Brand Name
Klonopin
Generic Name
ClonazePAM
View Brand Information FDA approval date: June 02, 1975
Classification: Benzodiazepine
Form: Tablet
What is Klonopin (ClonazePAM)?
Seizure Disorders: Clonazepam is useful alone or as an adjunct in the treatment of the Lennox-Gastaut syndrome , akinetic and myoclonic seizures. In patients with absence seizures who have failed to respond to succinimides, clonazepam may be useful. In some studies, up to 30% of patients have shown a loss of anticonvulsant activity, often within 3 months of administration. In some cases, dosage adjustment may re-establish efficacy. Panic Disorder: Clonazepam is indicated for the treatment of panic disorder, with or without agoraphobia, as defined in DSM-V. Panic disorder is characterized by the occurrence of unexpected panic attacks and associated concern about having additional attacks, worry about the implications or consequences of the attacks, and/or a significant change in behavior related to the attacks. The efficacy of clonazepam was established in two 6- to 9-week trials in panic disorder patients whose diagnoses corresponded to the DSM-IIIR category of panic disorder. Panic disorder is characterized by recurrent unexpected panic attacks, i.e., a discrete period of intense fear or discomfort in which four of the following symptoms develop abruptly and reach a peak within 10 minutes: palpitations, pounding heart or accelerated heart rate; sweating; trembling or shaking; sensations of shortness of breath or smothering; feeling of choking; chest pain or discomfort; nausea or abdominal distress; feeling dizzy, unsteady, lightheaded or faint; derealization or depersonalization ; fear of losing control; fear of dying; paresthesias ; chills or hot flushes. The effectiveness of clonazepam in long-term use, that is, for more than 9 weeks, has not been systematically studied in controlled clinical trials. The physician who elects to use clonazepam for extended periods should periodically re-evaluate the long-term usefulness of the drug for the individual patient.
Approved To Treat
Top Global Experts
There are no experts for this drug
Save this treatment for later
Not sure about your diagnosis?
Related Clinical Trials
There is no clinical trials being done for this treatment
Related Latest Advances
There is no latest advances for this treatment
Brand Information
Klonopin (Clonazepam)
WARNING: RISKS FROM CONCOMITANT USE WITH OPIOIDS; ABUSE, MISUSE, AND ADDICTION; and DEPENDENCE AND WITHDRAWAL REACTIONS
- Concomitant use of benzodiazepines and opioids may result in profound sedation, respiratory depression, coma, and death. Reserve concomitant prescribing of these drugs for patients for whom alternative treatment options are inadequate. Limit dosages and durations to the minimum required. Follow patients for signs and symptoms of respiratory depression and sedation (see
- The use of benzodiazepines, including Klonopin, exposes users to risks of abuse, misuse, and addiction, which can lead to overdose or death. Abuse and misuse of benzodiazepines commonly involve concomitant use of other medications, alcohol, and/or illicit substances, which is associated with an increased frequency of serious adverse outcomes. Before prescribing Klonopin and throughout treatment, assess each patient's risk for abuse, misuse, and addiction (see
- The continued use of benzodiazepines, including Klonopin, may lead to clinically significant physical dependence. The risks of dependence and withdrawal increase with longer treatment duration and higher daily dose. Abrupt discontinuation or rapid dosage reduction of Klonopin after continued use may precipitate acute withdrawal reactions, which can be life-threatening. To reduce the risk of withdrawal reactions, use a gradual taper to discontinue Klonopin or reduce the dosage (see
1DESCRIPTION
Klonopin, a benzodiazepine, is available as scored tablets with a K-shaped perforation containing 0.5 mg of clonazepam and unscored tablets with a K-shaped perforation containing 1 mg or 2 mg of clonazepam. Each tablet also contains lactose, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose and corn starch, with the following colorants: 0.5 mg—FD&C Yellow No. 6 Lake; 1 mg—FD&C Blue No. 1 Lake and FD&C Blue No. 2 Lake.
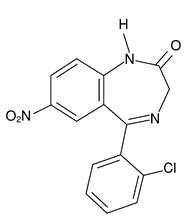
Chemically, clonazepam is 5-(2-chlorophenyl)-1,3-dihydro-7-nitro-2
2CONTRAINDICATIONS
Klonopin is contraindicated in patients with the following conditions:
- History of sensitivity to benzodiazepines
- Clinical or biochemical evidence of significant liver disease
- Acute narrow angle glaucoma (it may be used in patients with open angle glaucoma who are receiving appropriate therapy).
3ADVERSE REACTIONS
The adverse experiences for Klonopin are provided separately for patients with seizure disorders and with panic disorder.
3.1Seizure Disorders
The most frequently occurring side effects of Klonopin are referable to CNS depression. Experience in treatment of seizures has shown that drowsiness has occurred in approximately 50% of patients and ataxia in approximately 30%. In some cases, these may diminish with time; behavior problems have been noted in approximately 25% of patients. Others, listed by system, including those identified during postapproval use of Klonopin are:
Cardiovascular: Palpitations
Dermatologic: Hair loss, hirsutism, skin rash, ankle and facial edema
Gastrointestinal: Anorexia, coated tongue, constipation, diarrhea, dry mouth, encopresis, gastritis, increased appetite, nausea, sore gums
Genitourinary: Dysuria, enuresis, nocturia, urinary retention
Hematopoietic: Anemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, eosinophilia
Hepatic: Hepatomegaly, transient elevations of serum transaminases and alkaline phosphatase
Musculoskeletal: Muscle weakness, pains
Miscellaneous: Dehydration, general deterioration, fever, lymphadenopathy, weight loss or gain
Neurologic: Abnormal eye movements, aphonia, choreiform movements, coma, diplopia, dysarthria, dysdiadochokinesis, ''glassy-eyed'' appearance, headache, hemiparesis, hypotonia, nystagmus, respiratory depression, slurred speech, tremor, vertigo
Psychiatric: Confusion, depression, amnesia, hysteria, increased libido, insomnia, psychosis (the behavior effects are more likely to occur in patients with a history of psychiatric disturbances).
The following paradoxical reactions have been observed: irritability, aggression, agitation, nervousness, hostility, anxiety, sleep disturbances, nightmares, abnormal dreams, hallucinations.
Respiratory: Chest congestion, rhinorrhea, shortness of breath, hypersecretion in upper respiratory passages
3.2Panic Disorder
Adverse events during exposure to Klonopin were obtained by spontaneous report and recorded by clinical investigators using terminology of their own choosing. Consequently, it is not possible to provide a meaningful estimate of the proportion of individuals experiencing adverse events without first grouping similar types of events into a smaller number of standardized event categories. In the tables and tabulations that follow, CIGY dictionary terminology has been used to classify reported adverse events, except in certain cases in which redundant terms were collapsed into more meaningful terms, as noted below.
The stated frequencies of adverse events represent the proportion of individuals who experienced, at least once, a treatment-emergent adverse event of the type listed. An event was considered treatment-emergent if it occurred for the first time or worsened while receiving therapy following baseline evaluation.
4OVERDOSAGE
Overdosage of benzodiazepines is characterized by central nervous system depression ranging from drowsiness to coma. In mild to moderate cases, symptoms can include drowsiness, confusion, dysarthria, lethargy, hypnotic state, diminished reflexes, ataxia, and hypotonia. Rarely, paradoxical or disinhibitory reactions (including agitation, irritability, impulsivity, violent behavior, confusion, restlessness, excitement, and talkativeness) may occur. In severe overdosage cases, patients may develop respiratory depression and coma. Overdosage of benzodiazepines in combination with other CNS depressants (including alcohol and opioids) may be fatal (see
In managing benzodiazepine overdosage, employ general supportive measures, including intravenous fluids and airway maintenance. Flumazenil, a specific benzodiazepine receptor antagonist indicated for the complete or partial reversal of the sedative effects of benzodiazepines in the management of benzodiazepine overdosage, can lead to withdrawal and adverse reactions, including seizures, particularly in the context of mixed overdosage with drugs that increase seizure risk (e.g., tricyclic and tetracyclic antidepressants) and in patients with long-term benzodiazepine use and physical dependency. The risk of withdrawal seizures with flumazenil use may be increased in patients with epilepsy. Flumazenil is contraindicated in patients who have received a benzodiazepine for control of a potentially life-threatening condition (e.g., status epilepticus). If the decision is made to use flumazenil, it should be used as an adjunct to, not as a substitute for, supportive management of benzodiazepine overdosage. See the flumazenil injection Prescribing Information.
Consider contacting the Poison Help line (1-800-222-1222) or a medical toxicologist for additional overdosage management recommendations.
5DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Clonazepam is available as a tablet. The tablets should be administered with water by swallowing the tablet whole.
5.1Seizure Disorders
The use of multiple anticonvulsants may result in an increase of CNS depressant adverse effects. This should be considered before adding Klonopin to an existing anticonvulsant regimen.
5.1.1Adults
The initial dose for adults with seizure disorders should not exceed 1.5 mg/day divided into three doses. Dosage may be increased in increments of 0.5 to 1 mg every 3 days until seizures are adequately controlled or until side effects preclude any further increase. Maintenance dosage must be individualized for each patient depending upon response. Maximum recommended daily dose is 20 mg.
5.1.2Pediatric Patients
Klonopin is administered orally. In order to minimize drowsiness, the initial dose for infants and children (up to 10 years of age or 30 kg of body weight) should be between 0.01 and 0.03 mg/kg/day but not to exceed 0.05 mg/kg/day given in two or three divided doses. Dosage should be increased by no more than 0.25 to 0.5 mg every third day until a daily maintenance dose of 0.1 to 0.2 mg/kg of body weight has been reached, unless seizures are controlled or side effects preclude further increase. Whenever possible, the daily dose should be divided into three equal doses. If doses are not equally divided, the largest dose should be given before retiring.
5.1.3Geriatric Patients
There is no clinical trial experience with Klonopin in seizure disorder patients 65 years of age and older. In general, elderly patients should be started on low doses of Klonopin and observed closely (see
5.2Discontinuation or Dosage Reduction of KLONOPIN
To reduce the risk of withdrawal reactions, increased seizure frequency, and status epilepticus, use a gradual taper to discontinue Klonopin or reduce the dosage. If a patient develops withdrawal reactions, consider pausing the taper or increasing the dosage to the previous tapered dosage level. Subsequently decrease the dosage more slowly (see
6HOW SUPPLIED
Klonopin tablets are available as scored tablets with a K-shaped perforation—0.5 mg, orange (NDC 61269-605-10); and unscored tablets with a K-shaped perforation—1 mg, blue (NDC 61269-610-10); 2 mg, white (NDC 61269-620-10)—bottles of 100.
Imprint on tablets:
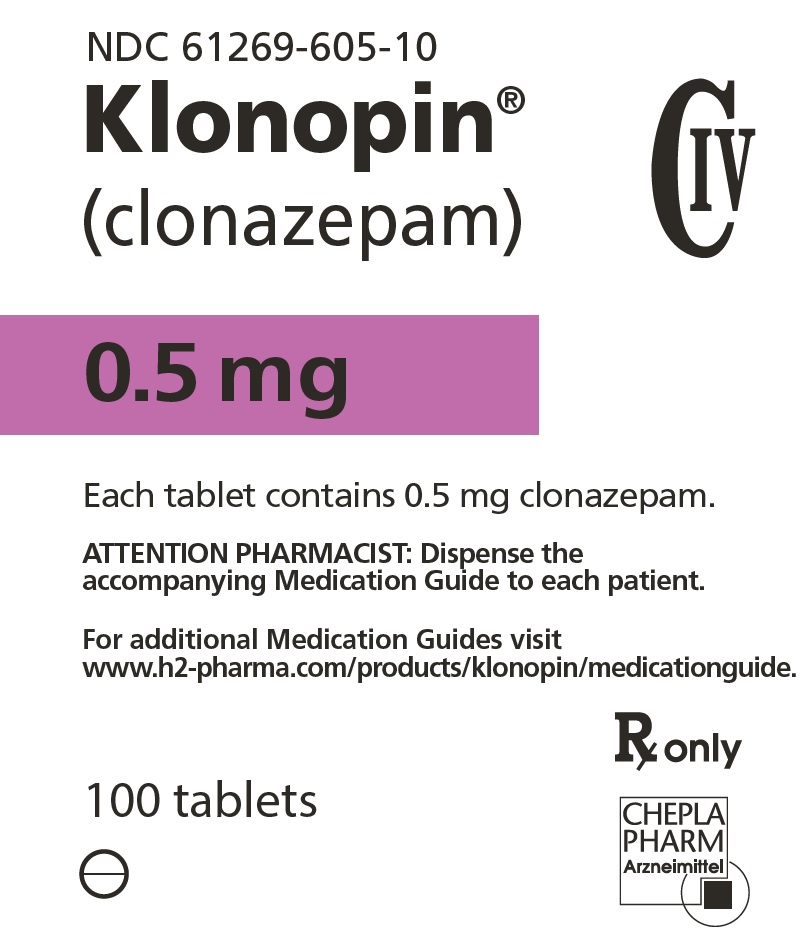
7PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 0.5 mg Tablet Bottle Label
NDC 61269-605-10
Klonopin
0.5 mg
Each tablet contains 0.5 mg clonazepam.
ATTENTION PHARMACIST: Dispense the
For additional Medication Guides visit
www.h2-pharma.com/products/klonopin/medicationguide.
100 tablets
Rx only
CHEPLAPHARM Arzneimittel
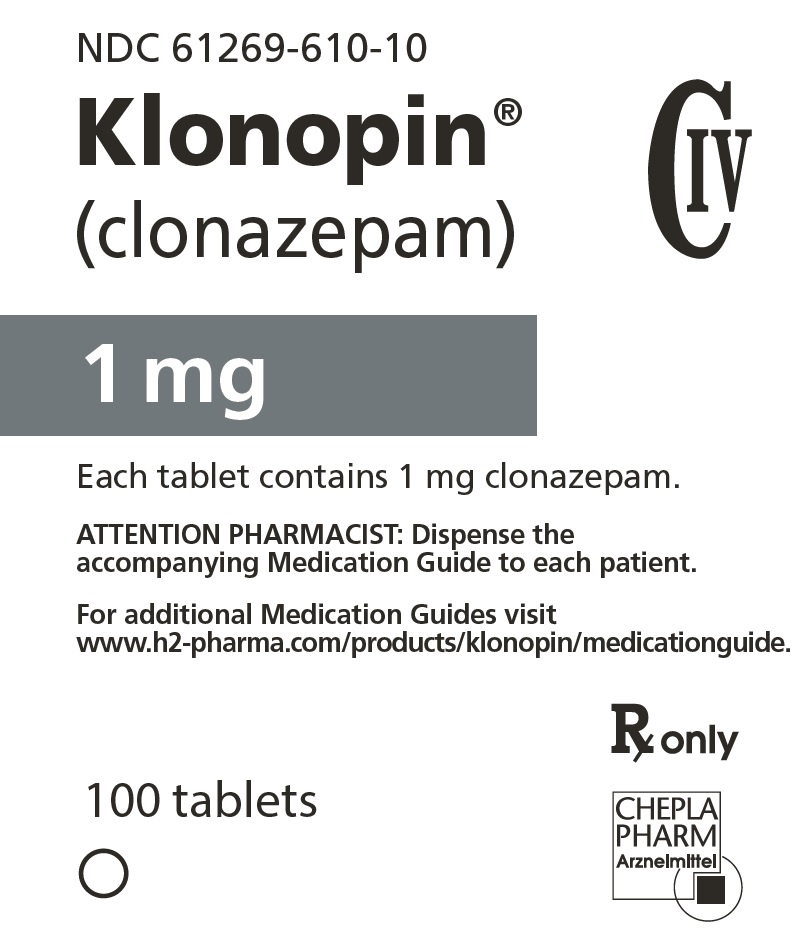
8PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 1 mg Tablet Bottle Label
NDC 61269-610-10
Klonopin
1 mg
Each tablet contains 1 mg clonazepam.
ATTENTION PHARMACIST: Dispense the
For additional Medication Guides visit
www.h2-pharma.com/products/klonopin/medicationguide.
100 tablets
Rx only
CHEPLAPHARM Arzneimittel
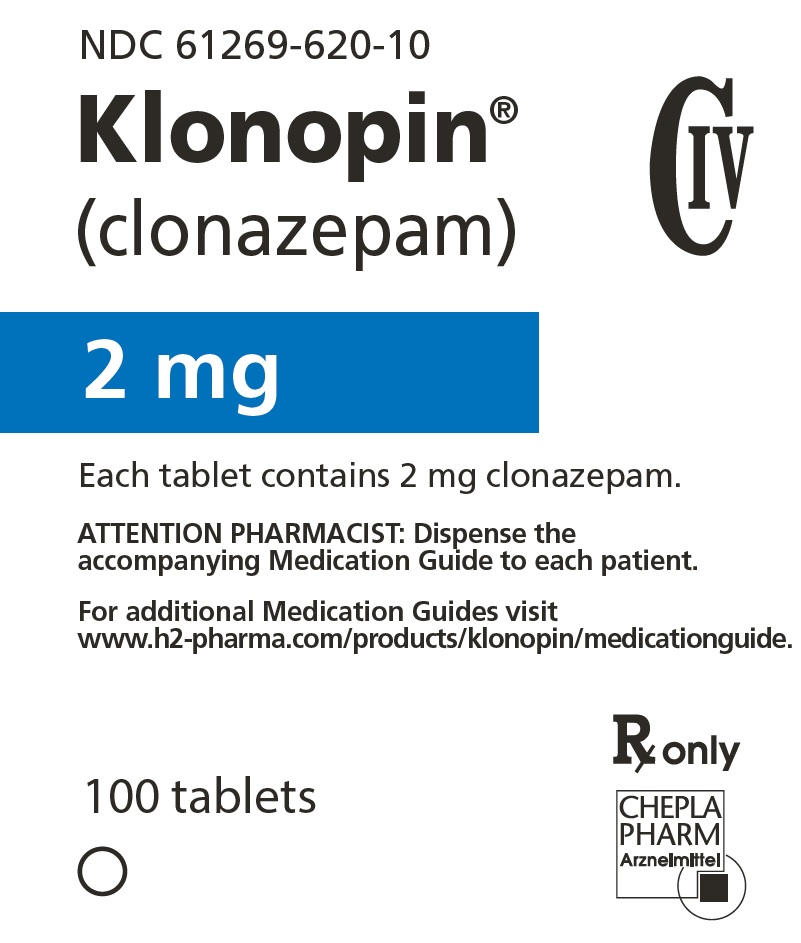
9PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 2 mg Tablet Bottle Label
NDC 61269-620-10
Klonopin
2 mg
Each tablet contains 2 mg clonazepam.
ATTENTION PHARMACIST: Dispense the
For additional Medication Guides visit
www.h2-pharma.com/products/klonopin/medicationguide.
100 tablets
Rx only
CHEPLAPHARM Arzneimittel