Brand Name
Tigan
Generic Name
Trimethobenzamide
View Brand Information FDA approval date: August 01, 2008
Classification: Antiemetic
Form: Injection, Capsule
What is Tigan (Trimethobenzamide)?
Trimethobenzamide hydrochloride capsules are indicated in adults for the treatment of postoperative nausea and vomiting and for nausea associated with gastroenteritis. Limitation of Use: Trimethobenzamide hydrochloride capsules are not recommended for use in pediatric patients due to the risk of extrapyramidal signs and symptoms and other serious central nervous system effects, and the risk of exacerbation of the underlying disease in pediatric patients with Reye’s syndrome or other hepatic impairment. Trimethobenzamide hydrochloride capsules are an antiemetic indicated in adults for the treatment of postoperative nausea and vomiting and for nausea associated with gastroenteritis. Limitation of Use: Trimethobenzamide hydrochloride capsule is not recommended for use in pediatric patients due to the risk of extrapyramidal signs and symptoms and other serious central nervous system effects and the risk of exacerbation of the underlying disease in pediatric patients with Reye’s syndrome or other hepatic impairment. ( 1.
Approved To Treat
Top Global Experts
There are no experts for this drug
Save this treatment for later
Not sure about your diagnosis?
Related Clinical Trials
There is no clinical trials being done for this treatment
Related Latest Advances
Brand Information
Tigan (Trimethobenzamide Hydrochloride)
1Description
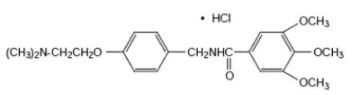
Chemically, trimethobenzamide (HCl) is N-[
Single Dose Vials: Each 2-mL single-dose vial contains 200 mg trimethobenzamide hydrochloride compounded with 1 mg sodium citrate and 0.4 mg citric acid as buffers and pH adjusted to approximately 5.0 with sodium hydroxide.
Multi-Dose Vials: Each mL contains 100 mg trimethobenzamide hydrochloride compounded with 0.45% phenol as preservative, 0.5 mg sodium citrate and 0.2 mg citric acid as buffers and pH adjusted to approximately 5.0 with sodium hydroxide.
2Clinical Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
The mechanism of action of
Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics of trimethobenzamide have been studied in healthy adult subjects. Following administration of 200 mg
Special Populations
Age
The clearance of trimethobenzamide is not known in patients with renal impairment. However, it may be advisable to consider
reduction in the dosing of trimethobenzamide in elderly patients with renal impairment considering that a substantial amount of
excretion and elimination of trimethobenzamide occurs via the kidney and that elderly patients may have various degrees of renal
impairment. (See PRECAUTIONS: General and DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
The clearance of trimethobenzamide is not known in patients with renal impairment. However, it may be advisable to consider
reduction in the dosing of trimethobenzamide in elderly patients with renal impairment considering that a substantial amount of
excretion and elimination of trimethobenzamide occurs via the kidney and that elderly patients may have various degrees of renal
impairment. (See PRECAUTIONS: General and DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
Gender
Systemic exposure to trimethobenzamide was similar between men (N=40) and women (N=28).
Systemic exposure to trimethobenzamide was similar between men (N=40) and women (N=28).
Race
Pharmacokinetics appeared to be similar for Caucasians (N=53) and African Americans (N=12).
Pharmacokinetics appeared to be similar for Caucasians (N=53) and African Americans (N=12).
Renal Impairment
The clearance of trimethobenzamide is not known in patients with renal impairment. However, it may be advisable to consider
reduction in the dosing of trimethobenzamide in patients with renal impairment considering that a substantial amount of
excretion and elimination of trimethobenzamide occurs via the kidney. (See PRECAUTIONS: General and DOSAGE AND
ADMINISTRATION).
The clearance of trimethobenzamide is not known in patients with renal impairment. However, it may be advisable to consider
reduction in the dosing of trimethobenzamide in patients with renal impairment considering that a substantial amount of
excretion and elimination of trimethobenzamide occurs via the kidney. (See PRECAUTIONS: General and DOSAGE AND
ADMINISTRATION).
3Indications
Tigan® is indicated for the treatment of postoperative nausea and vomiting and for nausea associated with gastroenteritis.
4Contraindications
The injectable form of
5Contraindications
The injectable form of
6Warnings
Tigan® may produce drowsiness. Patients should not operate motor vehicles or other dangerous machinery until their individual
responses have been determined.
responses have been determined.
Usage in Pregnancy:
Trimethobenzamide hydrochloride was studied in reproduction experiments in rats and rabbits and no teratogenicity was suggested.
The only effects observed were an increased percentage of embryonic resorptions or stillborn pups in rats administered 20 mg and
100 mg/kg and increased resorptions in rabbits receiving 100 mg/kg. In each study these adverse effects were attributed to one or
two dams. The relevance to humans is not known. Since there is no adequate experience in pregnant or lactating women who have
received this drug, safety in pregnancy or in nursing mothers has not been established.
Trimethobenzamide hydrochloride was studied in reproduction experiments in rats and rabbits and no teratogenicity was suggested.
The only effects observed were an increased percentage of embryonic resorptions or stillborn pups in rats administered 20 mg and
100 mg/kg and increased resorptions in rabbits receiving 100 mg/kg. In each study these adverse effects were attributed to one or
two dams. The relevance to humans is not known. Since there is no adequate experience in pregnant or lactating women who have
received this drug, safety in pregnancy or in nursing mothers has not been established.
Usage with Alcohol:
Concomitant use of alcohol with Tigan® may result in an adverse drug interaction.
Concomitant use of alcohol with Tigan® may result in an adverse drug interaction.
7Precautions
During the course of acute febrile illness, encephalitides, gastroenteritis, dehydration and electrolyte imbalance, especially in
General
Adjustment of Dose in Renal Failure
A substantial route of elimination of unchanged trimethobenzamide is via the kidney. Dosage adjustment should be considered in
Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of trimethobenzamide hydrochloride did not include sufficient numbers of patients aged 65 and over to determine
This drug is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of toxic reactions to this drug may be greater in patients
8Adverse Reactions
There have been reports of hypersensitivity reactions and Parkinson-like symptoms. There have been instances of hypotension
For medical advice about adverse reactions contact your medical professional. To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS,
contact Endo at 1-800-828-9393 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 (1-800-332-1088) or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
contact Endo at 1-800-828-9393 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 (1-800-332-1088) or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
9Dosage and Administration
(See
Geriatric Patients
Dose adjustment such as reducing the total dose administered at each dosing or increasing the dosing interval should be considered
Patients with Renal Impairment
In subjects with renal impairment (creatinine clearance ≤ 70 mL/min/1.73m
INJECTABLE, 100 mg/mL (Not for use in pediatric patients)
NOTE: The injectable form is intended for intramuscular administration only; it is not recommended for intravenous use.
Intramuscular administration may cause pain, stinging, burning, redness and swelling at the site of injection. Such effects may be
10Storage
Store between 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F).
11How Supplied
Tigan
NDC 42023-119-25 100 mg/mL in 2 mL Single-Dose Vials,
Pack of 25
Rx Only
Manufactured for:
Endo USA
Malvern, PA 19355
© 2025 Endo, Inc. or one of its affiliates.
R08/2024
OS118J-01-90-04
3000358J
12Sample Package Label
