Brand Name
Arranon
Generic Name
Nelarabine
View Brand Information FDA approval date: October 05, 2016
Classification: Nucleoside Metabolic Inhibitor
Form: Injection
What is Arranon (Nelarabine)?
Nelarabine Injection is indicated for the treatment of T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia and T-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma in adult and pediatric patients age 1 year and older whose disease has not responded to or has relapsed following treatment with at least two chemotherapy regimens. Nelarabine Injection is a nucleoside metabolic inhibitor indicated for the treatment of patients with T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia and T-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma in adult and pediatric patients age 1 year and older whose disease has not responded to or has relapsed following treatment with at least two chemotherapy regimens.
Approved To Treat
Top Global Experts
There are no experts for this drug
Save this treatment for later
Not sure about your diagnosis?
Related Clinical Trials
There is no clinical trials being done for this treatment
Related Latest Advances
There is no latest advances for this treatment
Brand Information
Arranon (nelarabine)
WARNING: NEUROLOGIC ADVERSE REACTIONS
Severe neurologic adverse reactions have been reported with the use of ARRANON
Full recovery from these adverse reactions has not always occurred with cessation of therapy with ARRANON. Monitor frequently for signs and symptoms of neurologic toxicity during treatment with ARRANON. Discontinue ARRANON for neurologic adverse reactions of NCI Common Toxicity Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) Grade 2 or greater
1INDICATIONS AND USAGE
ARRANON is indicated for the treatment of T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) and T-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma (T-LBL) in adult and pediatric patients age 1 year and older whose disease has not responded to or has relapsed following treatment with at least 2 chemotherapy regimens.
2DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
ARRANON Injection 250 mg/50 mL (5 mg/mL) is supplied as a clear, colorless, sterile solution in Type I, clear glass single-dose vials with a gray bromobutyl rubber stopper (not made with natural rubber latex) and an aluminum seal with a snap-off cap.
3CONTRAINDICATIONS
None.
4ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically-significant adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the label:
- Neurologic
- Hematologic
- Tumor Lysis Syndrome
- Effects on Ability to Drive and Use Machines
4.1Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared with rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Relapsed or Refractory T-ALL and T-LBL
ARRANON was studied in 459 patients in Phase I and Phase II clinical trials.
Adult Patient: The safety profile of ARRANON is based on data from 103 adult patients treated with the recommended dose and schedule in 2 studies: an adult T-ALL/T-cell T-LBL trial and an adult chronic lymphocytic leukemia trial.
The most common adverse reactions in adults were fatigue; gastrointestinal disorders (nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, and constipation); hematologic disorders (anemia, neutropenia, and thrombocytopenia); respiratory disorders (cough and dyspnea); nervous system disorders (somnolence and dizziness); and pyrexia.
The most common adverse reactions in adults by Body System, including severe or life-threatening adverse reactions (NCI CTCAE Grade 3 or Grade 4) and fatal adverse reactions (Grade 5) are shown in Table 1.
Other Adverse Reactions: Blurred vision was also reported in 4% of adult patients.
There was a single report of biopsy-confirmed progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy in the adult patient population.
Neurologic Adverse Reactions: Nervous system adverse reactions, were reported for 76% of adult patients across the Phase I and Phase II trials. The most common neurologic adverse reactions (≥ 2%) in adult patients including all grades (NCI CTCAE) are shown in Table 2.
One patient had a fatal neurologic adverse reaction, cerebral hemorrhage/coma/leukoencephalopathy.
Most nervous system adverse reactions in the adult patients were evaluated as Grade 1 or 2. The additional Grade 3 adverse reactions in adult patients, were aphasia, convulsion, hemiparesis, and loss of consciousness, each reported in 1 patient (1%). The additional Grade 4 adverse reactions were cerebral hemorrhage, coma, intracranial hemorrhage, leukoencephalopathy, and metabolic encephalopathy, each reported in one patient (1%).
The other neurologic adverse reactions reported as Grade 1, 2, or unknown in adult patients were abnormal coordination, burning sensation, disturbance in attention, dysarthria, hyporeflexia, neuropathic pain, nystagmus, peroneal nerve palsy, sciatica, sensory disturbance, sinus headache, and speech disorder, each reported in one patient (1%).
Pediatric Patient: The safety profile for children is based on data from 84 pediatric patients treated with the recommended dose and schedule in a T-ALL/T-LBL treatment trial.
The most common adverse reactions in pediatric patients were hematologic disorders (anemia, leukopenia, neutropenia, and thrombocytopenia). Of the non-hematologic adverse reactions in pediatric patients, the most frequent adverse reactions reported were headache, increased transaminase levels, decreased blood potassium, decreased blood albumin, increased blood bilirubin, and vomiting.
The most common adverse reactions in pediatric patients by System Organ Class including severe or life threatening adverse reactions (NCI CTCAE Grade 3 or Grade 4) and fatal adverse reactions (Grade 5) are shown in Table 3.
Neurologic Adverse Reactions: Nervous system adverse reactions were reported for 42% of pediatric patients across the Phase I and Phase II trials. The most common neurologic adverse reactions (≥ 2%) in pediatric patients including all grades (NCI CTCAE) are shown in Table 4.
The other Grade 3 neurologic adverse reaction in pediatric patients was hypertonia reported in 1 patient (1%). The additional Grade 4 neurologic adverse reactions, were third nerve paralysis, and sixth nerve paralysis, each reported in 1 patient (1%).
The other neurologic adverse reactions reported as Grade 1, 2, or unknown in pediatric patients were dysarthria, encephalopathy, hydrocephalus, hyporeflexia, lethargy, mental impairment, paralysis, and sensory loss, each reported in 1 patient (1%).
ARRANON in Combination with Multi-Agent Chemotherapy in T-ALL and T-LBL
ARRANON was studied in combination with multi-agent chemotherapy in a randomized clinical trial [NCT00408005]. The safety population in this trial included 804 patients with newly-diagnosed T-ALL (85%) or T-LBL (15%) treated with (n = 411) or without (n =393) ARRANON in combination with the augmented Berlin-Frankfurt-Münster chemotherapy regimen (aBFM) after initial induction therapy. Patients assigned to ARRANON received 650 mg/m
There was one fatal neurological adverse reaction in the ARRANON arm. The incidence of the following Grades 3 and 4 adverse reactions were higher in the ARRANON treated arms compared to the control arms: abnormal transaminases, motor and sensory neuropathy, nausea and vomiting, and dehydration. The incidence of seizures of any grade was 3% (14 of 411). Rhabdomyolysis was diagnosed in 2% (7 of 411) of ARRANON treated patients and occurred after the first course of ARRANON during the consolidation phase of therapy.
4.2Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of ARRANON. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Infections and Infestations: Fatal opportunistic infections
Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders: Tumor lysis syndrome
Nervous System Disorders: Demyelination and ascending peripheral neuropathies similar in appearance to Guillain-Barré syndrome
Musculoskeletal and Connective Disorders: Rhabdomyolysis, blood creatine phosphokinase increased
5DRUG INTERACTIONS
Administration of ARRANON in combination with adenosine deaminase (ADA) inhibitors, such as pentostatin, is not recommended
6OVERDOSAGE
There is no known antidote for overdoses of ARRANON. It is anticipated that overdosage would result in severe neurotoxicity (possibly including paralysis, coma), myelosuppression, and potentially death. In the event of overdose, supportive care consistent with good clinical practice should be provided.
At a dose of 2200 mg/m
7DESCRIPTION
ARRANON (nelarabine) is a prodrug of the cytotoxic deoxyguanosine analogue, 9-β-
The chemical name for nelarabine is 2-amino-9-β-
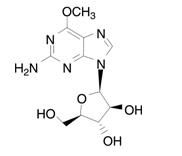
Nelarabine is slightly soluble to soluble in water and melts with decomposition between 209ºC and 217ºC.
ARRANON (nelarabine) injection is supplied as a clear, colorless, sterile solution in glass single-dose vials. Each vial contains 250 mg of nelarabine (5 mg nelarabine per mL) and the inactive ingredient sodium chloride (4.5 mg per mL) in Water for Injection, USP. ARRANON is intended for intravenous infusion.
Hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide may have been used to adjust the pH. The solution pH ranges from 5.0 to 7.0.
8REFERENCES
- “OSHA Hazardous Drugs.” OSHA.
9HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
ARRANON (nelarabine) injection is supplied as a clear, colorless, sterile solution in Type I, clear glass single-dose vials with a gray bromobutyl rubber stopper (not made with natural rubber latex) and an aluminum seal with a snap-off cap.
Single-dose Vials are available in 250 mg/50 mL (5 mg/mL) strength and the following carton sizes:
NDC 66758-165-94 (package of 1). Discard Unused Portion.
Store ARRANON (nelarabine) Injection between 20°C and 25°C (68°F and 77°F); excursions permitted to 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F). See USP Controlled Room Temperature.
10PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
Hematologic Adverse Reactions
- Advise patients that leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, anemia, and neutropenia, including febrile neutropenia, have been associated with ARRANON.
- Advise patients that complete blood counts, including platelets, will be monitored regularly during treatment
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
- Advise pregnant females of reproductive potential and males with female partners of reproductive potential of the potential risk to the fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with ARRANON. Instruct females to inform their physician of a known or suspected pregnancy.
- Advise male patients with partners of reproductive potential to use condoms during treatment with ARRANON and for 3 months after the last dose
Tumor Lysis Syndrome
- Advise patients of the risk of tumor lysis syndrome
Vaccinations
- Instruct patients not to receive live vaccines during treatment with ARRANON
Effects on Ability to Drive and Use Machines
- Patients receiving ARRANON may experience somnolence during and for several days after treatment. Instruct patients to not drive or engage in hazardous occupations or activities until somnolence has resolved
Neurologic Adverse Reactions
- Instruct patients to contact their physician if they experience new or worsening symptoms of peripheral neuropathy
- Advise patients of the risk of seizures
Infection
- Instruct patients to promptly notify their physician if they develop fever or signs of infection while on therapy
Lactation
- Advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with ARRANON
Manufactured by
FAREVA Unterach GmbH,
Mondseestraße 11
4866 Unterach am Attersee, Austria for
Sandoz Inc., Princeton, NJ 08540
46330594-03
11PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC 66758-165-94 Rx only
ARRANON
250 mg/50 mL
For Intravenous Infusion Only
One 50 mL Vial
Single-Dose Vial
Discard Unused Portion.
WARNING: Hazardous Drug
SANDOZ
