Latanoprost
What is Xalatan (Latanoprost)?
For millions of people living with glaucoma or ocular hypertension, protecting their eyesight is a daily priority. These conditions often develop silently, with increased pressure inside the eye slowly damaging the optic nerve, the vital connection between the eye and the brain. Without proper treatment, vision loss can become permanent. Xalatan (latanoprost) is one of the most commonly prescribed drugs to manage this risk.
Xalatan is an ophthalmic (eye) drug belonging to a class of drugs known as prostaglandin analogs. It helps lower intraocular pressure (IOP), the pressure inside the eye which is the primary cause of nerve damage in glaucoma and ocular hypertension. As a once-daily eye drop, Xalatan offers a convenient, effective, and well-tolerated option for maintaining healthy eye pressure and preserving vision. Since its FDA approval in 1996, it has become a first-line therapy for many patients worldwide.
What does Xalatan do?
Xalatan is prescribed to treat open-angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension, two common eye conditions that can lead to progressive vision loss if not properly controlled. Both conditions involve an imbalance between the production and drainage of fluid inside the eye, causing elevated intraocular pressure.
By reducing eye pressure, Xalatan helps protect the optic nerve from damage and slow the progression of vision loss. While it does not cure glaucoma, it plays a key role in preventing or delaying its complications, allowing patients to maintain clear vision and quality of life for many years.
Clinical studies have shown that latanoprost effectively lowers eye pressure by about 25% to 35%, often more than other first-line glaucoma medications (NIH, 2024). Many patients experience sustained pressure control with once-daily dosing, making it easier to stay consistent with treatment.
How does Xalatan work?
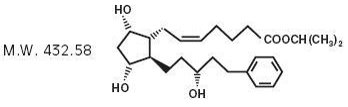
Xalatan contains latanoprost, a synthetic version of a natural body substance called prostaglandin F2α. In simple terms, prostaglandins help regulate fluid flow in the eye.
Inside the eye, a clear liquid called aqueous humor continuously circulates to nourish tissues and maintain shape. When too much fluid accumulates or doesn’t drain properly pressure builds up, increasing the risk of optic nerve damage. Xalatan works by increasing the outflow of this fluid through a natural drainage pathway known as the uveoscleral route.
This mechanism gently lowers intraocular pressure without significantly affecting fluid production or blood flow to the eye. Clinically, this matters because reducing pressure helps prevent damage to the delicate optic nerve fibers responsible for transmitting visual information to the brain. Over time, consistent pressure control with Xalatan can help slow or prevent vision loss associated with glaucoma and ocular hypertension.
Xalatan side effects
Like all medications, Xalatan can cause side effects, although most are mild and manageable. Because it is applied directly to the eye, its effects are usually localized rather than systemic.
Common side effects may include:
- Mild eye irritation, burning, or stinging upon application
- Temporary blurred vision
- Redness or dryness of the eyes
- Gradual darkening of the iris (eye color)
- Increased length, thickness, or number of eyelashes
The iris color change typically darkening from blue or green to brown occurs gradually and may be permanent, though it does not affect vision or eye health. Some people also notice darker skin around eyelids or thicker eyelashes, which are harmless cosmetic effects of the drug.
Serious side effects (rare):
- Eye pain or swelling
- Sensitivity to light
- Vision changes
- Signs of infection (discharge, redness, or swelling that worsens)
If these occur, patients should contact their doctor promptly. Those with a history of eye inflammation, macular edema, or herpes simplex eye infections should inform their healthcare provider before using Xalatan, as it may not be suitable in these cases.
To avoid contamination, patients should avoid touching the dropper tip to any surface including the eye and always replace the cap securely after use.
Xalatan dosage
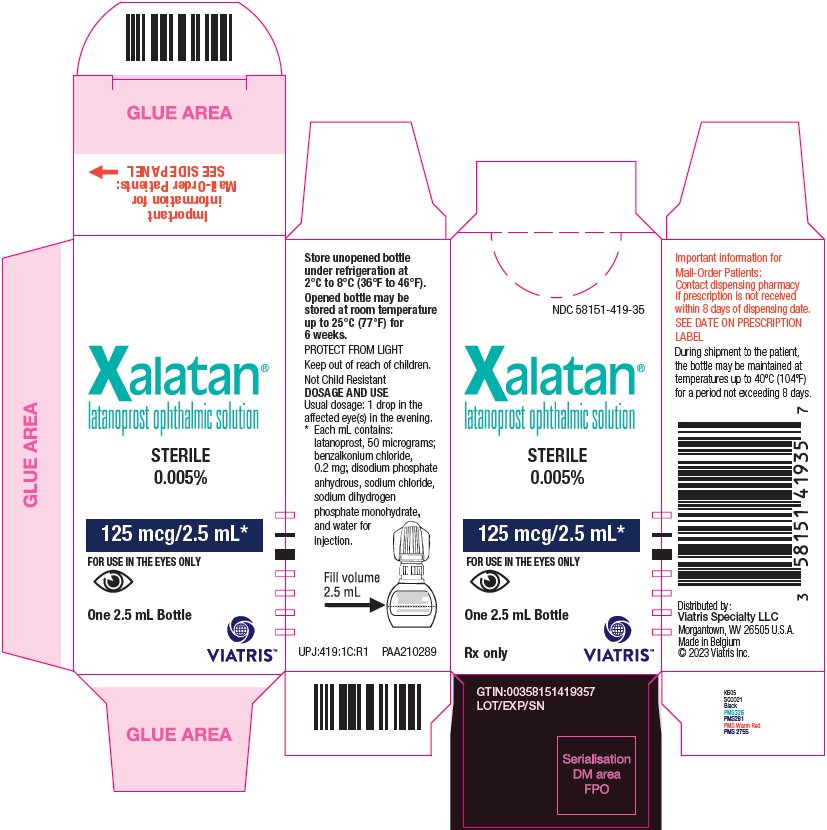
Xalatan eye drops are applied once daily in the evening. Wash hands before use. If using other eye medications, wait five minutes between applications. Remove contact lenses before use, reinserting after 15 minutes. Overuse reduces effectiveness.
Doctors often monitor intraocular pressure regularly during treatment to ensure the medication is working effectively. Patients should continue using Xalatan even if they feel fine, as glaucoma often has no noticeable symptoms in its early stages.
For older adults, the standard dosing remains the same, but those with severe eye inflammation or recent eye surgery may require closer monitoring to prevent complications.
Does Xalatan have a generic version?
Yes. Latanoprost, the active ingredient in Xalatan, is available in generic form and has been FDA-approved since 2011. Generic latanoprost eye drops are widely available and are considered equally effective and safe as the brand-name version.
Generic latanoprost lowers treatment costs without sacrificing quality or results, as it contains the same active ingredient as brand-name versions like Xalatan. Patients can trust that both generic and brand-name options meet the same safety and efficacy standards.
Conclusion
Xalatan (latanoprost) is a trusted and effective treatment for glaucoma and ocular hypertension, helping to protect vision by safely lowering eye pressure. Its once-daily dosing, long track record of success, and strong safety profile make it one of the most widely used medications for long-term eye pressure control.
Most patients tolerate Xalatan well, experiencing mild side effects like irritation or eye color change. Affordable generics make it accessible. Consistent medication, regular exams, and professional collaboration are vital for lifelong glaucoma management, protecting sight and independence.
References
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). (2024). Xalatan (latanoprost) ophthalmic solution prescribing information. Retrieved from https://www.accessdata.fda.gov
- Mayo Clinic. (2024). Latanoprost (ophthalmic route) drug information. Retrieved from https://www.mayoclinic.org
- MedlinePlus. (2024). Latanoprost ophthalmic: Uses, side effects, and precautions. National Library of Medicine. Retrieved from https://medlineplus.gov
- National Institutes of Health (NIH). (2024). Glaucoma management and intraocular pressure control with prostaglandin analogs. Retrieved from https://www.nih.gov
Top Global Experts
There are no experts for this drug
Related Clinical Trials
There is no clinical trials being done for this treatment
Related Latest Advances
There is no latest advances for this treatment
Brand Information
- Iris pigmentation changes
- Eyelid skin darkening
- Eyelash changes (increased length, thickness, pigmentation, and number of lashes)
- Intraocular inflammation (iritis/uveitis)
- Macular edema, including cystoid macular edema
Usual dosage: 1 drop in the
affected eye(s) in the evening.