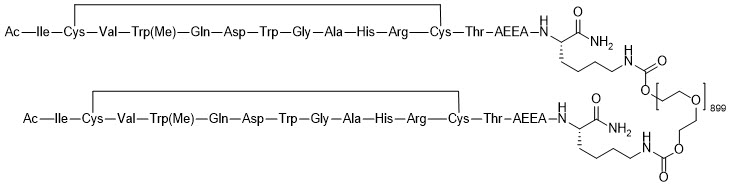
Pegcetacoplan
What is Empaveli (Pegcetacoplan)?
For people living with rare, chronic blood disorders like paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH), everyday life can feel unpredictable, marked by fatigue, shortness of breath, and dark-colored urine due to the destruction of red blood cells. Empaveli (pegcetacoplan) offers a newer, targeted approach that helps control this destruction and improve overall quality of life.
Empaveli is a complement inhibitor, a type of medication that works by regulating part of the immune system responsible for breaking down red blood cells in people with PNH. Developed by Apellis Pharmaceuticals and approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2021, it represents a significant advancement for patients who need better control over their symptoms or who do not respond adequately to older treatments like eculizumab or ravulizumab.
As one of the first drugs to directly inhibit the complement protein C3, Empaveli provides a more complete suppression of red blood cell destruction helping patients maintain higher hemoglobin levels, reduce transfusion needs, and regain energy for daily living.
What does Empaveli do?
Empaveli is primarily used to treat paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH), a rare, life-threatening condition in which the immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys red blood cells. This destruction, called hemolysis, leads to anemia, fatigue, and an increased risk of blood clots.
The medication helps prevent red blood cell breakdown, allowing more oxygen-carrying cells to stay intact in the bloodstream. As a result, patients may experience improved energy, fewer blood transfusions, and reduced symptoms related to anemia.
Clinical trials have shown promising outcomes. In a head-to-head study comparing Empaveli with eculizumab, patients on Empaveli achieved significantly higher hemoglobin levels and a reduction in transfusion dependence (FDA, 2021). Many patients report improved stamina, better physical function, and enhanced overall well-being after transitioning to Empaveli.
Empaveli may also be used under certain circumstances for other complement-mediated conditions under physician supervision, but its primary indication remains PNH.
How does Empaveli work?
Empaveli works by targeting and inhibiting the complement protein C3, a central component of the body’s immune defense system. The complement system normally helps the body fight infections by marking damaged or foreign cells for destruction. However, in people with PNH, this system becomes overactive and mistakenly attacks the body’s own red blood cells.
By blocking the action of C3, Empaveli prevents this destructive immune response, protecting red blood cells from premature breakdown. This helps maintain stable hemoglobin levels and reduces the symptoms associated with chronic anemia, such as weakness and shortness of breath.
Clinically, this mechanism is important because it offers broader control of complement activation compared to older drugs that only block downstream components like C5. That means Empaveli can help address both intravascular (inside the blood vessels) and extravascular (outside the blood vessels) hemolysis, providing more comprehensive protection for patients with PNH.
Empaveli side effects
While Empaveli offers significant benefits, it can cause side effects that vary from mild to serious.
Common side effects may include:
- Injection site reactions (pain, redness, swelling)
- Headache or fatigue
- Diarrhea or nausea
- Upper respiratory infections
Serious side effects (less common) include:
- Increased risk of serious infections, particularly from encapsulated bacteria such as Neisseria meningitidis (meningitis), Streptococcus pneumoniae, and Haemophilus influenzae type b
- Hypersensitivity reactions, including rash or swelling
- Liver function changes detected by blood tests
Because Empaveli suppresses part of the immune system, patients are at higher risk of certain bacterial infections. To reduce this risk, patients must receive specific vaccinations (meningococcal, pneumococcal, and Haemophilus influenzae type b) at least two weeks before starting treatment.
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience fever, neck stiffness, rash, confusion, or sensitivity to light, which could signal meningococcal infection.
Patients with active infections should delay treatment until fully recovered. Regular monitoring by a healthcare provider is essential to ensure safe, ongoing use.
Empaveli dosage
Empaveli is given as a subcutaneous (under the skin) infusion, typically administered using an infusion pump. The medication can be self-administered at home once patients are properly trained, though some may initially receive doses under medical supervision.
Consistent treatment is vital for stable complement inhibition. Missing doses can cause hemolysis symptoms to recur, so adhere strictly to the schedule.
Doctors regularly monitor patients via blood tests (hemoglobin, red blood cell destruction), kidney and liver function tests (drug tolerance), and infection screening (immune risks).
Older adults and those with kidney/liver issues may need closer monitoring; dosage adjustments are individualized.
Does Empaveli have a generic version?
Currently, no generic version of Empaveli (pegcetacoplan) is available. As a biologic medication, Empaveli would eventually be eligible for a biosimilar rather than a traditional generic version once its patent exclusivity period ends. However, international versions may exist in other markets.
Empaveli, by Apellis Pharmaceuticals, is the sole FDA-approved C3 complement inhibitor for PNH. Future biosimilars must demonstrate comparable safety, purity, and effectiveness.
Conclusion
Empaveli (pegcetacoplan) represents a major step forward in the treatment of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. By directly targeting the C3 protein in the complement system, it helps protect red blood cells from destruction, improve hemoglobin levels, and reduce the need for blood transfusions.
Despite infection risks, regular monitoring, proper vaccination, and medical guidance make Empaveli a safe and effective treatment for PNH. As a next-generation therapy, it offers patients improved stability, energy, and health control. Patients should maintain open communication with their healthcare team for optimal outcomes.
References
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). (2021). FDA approves new treatment for adults with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH). Retrieved from https://www.fda.gov
- MedlinePlus. (2024). Pegcetacoplan injection: Drug information. National Library of Medicine. Retrieved from https://medlineplus.gov
- Mayo Clinic. (2024). Pegcetacoplan (subcutaneous route) overview. Retrieved from https://www.mayoclinic.org
- National Institutes of Health (NIH). (2024). Complement-mediated hemolysis and treatment advances. Retrieved from https://www.nih.gov
Approved To Treat
Top Global Experts
There are no experts for this drug
Related Clinical Trials
There is no clinical trials being done for this treatment
Related Latest Advances
There is no latest advances for this treatment
Brand Information
- Complete or update vaccination for encapsulated bacteria at least 2 weeks prior to the first dose of EMPAVELI, unless the risks of delaying therapy with EMPAVELI outweigh the risk of developing a serious infection. Comply with the most current Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) recommendations for vaccinations against encapsulated bacteria in patients receiving a complement inhibitor.
- Patients receiving EMPAVELI are at increased risk for invasive disease caused by encapsulated bacteria, even if they develop antibodies following vaccination. Monitor patients for early signs and symptoms of serious infections and evaluate immediately if infection is suspected.
- in patients with hypersensitivity to pegcetacoplan or to any of the excipients
- for initiation in patients with unresolved serious infection caused by encapsulated bacteria including
- Serious Infections Caused by Encapsulated Bacteria
- Infusion-Related Reactions
- Anaphylaxis and urticaria