Aubagio
What is Aubagio (Teriflunomide)?
Living with multiple sclerosis (MS) often means facing unpredictable fatigue, muscle weakness, and changes in coordination that can disrupt everyday life. For many patients, the uncertainty of when the next relapse will occur can be as challenging as the symptoms themselves. Aubagio (teriflunomide) is a treatment designed to help manage that unpredictability reducing relapses and slowing disease progression so patients can maintain stability and independence.
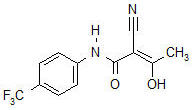
Aubagio is an oral medication used to treat relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis (MS), including clinically isolated syndrome, relapsing-remitting MS, and active secondary progressive MS. It belongs to a class of medications called pyrimidine synthesis inhibitors, which work by controlling certain immune system cells that damage the nervous system. Approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2012, Aubagio is considered a first-line disease-modifying therapy (DMT), meaning it can be started early in treatment to help manage the disease over time.
What does Aubagio do?
Aubagio is prescribed to reduce relapse rates and slow the progression of physical disability in adults with multiple sclerosis. MS is a chronic autoimmune disorder in which the immune system mistakenly attacks the protective covering of nerve fibers, called myelin, in the brain and spinal cord. This leads to communication problems between the brain and the rest of the body.
By modifying immune system activity, Aubagio helps prevent these attacks and protects nerve function. In large clinical studies, patients taking Aubagio experienced fewer relapses and fewer new or enlarging brain lesions compared to those who received a placebo (NIH, 2024). Many people report greater day-to-day stability, fewer hospitalizations, and improved ability to maintain work or family routines.
While Aubagio does not cure MS, it helps patients manage the disease long-term by reducing inflammation and preventing future nerve damage, a key factor in maintaining mobility and quality of life.
How does Aubagio work?
Aubagio works by selectively blocking an enzyme called dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (DHODH), which is essential for rapidly dividing immune cells known as T and B lymphocytes. These cells play a central role in the autoimmune attack that characterizes multiple sclerosis.
By inhibiting DHODH, Aubagio slows the growth of these overactive immune cells, reducing their ability to damage the myelin sheath and nerve fibers in the central nervous system. Unlike broad immunosuppressants, Aubagio does not completely shut down the immune system. It helps rebalance it, targeting only the specific overactive cells while allowing the rest of the immune response to function normally.
Clinically, this mechanism is important because it provides long-term immune regulation with a lower risk of infection than some other immune-modifying treatments. The once-daily oral dosing also makes Aubagio convenient for patients who prefer tablets over injections or infusions.
Aubagio side effects
Like any prescription medication, Aubagio can cause side effects, though many are mild and manageable under a doctor’s supervision.
Common side effects may include:
- Hair thinning or mild hair loss
- Headache
- Nausea or diarrhea
- Increased liver enzymes (seen on blood tests)
- Tingling in hands or feet
Serious side effects (less common):
- Liver problems, which may present as fatigue, yellowing of the skin or eyes (jaundice), or dark urine
- High blood pressure
- Decreased white blood cell count
- Serious skin reactions or allergic responses
- Nerve damage causing persistent numbness or weakness (rare)
Because Aubagio can affect the liver, regular blood tests are required especially in the first six months of treatment to monitor liver function and ensure safety. Patients should contact their doctor immediately if they notice signs of liver distress or allergic reactions.
Avoid Aubagio if you have severe liver disease, are pregnant or planning pregnancy, or are allergic to leflunomide.
Women of childbearing potential need effective contraception during and after treatment. An “accelerated elimination procedure” can quickly remove the drug if pregnancy is desired.
Aubagio dosage
Aubagio is a daily oral tablet, taken with or without food, in strengths tailored to the patient. Consistent daily intake is crucial as the drug remains in the body for a long time. If discontinuation is necessary, for side effects or pregnancy planning, doctors may prescribe specific medications like cholestyramine to accelerate drug elimination.
Doctors monitor patients’ safety during treatment with blood tests and blood pressure checks, adjusting doses as needed. Closer supervision is required for patients with pre-existing liver disease or high blood pressure.
Older adults can use Aubagio at the usual dose, but liver and kidney function should be monitored due to potential processing changes.
Does Aubagio have a generic version?
Yes. Teriflunomide, the active ingredient in Aubagio, is available as a generic medication in the United States and several other countries. The FDA-approved generic versions contain the same active ingredient, dosage strength, and formulation as the brand-name product, ensuring they are equally effective and safe.
Generic teriflunomide provides a more affordable, yet equally effective, once-daily oral treatment. Patients should discuss switching with their healthcare provider or pharmacist, particularly if cost is a factor.
Conclusion
Aubagio (teriflunomide) is a proven, once-daily oral therapy that helps people living with multiple sclerosis reduce relapses, slow disability progression, and maintain a more stable daily life. By targeting overactive immune cells that damage nerve tissue, it offers effective long-term disease management in a convenient tablet form.
While requiring monitoring for side effects like liver issues, Aubagio offers hope for MS patients. With consistent use and medical guidance, it can improve quality of life, helping patients breathe easier, move more freely, and feel more confident.
References
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). (2024). Aubagio (teriflunomide) prescribing information. Retrieved from https://www.accessdata.fda.gov
- Mayo Clinic. (2024). Teriflunomide (oral route) drug information. Retrieved from https://www.mayoclinic.org
- MedlinePlus. (2024). Teriflunomide: Uses, side effects, and precautions. National Library of Medicine. Retrieved from https://medlineplus.gov
- National Institutes of Health (NIH). (2024). Disease-modifying therapies for multiple sclerosis. Retrieved from https://www.nih.gov
Approved To Treat
Top Global Experts
There are no experts for this drug
Related Clinical Trials
There is no clinical trials being done for this treatment
Related Latest Advances
There is no latest advances for this treatment
Brand Information
- Hepatotoxicity
- Embryofetal Toxicity
- Hepatotoxicity
- Bone Marrow Effects/Immunosuppression Potential/Infections
- Hypersensitivity Reactions
- Serious Skin Reactions
- Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms
- Peripheral Neuropathy
- Increased Blood Pressure
- Respiratory Effects
- Pancreatitis in Pediatric Patients
- Blood and Lymphatic System Disorders: Thrombocytopenia [see
- Gastrointestinal Disorders: Pancreatitis, colitis
- Hepatobiliary Disorders: Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) [see
- Immune System Disorders: Hypersensitivity reactions, some of which were severe, such as anaphylaxis and angioedema [see
- Respiratory, Thoracic, and Mediastinal Disorders: Interstitial lung disease [see
- Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders: Severe skin reactions, including toxic epidermal necrolysis and Stevens-Johnson syndrome [see ; drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) [see ; psoriasis or worsening of psoriasis (including pustular psoriasis and nail psoriasis); nail disorders