Generic Name
Rilpivirine
Brand Names
Cabenuva, Juluca, Edurant
FDA approval date: May 20, 2011
Classification: Human Immunodeficiency Virus Integrase Strand Transfer Inhibitor
Form: Tablet, Kit
What is Cabenuva (Rilpivirine)?
CABENUVA is indicated as a complete regimen for the treatment of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection in adults to replace the current antiretroviral regimen in those who are virologically suppressed on a stable antiretroviral regimen with no history of treatment failure and with no known or suspected resistance to either cabotegravir or rilpivirine [see Clinical Studies ( 1.
Approved To Treat
Top Global Experts
There are no experts for this drug
Save this treatment for later
Not sure about your diagnosis?
Related Clinical Trials
There is no clinical trials being done for this treatment
Related Latest Advances
Brand Information
Cabenuva (cabotegravir and rilpivirine)
1INDICATIONS AND USAGE
CABENUVA is indicated as a complete regimen for the treatment of HIV-1 infection in adults and adolescents 12 years of age and older and weighing at least 35 kg to replace the current antiretroviral regimen in those who are virologically suppressed (HIV-1 RNA <50 copies/mL) on a stable antiretroviral regimen with no history of treatment failure and with no known or suspected resistance to either cabotegravir or rilpivirine
2DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Injection:
- Kit of single-dose vials of 400 mg/2 mL (200 mg/mL) of cabotegravir extended-release injectable suspension and 600 mg/2 mL (300 mg/mL) of rilpivirine extended-release injectable suspension. (
- Kit of single-dose vials of 600 mg/3 mL (200 mg/mL) of cabotegravir extended-release injectable suspension and 900 mg/3 mL (300 mg/mL) of rilpivirine extended-release injectable suspension. (
3CONTRAINDICATIONS
CABENUVA is contraindicated in patients:
- with previous hypersensitivity reaction to cabotegravir or rilpivirine
- receiving the following coadministered drugs for which significant decreases in cabotegravir and/or rilpivirine plasma concentrations may occur due to uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase (UGT)1A1 and/or cytochrome P450 (CYP)3A enzyme induction, which may result in loss of virologic response
4ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions are described below and in other sections of the labeling:
- Hypersensitivity reactions
- Post-injection reactions
- Hepatotoxicity
- Depressive disorders
4.1Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared with rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect rates observed in practice.
Clinical Trials Experience in Adults
The safety assessment of CABENUVA is based on the analysis of pooled 48-week data from 1,182 virologically suppressed participants with HIV-1 infection in 2 international, multicenter, open-label pivotal trials, FLAIR and ATLAS, and 1,045 virologically suppressed participants from the ATLAS-2M trial
Adverse reactions were reported following exposure to CABENUVA extended-release injectable suspensions (median time exposure at the time of analysis: 54 weeks in FLAIR and ATLAS, and 64 weeks in ATLAS-2M) and data from VOCABRIA (cabotegravir) tablets and EDURANT (rilpivirine) tablets administered in combination as oral lead-in therapy (median time exposure: 5.3 weeks in FLAIR and ATLAS, and 5.6 weeks in ATLAS-2M). Adverse reactions included those attributable to both the oral and injectable formulations of cabotegravir and rilpivirine administered as a combination regimen. Refer to the prescribing information for EDURANT (rilpivirine) for other adverse reactions associated with oral rilpivirine.
The most common adverse reactions regardless of severity reported in ≥2% of adult participants from FLAIR and ATLAS at Week 48 are presented in
In the extension phase of the FLAIR study at Week 124, the overall safety profile was consistent with that observed at Week 48 and when injection therapy with CABENUVA was initiated directly without the oral lead-in phase.
Overall, 4% of participants in the group receiving CABENUVA and 2% of participants in the control group in FLAIR and ATLAS discontinued due to adverse events. Non-injection-site-related adverse events leading to discontinuation and occurring in more than 1 participant were headache, diarrhea, hepatitis A, and acute hepatitis B (all with an incidence <1%). In ATLAS-2M, 2% of participants in both treatment groups discontinued due to adverse events. Non-injection-site–related adverse events leading to discontinuation and occurring in more than 1 participant in ATLAS-2M were fatigue, pyrexia, headache, presyncope, acute hepatitis B, hyperhidrosis, and abnormal dreams that occurred with an incidence of ≤1% in either treatment group.
In ATLAS-2M, the type and frequency of adverse reactions reported in participants receiving CABENUVA once monthly or CABENUVA once every 2 months for 48 weeks were similar. Differences between treatment arms were reported for the types of injection-associated adverse reactions (see Injection-Associated Adverse Reactions for additional information).
Injection-Associated Adverse Reactions: Local Injection Site Reactions (ISRs): In the 3 Phase 3 studies, FLAIR, ATLAS, and ATLAS‑2M, the most frequent adverse reactions associated with the intramuscular administration of CABENUVA were ISRs.
In the pooled analysis of FLAIR and ATLAS, 83% of participants reported any injection site reaction with the monthly dosing regimen, with 1% of participants who discontinued treatment with CABENUVA because of ISRs. After 14,682 injections, 3,663 ISRs were reported. The severity of ISRs was generally mild (Grade 1: 75% of participants) or moderate (Grade 2: 36% of participants). Four percent (4%) of participants experienced severe (Grade 3) ISRs, and no participant experienced Grade 4 ISRs. The median duration of overall ISR events was 3 days. The most commonly reported ISR in FLAIR and ATLAS was pain/discomfort, with 79% reported in the group receiving CABENUVA.
In ATLAS-2M, 75% of participants reported any injection site reaction in both the monthly and every‑2‑month dosing regimens, with <1% of participants who discontinued treatment with CABENUVA because of ISRs. When dosing monthly, after 15,711 injections, 3,152 ISRs were reported. When dosing every 2 months, after 8,470 injections, 2,507 ISRs were reported. The severity of ISRs was generally mild (Grade 1: 70% and 71% of participants) or moderate (Grade 2: 28% and 27% of participants) in monthly and every‑2‑month dosing regimens, respectively. Four percent (4%) of participants in the monthly group and 3% of participants in the every‑2‑month group experienced severe (Grade 3) ISRs, and no participant experienced Grade 4 ISRs. The median duration of overall ISR events was 3 days for both dosing regimens. The most commonly reported ISR in ATLAS‑2M was pain/discomfort, with 71% and 73% reported in the monthly and every‑2‑month dosing regimens, respectively. The severity and duration of ISRs, including pain/discomfort, were similar for both dosing regimens and in participants without prior exposure to CABENUVA.
The most commonly reported ISR (Grades 1 to 3) in at least 1% of adult participants in the pooled analyses from FLAIR and ATLAS, and from ATLAS‑2M, are presented in
Other Injection-Associated Adverse Reactions: In the ATLAS and FLAIR clinical trials, an increased incidence of pyrexia (8%) was reported by participants receiving cabotegravir plus rilpivirine injections compared with no events among participants receiving current antiretroviral regimen. In ATLAS and FLAIR, no cases were serious or led to withdrawal and the occurrences of pyrexia may represent a response to administration of CABENUVA via intramuscular injection. In ATLAS-2M, 1 participant in each arm reported pyrexia that led to withdrawal.
In ATLAS and FLAIR, reports of musculoskeletal pain (3%) and less frequently, sciatica, were also more common in participants receiving cabotegravir plus rilpivirine compared with the current antiretroviral regimen and some events had a temporal association with injection.
Vasovagal or pre-syncopal reactions were reported in <1% of participants after injection with rilpivirine or cabotegravir.
Less Common Adverse Reactions: The following select adverse reactions (regardless of severity) occurred in <2% of participants receiving cabotegravir plus rilpivirine.
Gastrointestinal Disorders: Abdominal pain (including upper abdominal pain), gastritis, dyspepsia, vomiting, diarrhea, and flatulence.
Hepatobiliary Disorders: Hepatotoxicity.
Investigations: Weight increase (see below).
Psychiatric Disorders: Anxiety (including anxiety and irritability), depression, abnormal dreams, suicidal ideation, and suicide attempt (these events were observed primarily in participants with a pre-existing history of depression or other psychiatric illness).
Skin and Hypersensitivity Reactions: Hypersensitivity reactions.
Weight Increase: At Week 48, participants in FLAIR and ATLAS who received cabotegravir plus rilpivirine had a median weight gain of 1.5 kg; those in the current antiretroviral regimen group had a median weight gain of 1.0 kg (pooled analysis). In the FLAIR trial, the median weight gain in participants receiving cabotegravir plus rilpivirine or a dolutegravir-containing regimen was 1.3 kg and 1.5 kg, respectively, compared with 1.8 kg and 0.3 kg, respectively, in the ATLAS trial in participants receiving either cabotegravir plus rilpivirine or a protease inhibitor-, non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI)-, or integrase strand transfer inhibitor (INSTI)-containing regimen, respectively. At Week 48, participants in ATLAS-2M who received cabotegravir plus rilpivirine in both the monthly and every-2-month treatment arms had a median weight gain of 1.0 kg.
Laboratory Abnormalities: Selected laboratory abnormalities with a worsening grade from baseline and representing the worst-grade toxicity are presented in Table 7. The side-by-side tabulation is to simplify presentation; direct comparison across trials should not be made due to differing trials.
Changes in Total Bilirubin: Small, non-progressive increases in total bilirubin (without clinical jaundice) were observed with cabotegravir plus rilpivirine. These changes are not considered clinically relevant as they likely reflect competition between cabotegravir and unconjugated bilirubin for a common clearance pathway (UGT1A1) [see Clinical Pharmacology (
Serum Cortisol: In pooled Phase 3 trials of EDURANT (rilpivirine), the overall mean change from baseline in basal cortisol was -0.69 (-1.12, 0.27) mcg/dL in the group receiving EDURANT compared with -0.02 (-0.48, 0.44) mcg/dL in the control group. Abnormal responses to ACTH stimulation tests were also higher in the group receiving EDURANT. The clinical significance of the higher abnormal rate of ACTH stimulation tests in the group receiving EDURANT is not known. Refer to the prescribing information for EDURANT for additional information.
Clinical Trial Experience in Adolescents
Based on data from the Week 16 (cohort 1) and Week 24 (cohort 2) analyses of the MOCHA study, the safety profile in adolescents (aged 12 to younger than 18 years and weighing ≥35 kg) was consistent with the safety profile established with cabotegravir plus rilpivirine in adults
In cohort 1, 55 virologically suppressed adolescents with HIV-1 received background antiretroviral therapy in addition to either oral cabotegravir (n = 30) followed by injectable cabotegravir (n = 29), or oral rilpivirine (n = 25) followed by injectable rilpivirine (n = 23). Adverse reactions were reported in 38% of adolescents receiving either cabotegravir or rilpivirine. Thirty-three percent of participants reported at least 1 ISR. All ISRs were Grade 1 or Grade 2. Two participants had Grade 3 adverse reactions of hypersensitivity (n = 1, oral rilpivirine) and insomnia (n = 1, injectable cabotegravir). The Grade 3 adverse reaction of drug hypersensitivity led to discontinuation of rilpivirine during oral lead-in. The adverse reactions reported by more than one participant (regardless of severity) were injection site pain (n = 18), headache (n = 2), hypersensitivity (n = 2), insomnia (n = 2), and nausea (n = 2).
In cohort 2, 144 virologically suppressed adolescents with HIV-1 received oral cabotegravir plus oral rilpivirine followed by injectable cabotegravir plus injectable rilpivirine. Adverse reactions were reported in 35% of adolescents receiving cabotegravir plus rilpivirine. Thirty-four percent of participants reported at least 1 ISR. The majority of these participants experienced Grade 1 or Grade 2 ISRs. Two participants had Grade 3 ISRs consisting of injection site abscess (n = 2) and injection site pain in one of these two participants (symptoms resolved in both participants). All non-ISR adverse reactions were ≤ Grade 2. Non-injection-site associated adverse reactions reported by more than one participant (regardless of severity) were headache (n = 3), nausea (n = 2), rash (n = 2) and rash pruritic (n = 2).
4.2Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during postmarketing experience in patients receiving cabotegravir- or oral-rilpivirine-containing regimens. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Immune System Disorders
Hypersensitivity reactions (including angioedema and urticaria)
Renal and Genitourinary Disorders
Nephrotic syndrome.
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders
Severe skin and hypersensitivity reactions, including DRESS, Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS)/toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN)
5OVERDOSAGE
There is no known specific treatment for overdose with cabotegravir or rilpivirine. If overdose occurs, monitor the patient and apply standard supportive treatment as required, including monitoring of vital signs and ECG (QT interval) as well as observation of the clinical status of the patient. As both cabotegravir and rilpivirine are highly bound to plasma proteins, it is unlikely that either would be significantly removed by dialysis. Consider the prolonged exposure to cabotegravir and rilpivirine (components of CABENUVA) following an injection when assessing treatment needs and recovery
6DESCRIPTION
CABENUVA contains cabotegravir extended-release injectable suspension, an HIV INSTI, co-packaged with rilpivirine extended-release injectable suspension, an HIV NNRTI.
Cabotegravir
The chemical name for cabotegravir is (
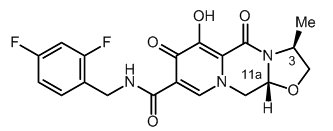
Cabotegravir extended-release injectable suspension is a white to light pink free-flowing suspension for intramuscular injection in a sterile single-dose vial. Each vial contains 2 mL or 3 mL of the following: cabotegravir 200 mg/mL and the inactive ingredients mannitol (35 mg/mL), polyethylene glycol (PEG) 3350 (20 mg/mL), polysorbate 20 (20 mg/mL), and Water for Injection.
The vial stoppers are not made with natural rubber latex.
Rilpivirine
The chemical name for rilpivirine is 4-[[4-[[4-[(E)-2-cyanoethenyl]-2,6-dimethylphenyl]amino]-2-pyrimidinyl]amino]benzonitrile. Its molecular formula is C
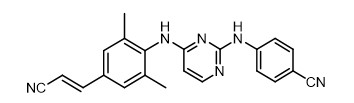
Rilpivirine extended-release injectable suspension is a white to off-white suspension for intramuscular injection. Each sterile single-dose vial contains 2 mL or 3 mL of the following: rilpivirine 300 mg/mL and the following inactive ingredients: citric acid monohydrate (1 mg/mL), dextrose to ensure isotonicity, monobasic sodium phosphate (1.74 mg/mL), poloxamer 338 (50 mg/mL), sodium hydroxide to adjust pH, and Water for Injection.
The vial stoppers are not made with natural rubber latex.
7HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
How Supplied
CABENUVA is supplied in 2 dosing kits. Each kit contains 1 vial of cabotegravir extended‑release injectable suspension and 1 vial of rilpivirine extended-release injectable suspension, co‑packaged as follows:
CABENUVA 400-mg/600-mg Kit (NDC 49702-253-15) containing:
- One single-dose vial of cabotegravir extended-release injectable suspension containing 400 mg/2 mL (200 mg/mL) of cabotegravir.
- One single-dose vial of rilpivirine extended-release injectable suspension containing 600 mg/2 mL (300 mg/mL) of rilpivirine
CABENUVA 600-mg/900-mg Kit (NDC 49702-240-15) containing:
- One single-dose vial of cabotegravir extended-release injectable suspension containing 600 mg/3 mL (200 mg/mL) of cabotegravir.
- One single-dose vial of rilpivirine extended-release injectable suspension containing 900 mg/3 mL (300 mg/mL) of rilpivirine.
Each dosing kit also contains 2 syringes, 2 syringe labels, 2 vial adapters, and 2 needles for intramuscular injection (23-gauge, 1½ inch). The vial stoppers are not made with natural rubber latex.
Storage and Handling
Store CABENUVA in the refrigerator at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) in the original carton until ready to use. Do not freeze. Do not mix with any other product or diluent.
Prior to administration, vials should be brought to room temperature (not to exceed 25°C [77°F]). Vials may remain in the carton at room temperature for up to 6 hours; do not put back into the refrigerator. If not used within 6 hours, they must be discarded.
Once the suspensions have been drawn into the respective syringes, the injections should be administered as soon as possible, but may remain in the syringes for up to 2 hours. The filled syringes should not be placed in the refrigerator. If the medicines remain in the syringes for more than 2 hours, the filled syringes and needles must be discarded
8PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
Hypersensitivity Reactions
Advise patients to immediately contact their healthcare provider if they develop a rash. Instruct patients to immediately stop taking CABENUVA and seek medical attention if they develop a rash associated with any of the following symptoms, as it may be a sign of a more serious reaction such as Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS)/toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) or drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS): fever; generally ill feeling; extreme tiredness; muscle or joint aches; blisters; oral blisters or lesions; eye inflammation; facial swelling; swelling of the eyes, lips, tongue, or mouth; difficulty breathing; and/or signs and symptoms of liver problems (e.g., yellowing of the skin or whites of the eyes; dark or tea-colored urine; pale-colored stools or bowel movements; nausea; vomiting; loss of appetite; or pain, aching, or sensitivity on the right side below the ribs). Advise patients that if hypersensitivity occurs, they will be closely monitored, laboratory tests will be ordered, and appropriate therapy will be initiated
Adverse Reactions Following Injections
Advise patients that injection site reactions have been reported in the majority of patients receiving CABENUVA. These local reactions typically consist of one or more of the following: pain, erythema, tenderness, pruritus, and local swelling. Systemic reactions have also been reported, such as fever, musculoskeletal pain, and sciatica pain
Hepatotoxicity
Inform patients that hepatotoxicity has been reported with cabotegravir and rilpivirine, components of CABENUVA
Depressive Disorders
Inform patients that depressive disorders (including depressed mood, depression, major depression, mood altered, mood swings, unusual mood, negative thoughts, suicidal ideation, suicide attempt) have been reported with at least one of the components of CABENUVA. Advise patients to seek prompt medical evaluation if they experience depressive symptoms
Drug Interactions
Inform patients that CABENUVA may interact with other drugs; therefore, advise patients to report to their healthcare provider the use of any other prescription or nonprescription medication or herbal products, including St. John’s wort. CABENUVA is an extended-release injectable that may be systemically present for 12 months or longer. These residual concentrations are not expected to affect the exposures of antiretroviral drugs that are initiated after discontinuation of CABENUVA
Adherence to CABENUVA
Counsel patients about the importance of continued medication adherence and scheduled visits to help maintain viral suppression and to reduce risk of loss of virologic response and development of resistance
Two Options for Dosing Frequency
Advise the patient that CABENUVA can be injected monthly or every 2 months after oral lead‑in with cabotegravir and rilpivirine to assess tolerability. Discuss the two injection dosing frequency options with the patient prior to starting CABENUVA and decide which injection dosing frequency would be the most appropriate option for the patient
Missed Dose
Inform patients that CABENUVA can remain in the body for up to 12 months or longer after receiving their last injection. Advise patients that they should contact their healthcare provider if they miss or plan to miss a scheduled injection visit and that oral therapy with VOCABRIA and EDURANT may be used up to 2 months to replace missed injection visits, or any other fully suppressive oral antiretroviral regimen may be used until injections are resumed. Advise patients that if they stop treatment with CABENUVA, they will need to take other medicines to treat their HIV-1 infection
Pregnancy Registry
Inform patients that there is an antiretroviral pregnancy registry to monitor fetal outcomes in those exposed to CABENUVA during pregnancy. Patients who are of reproductive potential should be informed of the long duration of exposure of CABENUVA and that there is very limited clinical experience in human pregnancy
Lactation
Inform individuals with HIV-1 infection that the potential risks of breastfeeding include: (1) HIV-1 transmission (in HIV-1–negative infants), (2) developing viral resistance (in HIV-1–positive infants), and (3) adverse reactions in a breastfed infant similar to those seen in adults
CABENUVA and VOCABRIA are trademarks owned by or licensed to the ViiV Healthcare group of companies.
The other brand listed is a trademark owned by or licensed to its respective owner and is not a trademark owned by or licensed to the ViiV Healthcare group of companies. The maker of this brand is not affiliated with and does not endorse the ViiV Healthcare group of companies or its products.
Manufactured for:
ViiV Healthcare
Durham, NC 27701
©2025 ViiV Healthcare group of companies or its licensor.
CBN:11PI
9Package/Label Display Panel
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC 49702-266-63
CABENUVA
Cabotegravir extended-release
injectable suspension
600 mg/3 mL
(200 mg/mL)
co-packaged with
Rilpivirine extended-release
injectable suspension
900 mg/3 mL
(300 mg/mL)
Rx Only
Sample-Not for Sale
ViiV Healthcare
For gluteal intramuscular use only.
Healthcare Professional administration only.
Contents:
- 1 Cabotegravir single-dose vial
- 1 Rilpivirine single-dose vial
- 2 Vial adapters
- 2 Syringes
- 2 Injection needles (23 gauge, 1 ½ inch)
- 2 Syringe labels
- Prescribing Information
- Patient Information
- Instructions for Use
Store in refrigerator at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F).
Do not freeze.
Discard unused portion.
Prior to administration, bring vials to room temperature (not to exceed 25°C (77°F). Vials may remain at room temperature for up to 6 hours. If not used within 6 hours, they must be discarded. Ensure vial adapter is used correctly.
600 mg/900 mg Kit
Cabotegravir – Made in Singapore and Belgium
Rilpivirine – Made in Belgium and Ireland
©2025 ViiV Healthcare group of companies or its licensor.
- Rev. 5/25
MCK-162620-01
