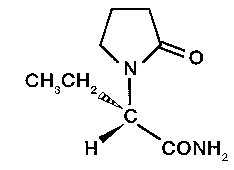
Levetiracetam
What is Keppra (Levetiracetam)?
A diagnosis of epilepsy can bring a great deal of uncertainty into one’s life. The possibility of a seizure can feel like a constant shadow, affecting everything from daily routines to long-term plans. The primary goal of treatment is to regain control and predictability, allowing individuals to live their lives as fully and freely as possible. For decades, one of the most widely prescribed and trusted medications to achieve this goal has been Levetiracetam.
Levetiracetam is a prescription medication that belongs to a class of drugs known as anticonvulsants or anti-epileptic drugs (AEDs). It is a well-established, often first-line therapy used to manage and prevent seizures. Unlike some older medications in its class, Levetiracetam is known for its relatively straightforward use and unique mechanism of action. Whether used alone or in combination with other medications, it is a cornerstone of modern epilepsy care for both children and adults.
What does Levetiracetam do?
Levetiracetam is approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of several different types of seizures in adults, children and even infants.
It is specifically used to treat:
- Partial-Onset Seizures: These seizures begin in one specific area of the brain. Levetiracetam is used for this type of seizure in patients as young as one month old.
- Myoclonic Seizures: These are characterized by brief, shock-like jerks of a muscle or group of muscles. It is used in patients 12 years and older with Juvenile Myoclonic Epilepsy.
- Primary Generalized Tonic-Clonic Seizures: Formerly known as “grand mal” seizures, these involve a loss of consciousness and violent muscle contractions. It is used in patients 6 years and older with Idiopathic Generalized Epilepsy.
Levetiracetam aims to reduce or eliminate seizures, improving safety, confidence and quality of life for epilepsy patients through consistent control. Clinical studies and years of real-world use have shown it to be a highly effective medication for a broad range of patients.
How does Levetiracetam work?
The exact way Levetiracetam works is unique and still not fully understood, setting it apart from many other anti-seizure medications. Seizures are caused by sudden, abnormal bursts of excessive electrical activity between brain cells (neurons). Many AEDs work by acting on common channels or receptors on the surface of these neurons to calm this activity.
Levetiracetam, however, is believed to work through a different, more specific mechanism. It targets a protein called synaptic vesicle protein 2A (SV2A). Think of the brain’s neurons as constantly sending messages to each other using chemical messengers called neurotransmitters. These messengers are stored in tiny bubbles called synaptic vesicles. For a message to be sent, these vesicles must release their contents.
Levetiracetam modulates neurotransmitter release by binding to the SV2A protein, stabilizing nerve cells, and preventing excessive firing, thus controlling seizures without broadly depressing the central nervous system.
Levetiracetam side effects
Like all medications, Levetiracetam has potential side effects. Many are mild and may decrease as your body gets used to the drug.
The most common side effects include:
- Drowsiness or sleepiness (somnolence)
- Weakness or fatigue (asthenia)
- Dizziness
- Infection (such as the common cold)
One of the most important side effects to be aware of involves changes in mood or behavior. A significant number of patients, particularly children, may experience:
- Irritability or agitation
- Anxiety
- Aggression
- Depression or mood swings
Rarely, severe side effects like suicidal thoughts or psychosis can occur. Patients and caregivers must immediately report any new or worsening behavioral changes to a doctor.
Serious side effects of Levetiracetam are rare but include severe skin reactions (e.g., Stevens-Johnson syndrome) or reduced blood cell counts. Do not stop Levetiracetam suddenly; this can increase seizures. Dose changes must be gradual and supervised by your doctor. Kidney problems may require lower doses (National Institutes of Health, 2022).
Levetiracetam dosage
Levetiracetam, a versatile medication, comes in various forms: immediate-release and extended-release oral tablets, oral solution and intravenous injection (for hospital use).
Your doctor will gradually increase your low starting dose over days or weeks to minimize side effects. Swallow tablets whole unless designed to be chewed or crushed.
One of the benefits of Levetiracetam is that it generally doesn’t need routine blood tests for drug levels, unlike many other AEDs. Your doctor will regularly monitor your progress, seizure control, and side effects. For kidney disease patients, kidney function will be monitored to adjust the dose.
Does Levetiracetam have a generic version?
Yes, Levetiracetam is widely available as a generic medication. The most common brand name is Keppra, but there are others as well, such as Elepsia XR and Spritam. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration requires that generic medications be just as safe, effective, and high-quality as their brand-name counterparts (FDA, 2021). The availability of a generic version makes this important treatment highly accessible and affordable for most patients.
Conclusion
Levetiracetam is a cornerstone in the treatment of epilepsy, offering effective and reliable seizure control for a wide variety of seizure types in both adults and children. Its unique mechanism of action and generally favorable side effect profile have made it one of the most prescribed anti-seizure medications worldwide.
While it is essential to be aware of the potential for mood and behavioral side effects, these can be managed through close partnership with your healthcare provider. When taken as prescribed, Levetiracetam is a safe and powerful tool that can help individuals break free from the unpredictability of seizures and live a more stable, confident life.
References
- Food and Drug Administration (FDA). (2021). Generic Drug Facts. Retrieved from https://www.fda.gov/drugs/generic-drugs/generic-drug-facts
- National Institutes of Health. (2022). Levetiracetam. MedlinePlus. Retrieved from https://medlineplus.gov/druginfo/meds/a601028.html
- Mayo Clinic. (2024). Levetiracetam (Oral Route). Retrieved from https://www.mayoclinic.org/drugs-supplements/levetiracetam-oral-route/side-effects/drg-20068010
Approved To Treat
Top Global Experts
There are no experts for this drug
Related Clinical Trials
There is no clinical trials being done for this treatment
Related Latest Advances
There is no latest advances for this treatment
Brand Information
- Behavioral abnormalities and Psychotic Symptoms
- Suicidal Behavior and Ideation
- Somnolence and Fatigue
- Anaphylaxis and Angioedema
- Serious Dermatological Reactions
- Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS)/Multiorgan Hypersensitivity
- Coordination Difficulties
- Hematologic Abnormalities