Brand Name
Juxtapid
Generic Name
Lomitapide
View Brand Information FDA approval date: January 03, 2013
Classification: Microsomal Triglyceride Transfer Protein Inhibitor
Form: Capsule
What is Juxtapid (Lomitapide)?
JUXTAPID is a microsomal triglyceride transfer protein inhibitor indicated as an adjunct to a low-fat diet and other lipid-lowering treatments, including LDL apheresis where available, to reduce low-density lipoprotein cholesterol , total cholesterol , apolipoprotein B , and non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol in patients with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia . Limitations of Use The safety and effectiveness of JUXTAPID have not been established in patients with hypercholesterolemia who do not have HoFH, including those with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia . The effect of JUXTAPID on cardiovascular morbidity and mortality has not been determined .
Approved To Treat
Save this treatment for later
Not sure about your diagnosis?
Related Clinical Trials
Evaluation of the Effect of Lomitapide Treatment on Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events (MACE) in Patients With Homozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia: A Multicenter, Retrospective and Prospective Observational Study
Summary: This observational, multicenter, retrospective and prospective study aims to evaluate the effect of lomitapide treatment on Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events (MACE) in patients with Homozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia (HoFH). HoFH is a rare genetic disorder characterized by extremely high levels of LDL cholesterol (LDL-C), leading to an increased risk of early cardiovascular diseases. Lomit...
LOWER: Lomitapide Observational Worldwide Evaluation Registry
Summary: This global product exposure registry is a multicentre, long-term, prospective, observational cohort study (exposure registry), designed to evaluate the long term safety and effectiveness of lomitapide.
Related Latest Advances
Brand Information
Juxtapid (lomitapide mesylate)
WARNING: RISK OF HEPATOTOXICITY
JUXTAPID can cause elevations in transaminases. In the JUXTAPID clinical trial, 10 (34%) of the 29 patients treated with JUXTAPID had at least one elevation in alanine aminotransferase (ALT) or aspartate aminotransferase (AST) ≥3× upper limit of normal (ULN). There were no concomitant clinically meaningful elevations of total bilirubin, international normalized ratio (INR), or alkaline phosphatase
JUXTAPID also increases hepatic fat, with or without concomitant increases in transaminases. The median absolute increase in hepatic fat was 6% after both 26 and 78 weeks of treatment, from 1% at baseline, measured by magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Hepatic steatosis associated with JUXTAPID treatment may be a risk factor for progressive liver disease, including steatohepatitis and cirrhosis
Measure ALT, AST, alkaline phosphatase, and total bilirubin before initiating treatment and then ALT and AST regularly as recommended. During treatment, adjust the dose of JUXTAPID if the ALT or AST are ≥3× ULN. Discontinue JUXTAPID for clinically significant liver toxicity [
Because of the risk of hepatotoxicity, JUXTAPID is available only through a restricted program under a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) called the JUXTAPID REMS Program
1DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
5 mg: Orange/orange hard gelatin capsule printed with black ink "A733" and "5 mg"
10 mg: Orange/white hard gelatin capsule printed with black ink "A733" and "10 mg"
20 mg: White/white hard gelatin capsule printed with black ink "A733" and "20 mg"
30 mg: Orange/yellow hard gelatin capsule printed with black ink "A733" and "30 mg"
2CONTRAINDICATIONS
JUXTAPID is contraindicated in the following conditions:
- Pregnancy
- Concomitant administration of JUXTAPID with moderate or strong CYP3A4 inhibitors, as this can increase JUXTAPID exposure
- Patients with moderate or severe hepatic impairment (based on Child-Pugh category B or C) and patients with active liver disease, including unexplained persistent elevations of serum transaminases
3ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following important adverse reactions have been observed and are discussed in detail in other sections of the label:
- Risk of hepatotoxicity
- Reduced absorption of fat-soluble vitamins, and serum fatty acids
- Gastrointestinal adverse reactions
3.1Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
One single-arm, open-label, 78-week trial has been conducted in 29 patients with HoFH, 23 of whom completed at least one year of treatment. The initial dosage of JUXTAPID was 5 mg daily, with titration up to 60 mg daily during an 18-week period based on safety and tolerability. In this trial, the mean age was 30.7 years (range, 18 to 55 years), 16 (55%) patients were men, 25 (86%) patients were Caucasian, 2 (7%) were Asian, 1 (3%) was African American, and 1 (3%) was multi-racial
Five (17%) of the 29 patients with HoFH that participated in the clinical trial discontinued treatment due to an adverse reaction. The adverse reactions that contributed to treatment discontinuations included diarrhea (2 patients; 7%) and abdominal pain, nausea, gastroenteritis, weight loss, headache, and difficulty controlling INR on warfarin (1 patient each; 3%).
The most common adverse reactions were gastrointestinal, reported by 27 (93%) of 29 patients. Adverse reactions reported by ≥8 (28%) patients in the HoFH clinical trial included diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, dyspepsia, and abdominal pain. Other common adverse reactions, reported by 5 to 7 (17-24%) patients, included weight loss, abdominal discomfort, abdominal distension, constipation, flatulence, increased ALT, chest pain, influenza, nasopharyngitis, and fatigue.
The adverse reactions reported in at least 10% of patients during the HoFH clinical trial are presented in Table 4.
Adverse reactions of severe intensity were reported by 8 (28%) of 29 patients, with the most common being diarrhea (4 patients, 14%), vomiting (3 patients, 10%), increased ALT or hepatotoxicity (3 patients, 10%), and abdominal pain, distension, and/or discomfort (2 patients, 7%).
3.2Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of JUXTAPID. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to JUXTAPID exposure.
Musculoskeletal disorders: Myalgia
Skin reactions: Alopecia
4OVERDOSAGE
There is no specific treatment in the event of overdose of JUXTAPID. In the event of overdose, the patient should be treated symptomatically and supportive measures instituted as required. Liver-related tests should be monitored. Hemodialysis is unlikely to be beneficial given that lomitapide is highly protein bound.
5DESCRIPTION
JUXTAPID capsules contain lomitapide mesylate, a synthetic lipid-lowering agent for oral administration.
The chemical name of lomitapide mesylate is N-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-9-[4-[4-[[[4'-(trifluoromethyl)[1,1'-biphenyl]-2-yl]carbonyl]amino]-1-piperidinyl]butyl]-9
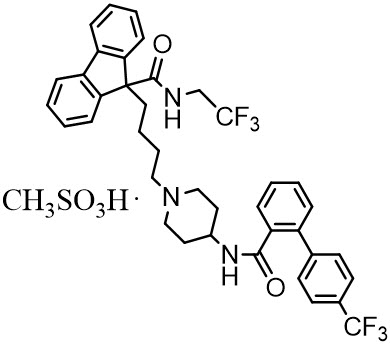
The empirical formula for lomitapide mesylate is C
Lomitapide mesylate is a white to off-white powder that is slightly soluble in aqueous solutions of pH 2 to 5. Lomitapide mesylate is freely soluble in acetone, ethanol, and methanol; soluble in 2-butanol, methylene chloride, and acetonitrile; sparingly soluble in 1-octanol and 2-propanol; slightly soluble in ethyl acetate; and insoluble in heptane.
Each JUXTAPID capsule contains lomitapide mesylate equivalent to 5, 10, 20, or 30 mg lomitapide free base and the following inactive ingredients: pregelatinized starch, sodium starch glycolate, microcrystalline cellulose, lactose monohydrate, silicon dioxide and magnesium stearate. The capsule shells of all strengths contain gelatin and titanium dioxide; the 5 mg, 10 mg and 30 mg capsules also contain red iron oxide; and the 30 mg capsules also contain yellow iron oxide. The imprinting ink contains shellac, black iron oxide, and propylene glycol.
6CLINICAL STUDIES
The safety and effectiveness of JUXTAPID as an adjunct to a low-fat diet and other lipid-lowering treatments, including LDL apheresis where available, were evaluated in a multinational, single-arm, open-label, 78-week trial involving 29 adults with HoFH. A diagnosis of HoFH was defined by the presence of at least one of the following clinical criteria: (1) documented functional mutation(s) in both LDL receptor alleles or alleles known to affect LDL receptor functionality, or (2) skin fibroblast LDL receptor activity <20% normal, or (3) untreated TC >500 mg/dL and TG <300 mg/dL
Among the 29 patients enrolled, the mean age was 30.7 years (range, 18 to 55 years), 16 (55%) were men, and the majority (86%) were Caucasian. The mean body mass index (BMI) was 25.8 kg/m
After a six-week run-in period to stabilize lipid-lowering treatments, including the establishment of an LDL apheresis schedule if applicable, JUXTAPID was initiated at 5 mg daily and titrated to daily doses of 10 mg, 20 mg, 40 mg, and 60 mg at weeks 2, 6, 10, and 14, respectively, based on tolerability and acceptable levels of transaminases. Patients were instructed to maintain a low-fat diet (<20% calories from fat) and to take dietary supplements that provided approximately 400 international units vitamin E, 210 mg alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), 200 mg linoleic acid, 110 mg eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), and 80 mg docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) per day. After efficacy was assessed at Week 26, patients remained on JUXTAPID for an additional 52 weeks to assess long-term safety. During this safety phase, the dose of JUXTAPID was not increased above each patient's maximum tolerated dose established during the efficacy phase, but changes to concomitant lipid-lowering treatments were allowed.
Twenty-three (79%) patients completed the efficacy endpoint at Week 26, all of whom went on to complete 78 weeks of treatment. Adverse events contributed to premature discontinuation for five patients
The primary efficacy endpoint was percent change in LDL-C from baseline to Week 26. At Week 26, the mean and median percent changes in LDL-C from baseline were -40% (paired t-test p<0.001) and -50%, respectively, based on the intent-to-treat population with last observation carried forward (LOCF) for patients who discontinued prematurely. The mean percent change in LDL-C from baseline through Week 26 is shown in Figure 1 for the 23 patients who completed the efficacy period.
Changes in lipids and lipoproteins through the efficacy endpoint at Week 26 are presented in Table 8.
After Week 26, during the safety phase of the study, adjustments to concomitant lipid-lowering treatments were allowed. For the study population overall, average reductions in LDL-C, TC, apo B, and non-HDL-C were sustained during chronic therapy.
7PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
See
Patients should be informed that a registry for patients taking JUXTAPID has been established in order to monitor and evaluate the long-term effects of JUXTAPID. Patients are encouraged to participate in the registry and should be informed that their participation is voluntary. For information regarding the registry program visit www.JUXTAPID.com or call 1-877-902-4099.
Advise patients of the following:
8PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 5 mg Capsule Bottle Label
NDC 10122-405-28
28 capsules
Juxtapid
5 mg
Chiesi

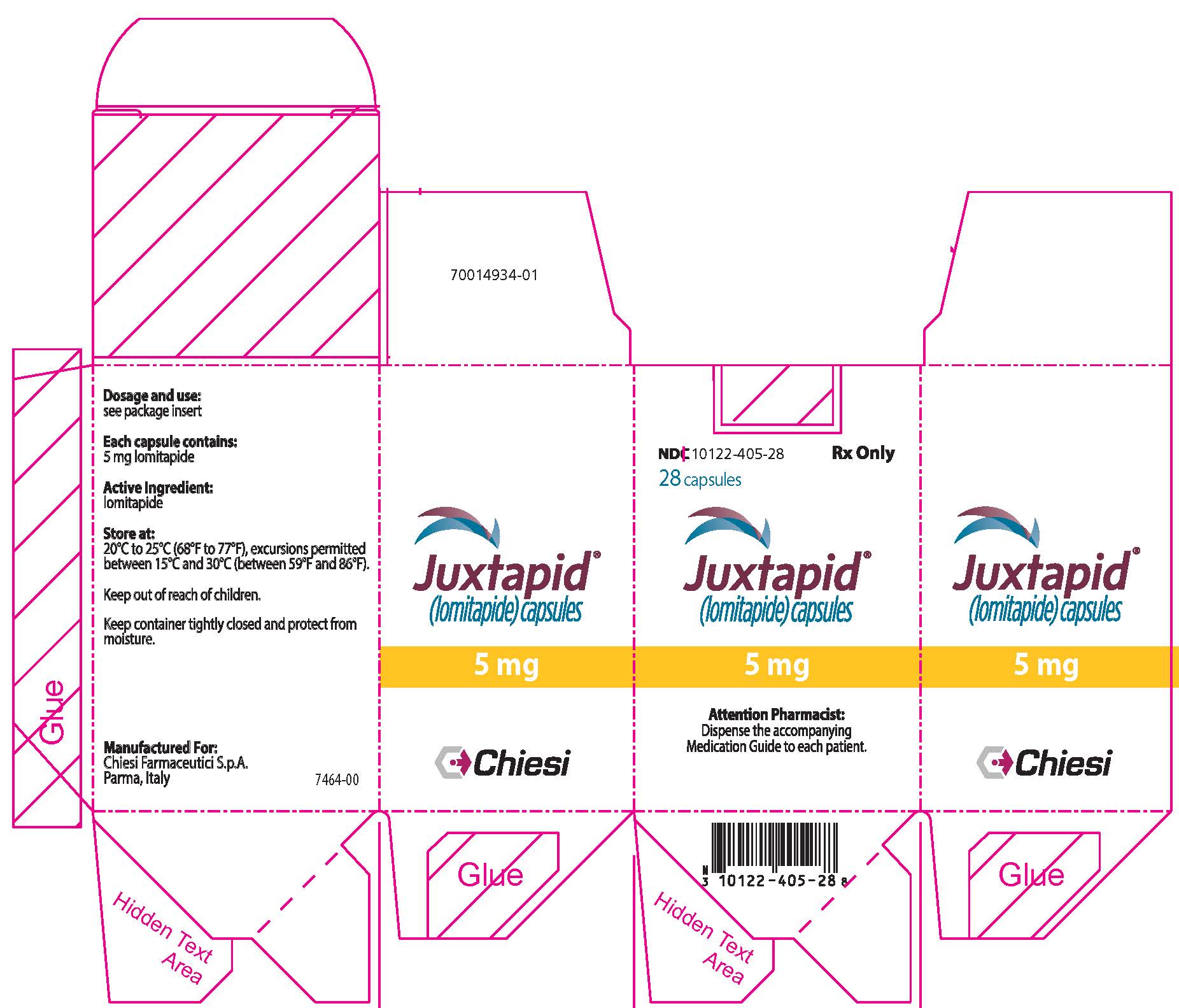
9PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 5 mg Capsule Bottle Carton
NDC 10122-405-28
28 capsules
Juxtapid
5 mg
Attention Pharmacist:
Chiesi
10PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 10 mg Capsule Bottle Label
NDC 10122-410-28
28 capsules
Juxtapid
10 mg
Chiesi

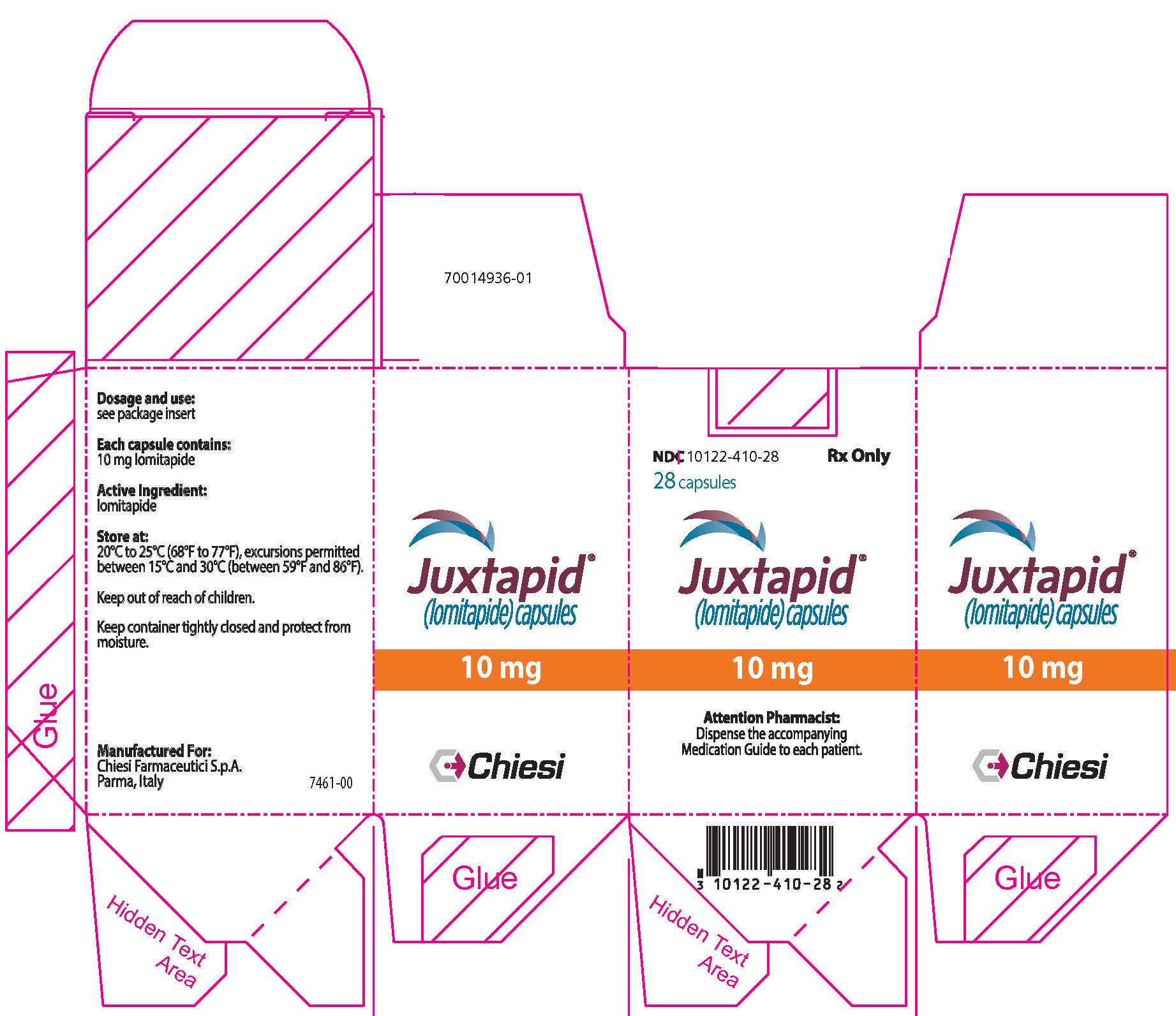
11PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 10 mg Capsule Bottle Carton
NDC 10122-410-28
28 capsules
Juxtapid
10 mg
Attention Pharmacist:
Chiesi
12PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 20 mg Capsule Bottle Label
NDC 10122-420-28
28 capsules
Juxtapid
20 mg
Chiesi

13PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 20 mg Capsule Bottle Carton
NDC 10122-420-28
28 capsules
Juxtapid
20 mg
Attention Pharmacist:
Chiesi
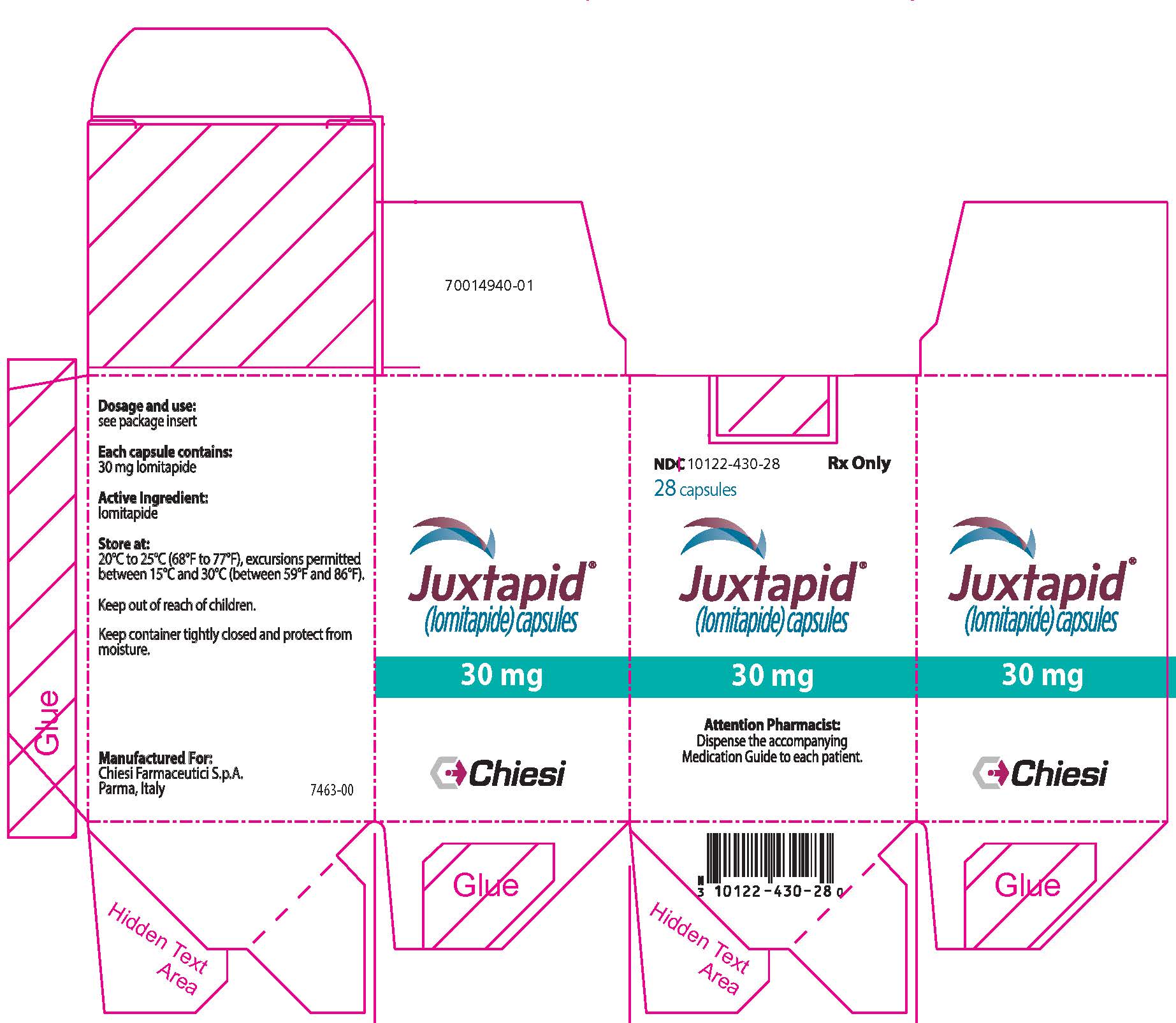
14PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 30 mg Capsule Bottle Label
NDC 10122-430-28
28 capsules
Juxtapid
30 mg
Chiesi

15PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 30 mg Capsule Bottle Carton
NDC 10122-430-28
28 capsules
Juxtapid
30 mg
Attention Pharmacist:
Chiesi