to monitor their glucose levels more frequently when repaglinide is used concomitantly with deferasirox [see .
Handling Instructions
Advise patients to store deferasirox in a dry, room-temperature environment [see .
Driving and Using Machines
Caution patients experiencing dizziness to avoid driving or operating machinery [see .
Manufactured by:
MSN Laboratories Private Limited
Telangana – 509 228,
INDIA
Distributed by:Piscataway, NJ 08854-3714
Issued on:
March 2022
9PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Deferasirox Oral Granules 180 mg Carton Label (30's Count)
Deferasirox Oral Granules 90 mg Carton Label (30's Count)
Deferasirox Oral Granules 90 mg Sachet Label