Brand Name
Anafranil
Generic Name
Clomipramine
View Brand Information FDA approval date: December 29, 1989
Classification: Tricyclic Antidepressant
Form: Capsule
What is Anafranil (Clomipramine)?
Clomipramine hydrochloride capsules are indicated for the treatment of obsessions and compulsions in patients with Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder . The obsessions or compulsions must cause marked distress, be time-consuming, or significantly interfere with social or occupational functioning, in order to meet the DSM-III-R diagnosis of OCD. Obsessions are recurrent, persistent ideas, thoughts, images, or impulses that are ego-dystonic. Compulsions are repetitive, purposeful, and intentional behaviors performed in response to an obsession or in a stereotyped fashion, and are recognized by the person as excessive or unreasonable. The effectiveness of clomipramine hydrochloride capsules for the treatment of OCD was demonstrated in multicenter, placebo-controlled, parallel-group studies, including two 10-week studies in adults and one 8-week study in children and adolescents 10 to 17 years of age. Patients in all studies had moderate-to-severe OCD , with mean baseline ratings on the Yale-Brown Obsessive Compulsive Scale ranging from 26 to 28 and a mean baseline rating of 10 on the NIMH Clinical Global Obsessive Compulsive Scale . Patients taking CMI experienced a mean reduction of approximately 10 on the YBOCS, representing an average improvement on this scale of 35% to 42% among adults and 37% among children and adolescents. CMI-treated patients experienced a.
Approved To Treat
Top Global Experts
There are no experts for this drug
Save this treatment for later
Not sure about your diagnosis?
Related Clinical Trials
There is no clinical trials being done for this treatment
Related Latest Advances
There is no latest advances for this treatment
Brand Information
ANAFRANIL (clomipramine hydrochloride)
1DESCRIPTION
Anafranil
Clomipramine hydrochloride USP is 3-chloro-5-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]-10,11-dihydro-
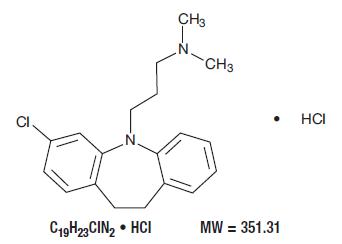
Clomipramine hydrochloride USP is a white to off-white crystalline powder. It is freely soluble in water, in methanol, and in methylene chloride, and insoluble in ethyl ether and in hexane.
Inactive Ingredients. D&C Red No. 33 (25 mg capsules only), D&C Yellow No. 10, FD&C Blue No. 1 (50 mg capsules only), FD&C Yellow No. 6, gelatin, magnesium stearate, methylparaben, propylparaben, starch (corn), and titanium dioxide.
2INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Anafranil
Obsessions are recurrent, persistent ideas, thoughts, images, or impulses that are ego-dystonic. Compulsions are repetitive, purposeful, and intentional behaviors performed in response to an obsession or in a stereotyped fashion, and are recognized by the person as excessive or unreasonable.
The effectiveness of Anafranil for the treatment of OCD was demonstrated in multicenter, placebo-controlled, parallel-group studies, including two 10-week studies in adults and one 8-week study in children and adolescents 10 to 17 years of age. Patients in all studies had moderate-to-severe OCD (DSM-III), with mean baseline ratings on the Yale-Brown Obsessive Compulsive Scale (YBOCS) ranging from 26 to 28 and a mean baseline rating of 10 on the NIMH Clinical Global Obsessive Compulsive Scale (NIMH-OC). Patients taking CMI experienced a mean reduction of approximately 10 on the YBOCS, representing an average improvement on this scale of 35% to 42% among adults and 37% among children and adolescents. CMI-treated patients experienced a 3.5 unit decrement on the NIMH-OC. Patients on placebo showed no important clinical response on either scale. The maximum dose was 250 mg/day for most adults and 3 mg/kg/day (up to 200 mg) for all children and adolescents.
The effectiveness of Anafranil for long-term use (i.e., for more than 10 weeks) has not been systematically evaluated in placebo-controlled trials. The physician who elects to use Anafranil for extended periods should periodically reevaluate the long-term usefulness of the drug for the individual patient (
3CONTRAINDICATIONS
Anafranil is contraindicated in patients with a history of hypersensitivity to Anafranil or other tricyclic antidepressants.
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs)
The use of MAOIs intended to treat psychiatric disorders with Anafranil or within 14 days of stopping treatment with Anafranil is contraindicated because of an increased risk of serotonin syndrome. The use of Anafranil within 14 days of stopping an MAOI intended to treat psychiatric disorders is also contraindicated (
Starting Anafranil in a patient who is being treated with linezolid or intravenous methylene blue is also contraindicated because of an increased risk of serotonin syndrome (
Myocardial Infarction
Anafranil is contraindicated during the acute recovery period after a myocardial infarction.
4DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
Anafranil has not been systematically studied in animals or humans for its potential for abuse, tolerance, or physical dependence. While a variety of withdrawal symptoms have been described in association with Anafranil discontinuation (
Despite the lack of evidence suggesting an abuse liability for Anafranil in foreign marketing, it is not possible to predict the extent to which Anafranil might be misused or abused once marketed in the U.S. Consequently, physicians should carefully evaluate patients for a history of drug abuse and follow such patients closely.
5OVERDOSAGE
Deaths may occur from overdosage with this class of drugs. Multiple drug ingestion (including alcohol) is common in deliberate tricyclic overdose. As the management is complex and changing, it is recommended that the physician contact a poison control center for current information on treatment. Signs and symptoms of toxicity develop rapidly after tricyclic overdose. Therefore, hospital monitoring is required as soon as possible.
5.1Human Experience
In U.S. clinical trials, 2 deaths occurred in 12 reported cases of acute overdosage with Anafranil either alone or in combination with other drugs. One death involved a patient suspected of ingesting a dose of 7000 mg. The second death involved a patient suspected of ingesting a dose of 5750 mg. The 10 nonfatal cases involved doses of up to 5000 mg, accompanied by plasma levels of up to 1010 ng/mL. All 10 patients completely recovered. Among reports from other countries of Anafranil overdose, the lowest dose associated with a fatality was 750 mg. Based upon postmarketing reports in the United Kingdom, CMI's lethality in overdose is considered to be similar to that reported for closely related tricyclic compounds marketed as antidepressants.
5.2Manifestations
Signs and symptoms vary in severity depending upon factors such as the amount of drug absorbed, the age of the patient, and the time elapsed since drug ingestion. Critical manifestations of overdose include cardiac dysrhythmias, severe hypotension, convulsions, and CNS depression including coma. Changes in the electrocardiogram, particularly in QRS axis or width, are clinically significant indicators of tricyclic toxicity. Other CNS manifestations may include drowsiness, stupor, ataxia, restlessness, agitation, delirium, severe perspiration, hyperactive reflexes, muscle rigidity, and athetoid and choreiform movements. Cardiac abnormalities may include tachycardia, signs of congestive heart failure, and in very rare cases, cardiac arrest. Respiratory depression, cyanosis, shock, vomiting, hyperpyrexia, mydriasis, and oliguria or anuria may also be present.
5.3Management
Obtain an ECG and immediately initiate cardiac monitoring. Protect the patient's airway, establish an intravenous line, and initiate gastric decontamination. A minimum of 6 hours of observation with cardiac monitoring and observation for signs of CNS or respiratory depression, hypotension, cardiac dysrhythmias and/or conduction blocks, and seizures is necessary.
If signs of toxicity occur at any time during this period, extended monitoring is required. There are case reports of patients succumbing to fatal dysrhythmias late after overdose; these patients had clinical evidence of significant poisoning prior to death and most received inadequate gastrointestinal decontamination. Monitoring of plasma drug levels should not guide management of the patient.
6DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
The treatment regimens described below are based on those used in controlled clinical trials of Anafranil in 520 adults, and 91 children and adolescents with OCD. During initial titration, Anafranil should be given in divided doses with meals to reduce gastrointestinal side effects. The goal of this initial titration phase is to minimize side effects by permitting tolerance to side effects to develop or allowing the patient time to adapt if tolerance does not develop.
Because both CMI and its active metabolite, DMI, have long elimination half-lives, the prescriber should take into consideration the fact that steady-state plasma levels may not be achieved until 2 to 3 weeks after dosage change (
6.1Initial Treatment/Dose Adjustment (Adults)
Treatment with Anafranil should be initiated at a dosage of 25 mg daily and gradually increased, as tolerated, to approximately 100 mg during the first 2 weeks. During initial titration, Anafranil should be given in divided doses with meals to reduce gastrointestinal side effects. Thereafter, the dosage may be increased gradually over the next several weeks, up to a maximum of 250 mg daily. After titration, the total daily dose may be given once daily at bedtime to minimize daytime sedation.
6.2Initial Treatment/Dose Adjustment (Children and Adolescents)
As with adults, the starting dose is 25 mg daily and should be gradually increased (also given in divided doses with meals to reduce gastrointestinal side effects) during the first 2 weeks, as tolerated, up to a daily maximum of 3 mg/kg or 100 mg, whichever is smaller. Thereafter, the dosage may be increased gradually over the next several weeks up to a daily maximum of 3 mg/kg or 200 mg, whichever is smaller (
6.3Maintenance/Continuation Treatment (Adults, Children, and Adolescents)
While there are no systematic studies that answer the question of how long to continue Anafranil, OCD is a chronic condition and it is reasonable to consider continuation for a responding patient. Although the efficacy of Anafranil after 10 weeks has not been documented in controlled trials, patients have been continued in therapy under double-blind conditions for up to 1 year without loss of benefit. However, dosage adjustments should be made to maintain the patient on the lowest effective dosage, and patients should be periodically reassessed to determine the need for treatment. During maintenance, the total daily dose may be given once daily at bedtime.
6.4Switching a Patient To or From a Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitor (MAOI) Intended to Treat Psychiatric Disorders
At least 14 days should elapse between discontinuation of an MAOI intended to treat psychiatric disorders and initiation of therapy with Anafranil. Conversely, at least 14 days should be allowed after stopping Anafranil before starting an MAOI intended to treat psychiatric disorders (
6.5Use of Anafranil With Other MAOIs, Such as Linezolid or Methylene Blue
Do not start Anafranil in a patient who is being treated with linezolid or intravenous methylene blue because there is increased risk of serotonin syndrome. In a patient who requires more urgent treatment of a psychiatric condition, other interventions, including hospitalization, should be considered (
In some cases, a patient already receiving Anafranil therapy may require urgent treatment with linezolid or intravenous methylene blue. If acceptable alternatives to linezolid or intravenous methylene blue treatment are not available and the potential benefits of linezolid or intravenous methylene blue treatment are judged to outweigh the risks of serotonin syndrome in a particular patient, Anafranil should be stopped promptly, and linezolid or intravenous methylene blue can be administered. The patient should be monitored for symptoms of serotonin syndrome for two weeks or until
The risk of administering methylene blue by non-intravenous routes (such as oral tablets or by local injection) or in intravenous doses much lower than 1 mg/kg with Anafranil is unclear. The clinician should, nevertheless, be aware of the possibility of emergent symptoms of serotonin syndrome with such use (
7HOW SUPPLIED
Anafranil™ (clomipramine hydrochloride) Capsules USP
Capsules 25 mg – ivory body imprinted in black with " " and melon-yellow cap imprinted in black with "ANAFRANIL 25 mg"
" and melon-yellow cap imprinted in black with "ANAFRANIL 25 mg"
Bottles of 30………....………...……….....………… NDC 0406-9906-03
Capsules 25 mg – ivory body imprinted in black with "
 " and melon-yellow cap imprinted in black with "ANAFRANIL 25 mg"
" and melon-yellow cap imprinted in black with "ANAFRANIL 25 mg"Bottles of 30………....………...……….....………… NDC 0406-9906-03
Capsules 50 mg – ivory body imprinted in black with " " and aqua blue cap imprinted in black with "ANAFRANIL 50 mg"
" and aqua blue cap imprinted in black with "ANAFRANIL 50 mg"
Bottles of 30………..………....………...……….....…NDC 0406-9907-03
 " and aqua blue cap imprinted in black with "ANAFRANIL 50 mg"
" and aqua blue cap imprinted in black with "ANAFRANIL 50 mg"Bottles of 30………..………....………...……….....…NDC 0406-9907-03
Capsules 75 mg – ivory body imprinted in black with " " and yellow cap imprinted in black with "ANAFRANIL 75 mg"
" and yellow cap imprinted in black with "ANAFRANIL 75 mg"
Bottles of 30………..………...……….....………....…NDC 0406-9908-03
 " and yellow cap imprinted in black with "ANAFRANIL 75 mg"
" and yellow cap imprinted in black with "ANAFRANIL 75 mg"Bottles of 30………..………...……….....………....…NDC 0406-9908-03
Storage – Store at 20º to 25ºC (68° to 77°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Dispense in well-closed containers with a child-resistant closure. Protect from moisture.
8ANIMAL TOXICOLOGY
Phospholipidosis and testicular changes, commonly associated with tricyclic compounds, have been observed with Anafranil. In chronic rat studies, changes related to Anafranil consisted of systemic phospholipidosis, alterations in the testes (atrophy, mineralization) and secondary changes in other tissues. In addition cardiac thrombosis and dermatitis/keratitis were observed in rats treated for 2 years at doses which were 24 and 10 times the maximum recommended human daily dose (MRHD), respectively, on a mg/kg basis, and 4 and 1.5 times the MRHD, respectively, on a mg/m
Mallinckrodt, the “M” brand mark, the Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals logo,
© 2024 Mallinckrodt.
Product of Canada, Active Ingredient made in Ireland
Manufactured by
Patheon Inc.
Whitby, Ontario, Canada
Rev 09/2024
Mallinckrodt™
Pharmaceuticals
Pharmaceuticals
9Medication Guide - Anafranil™ (clomipramine hydrochloride) Capsules USP Antidepressant Medicines, Depression and other Serious Mental Illnesses, and Suicidal Thoughts or Actions
Read the Medication Guide that comes with you or your family member's antidepressant medicine. This Medication Guide is only about the risk of suicidal thoughts and actions with antidepressant medicines.
- all risks and benefits of treatment with antidepressant medicines
- all treatment choices for depression or other serious mental illness
What is the most important information I should know about antidepressant medicines, depression and other serious mental illnesses, and suicidal thoughts or actions?
- Antidepressant medicines may increase suicidal thoughts or actions in some children, teenagers, and young adults within the first few months of treatment.
- Depression and other serious mental illnesses are the most important causes of suicidal thoughts and actions. Some people may have a particularly high risk of having suicidal thoughts or actions. These include people who have (or have a family history of) bipolar illness (also called manic-depressive illness) or suicidal thoughts or actions.
- How can I watch for and try to prevent suicidal thoughts and actions in myself or a family member?
- Pay close attention to any changes, especially sudden changes, in mood, behaviors, thoughts, or feelings. This is very important when an antidepressant medicine is started or when the dose is changed.
- Call the healthcare provider right away to report new or sudden changes in mood, behavior, thoughts, or feelings.
- Keep all follow-up visits with the healthcare provider as scheduled. Call the healthcare provider between visits as needed, especially if you have concerns about symptoms.
Call a healthcare provider right away if you or your family member has any of the following symptoms, especially if they are new, worse, or worry you:
- thoughts about suicide or dying
- attempts to commit suicide
- new or worse depression
- new or worse anxiety
- feeling very agitated or restless
- panic attacks
- trouble sleeping (insomnia)
- new or worse irritability
- acting aggressive, being angry, or violent
- acting on dangerous impulses
- an extreme increase in activity and talking (mania)
- other unusual changes in behavior or mood
Low salt (sodium) levels in the blood. Elderly people may be at greater risk for this. Symptoms may include:
- headache
- weakness or feeling unsteady
- confusion, problems concentrating or thinking or memory problems
Visual problems
- eye pain
- changes in vision
- swelling or redness in or around the eye
Only some people are at risk for these problems. You may want to undergo an eye examination to see if you are at risk and receive preventative treatment if you are.
Who should not take Anafranil?
Do not take Anafranil if you:
- take a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI). Ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist if you are not sure if you take an MAOI, including the antibiotic linezolid.
What else do I need to know about antidepressant medicines?
- Never stop an antidepressant medicine without first talking to a healthcare provider. Stopping an antidepressant medicine suddenly can cause other symptoms.
- Antidepressants are medicines used to treat depression and other illnesses. It is important to discuss all the risks of treating depression and also the risks of not treating it. Patients and their families or other caregivers should discuss all treatment choices with the healthcare provider, not just the use of antidepressants.
- Antidepressant medicines have other side effects. Talk to the healthcare provider about the side effects of the medicine prescribed for you or your family member.
- Antidepressant medicines can interact with other medicines. Know all of the medicines that you or your family member takes. Keep a list of all medicines to show the healthcare provider. Do not start new medicines without first checking with your healthcare provider.
- Not all antidepressant medicines prescribed for children are FDA approved for use in children. Talk to your child's healthcare provider for more information.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Anafranil is a trademark of Mallinckrodt LLC.
Product of Canada, Active Ingredient made in Ireland
Manufactured by
Rev 09/2024
Mallinckrodt™
10PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 25 mg Bottle
NDC 0406-9906-03
Rev 09/2024
2000017741

11PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 50 mg Bottle
NDC 0406-9907-03
Rev 9/2024
2000017742

12PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 75 mg Bottle
NDC 0406-9908-03
Rev 09/2024
2000017743
