Brand Name
Felopdipine
Generic Name
Felodipine
View Brand Information FDA approval date: March 31, 2009
Classification: Dihydropyridine Calcium Channel Blocker
Form: Tablet
What is Felopdipine (Felodipine)?
Felodipine extended-release tablets are indicated for the treatment of hypertension. Felodipine extended-release tablets may be used alone or concomitantly with other antihypertensive agents.
Top Global Experts
There are no experts for this drug
Save this treatment for later
Not sure about your diagnosis?
Related Clinical Trials
There is no clinical trials being done for this treatment
Related Latest Advances
There is no latest advances for this treatment
Brand Information
Felopdipine (Felodipine)
1DESCRIPTION
Felodipine is a calcium antagonist (calcium channel blocker). Felodipine is a dihydropyridine derivative that is chemically described as ± ethyl methyl 4-(2,3-dichlorophenyl) -1,4-dihydro-2, 6-dimethyl-3, 5-pyridinedicarboxylate. Its empirical formula is C
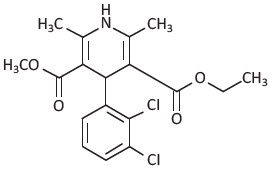
Felodipine is a slightly yellowish, crystalline powder with a molecular weight of 384.26. It is insoluble in water and is freely soluble in dichloromethane and ethanol. Felodipine is a racemic mixture.
Felodipine Extended-release Tablets, USP provide extended release of felodipine. They are available as tablets containing 2.5mg, 5mg, or 10mg of felodipine for oral administration.
Inactive ingredients for core tablets are:anhydrous lactose, butylated hydroxyanisole, butylated hydroxytoluene,colloidal silicon dioxide, hypromellose, polyoxyl 40 hydrogenated castor oil,microcrystalline cellulose, povidone K30 and sodium stearyl fumarate.
Film coating materials of 2.5mg: ferrosoferric oxide, hypromellose, iron oxide red, iron oxide yellow, maltodextrin, medium chain triglycerides, polydextrose, talc and titanium dioxide.
Film coating materials of 5mg: ferrosoferric oxide, hypromellose, iron oxide red, iron oxide yellow, maltodextrin, medium chain triglycerides, polydextrose, talc and titanium dioxide.
Film coating materials of 10mg: ferrosoferric oxide, hypromellose, iron oxide red, iron oxide yellow, maltodextrin, medium chain triglycerides, polydextrose, talc and titanium dioxide.
2INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Felodipine Extended-release Tablets, USP are indicated for the treatment of hypertension, to lower blood pressure. Lowering blood pressure lowers the risk of fatal and non-fatal cardiovascular events, primarily strokes and myocardial infarctions. These benefits have been seen in controlled trials of antihypertensive drugs from a wide variety of pharmacologic classes including felodipine. Control of high blood pressure should be part of comprehensive cardiovascular risk management, including, as appropriate, lipid control, diabetes management, antithrombotic therapy, smoking cessation, exercise, and limited sodium intake. Many patients will require more than 1 drug to achieve blood pressure goals. For specific advice on goals and management, see published guidelines, such as those of the National High Blood Pressure Education Program's Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure (JNC). Numerous antihypertensive drugs, from a variety of pharmacologic classes and with different mechanisms of action, have been shown in randomized controlled trials to reduce cardiovascular morbidity and mortality, and it can be concluded that it is blood pressure reduction, and not some other pharmacologic property of the drugs, that is largely responsible for those benefits. The largest and most consistent cardiovascular outcome benefit has been a reduction in the risk of stroke, but reductions in myocardial infarction and cardiovascular mortality also have been seen regularly.
Elevated systolic or diastolic pressure causes increased cardiovascular risk, and the absolute risk increase per mmHg is greater at higher blood pressures, so that even modest reductions of severe hypertension can provide substantial benefit. Relative risk reduction from blood pressure reduction is similar across populations with varying absolute risk, so the absolute benefit is greater in patients who are at higher risk independent of their hypertension (for example, patients with diabetes or hyperlipidemia), and such patients would be expected to benefit from more aggressive treatment to a lower blood pressure goal.
Some antihypertensive drugs have smaller blood pressure effects (as monotherapy) in black patients, and many antihypertensive drugs have additional approved indications and effects (eg, on angina, heart failure, or diabetic kidney disease).
These considerations may guide selection of therapy.
Felodipine Extended-release Tablets, USP may be administered with other antihypertensive agents.
3CONTRAINDICATIONS
Felodipine is contraindicated in patients who are hypersensitive to this product.
4ADVERSE REACTIONS
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Westminster Pharmaceuticals, LLC at 1-844-221-7294 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
In controlled studies in the United States and overseas, approximately 3000 patients were treated with felodipine as either the extended-release or the immediate-release formulation.
The most common clinical adverse events reported with Felodipine administered as monotherapy at the recommended dosage range of 2.5 mg to 10 mg once a day were peripheral edema and headache. Peripheral edema was generally mild, but it was age and dose related and resulted in discontinuation of therapy in about 3% of the enrolled patients. Discontinuation of therapy due to any clinical adverse event occurred in about 6% of the patients receiving Felodipine, principally for peripheral edema, headache, or flushing.
Adverse events that occurred with an incidence of 1.5% or greater at any of the recommended doses of 2.5 mg to 10 mg once a day (Felodipine, N = 861; Placebo, N = 334), without regard to causality, are compared to placebo and are listed by dose in the table below. These events are reported from controlled clinical trials with patients who were randomized to a fixed dose of Felodipine or titrated from an initial dose of 2.5 mg or 5 mg once a day. A dose of 20 mg once a day has been evaluated in some clinical studies. Although the antihypertensive effect of Felodipineis increased at 20 mg once a day, there is a disproportionate increase in adverse events, especially those associated with vasodilatory effects (see
Adverse events that occurred in 0.5 up to 1.5% of patients who received Felodipine in all controlled clinical trials at the recommended dosage range of 2.5 mg to 10 mg once a day, and serious adverse events that occurred at a lower rate, or events reported during marketing experience (those lower rate events are in italics) are listed below. These events are listed in order of decreasing severity within each category, and the relationship of these events to administration of Felodipine is uncertain:
Body as a Whole: Chest pain, facial edema, flu-like illness;
Cardiovascular: Myocardial infarction, hypotension, syncope, angina pectoris, arrhythmia, tachycardia, premature beats;
Digestive: Abdominal pain, diarrhea, vomiting, dry mouth, flatulence, acid regurgitation;
Endocrine: Gynecomastia;
Hematologic: Anemia;
Metabolic: ALT (SGPT) increased;
Musculoskeletal: Arthralgia, back pain, leg pain, foot pain, muscle cramps, myalgia, arm pain, knee pain, hip pain;
Nervous/Psychiatric: Insomnia, depression, anxiety disorders, irritability, nervousness, somnolence, decreased libido;
Respiratory: Dyspnea, pharyngitis, bronchitis, influenza, sinusitis, epistaxis, respiratory infection;
Skin: Angioedema, contusion, erythema, urticaria, leukocytoclastic vasculitis;
Special Senses: Visual disturbances;
Urogenital: Impotence, urinary frequency, urinary urgency, dysuria, polyuria.
4.1Gingival Hyperplasia
Gingival hyperplasia, usually mild, occurred in < 0.5% of patients in controlled studies. This condition may be avoided or may regress with improved dental hygiene. (See
5OVERDOSAGE
Oral doses of 240 mg/kg and 264 mg/kg in male and female mice, respectively, and 2390 mg/kg and 2250 mg/kg in male and female rats, respectively, caused significant lethality.
In a suicide attempt, one patient took 150 mg felodipine together with 15 tablets each of atenolol and spironolactone and 20 tablets of nitrazepam. The patient's blood pressure and heart rate were normal on admission to hospital; he subsequently recovered without significant sequelae.
Overdosage might be expected to cause excessive peripheral vasodilation with marked hypotension and possibly bradycardia.
If severe hypotension occurs, symptomatic treatment should be instituted. The patient should be placed supine with the legs elevated. The administration of intravenous fluids may be useful to treat hypotension due to overdosage with calcium antagonists. In case of accompanying bradycardia, atropine (0.5–1 mg) should be administered intravenously. Sympathomimetic drugs may also be given if the physician feels they are warranted.
It has not been established whether felodipine can be removed from the circulation by hemodialysis.
To obtain up-to-date information about the treatment of overdose, consult your Regional Poison-Control Center. Telephone numbers of certified poison-control centers are listed in the Physicians' Desk Reference (PDR). In managing overdose, consider the possibilities of multiple-drug overdoses, drug-drug interactions, and unusual drug kinetics in your patient.
6DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
The recommended starting dose is 5 mg once a day. Depending on the patient's response, the dosage can be decreased to 2.5 mg or increased to 10 mg once a day. These adjustments should occur generally at intervals of not less than 2 weeks. The recommended dosage range is 2.5–10 mg once daily. In clinical trials, doses above 10 mg daily showed an increased blood pressure response but a large increase in the rate of peripheral edema and other vasodilatory adverse events (see
Felodipine should regularly be taken either without food or with a light meal (see
6.1Geriatric Use
Patients over 65 years of age are likely to develop higher plasma concentrations of felodipine (see
6.2Patients with Impaired Liver Function
Patients with impaired liver function may have elevated plasma concentrations of felodipine and may respond to lower doses of Felodipine; therefore, patients should have their blood pressure monitored closely during dosage adjustment of Felodipine (see
7HOW SUPPLIED
Product: 50090-7206
NDC: 50090-7206-0 30 TABLET, EXTENDED RELEASE in a BOTTLE
8Felodipine
