Brand Name
Soltamox
Generic Name
Tamoxifen
View Brand Information FDA approval date: February 20, 2003
Classification: Estrogen Agonist/Antagonist
Form: Tablet, Liquid
What is Soltamox (Tamoxifen)?
Metastatic Breast Cancer: Tamoxifen citrate tablets are effective in the treatment of metastatic breast cancer in women and men. In premenopausal women with metastatic breast cancer, tamoxifen citrate tablets are an alternative to oophorectomy or ovarian irradiation. Available evidence indicates that patients whose tumors are estrogen receptor positive are more likely to benefit from tamoxifen citrate tablets therapy. Adjuvant Treatment of Breast Cancer: Tamoxifen citrate tablets are indicated for the treatment of node-positive breast cancer in women following total mastectomy or segmental mastectomy, axillary dissection, and breast irradiation. In some tamoxifen citrate adjuvant studies, most of the benefit to date has been in the subgroup with four or more positive axillary nodes. Tamoxifen citrate tablets are indicated for the treatment of axillary node-negative breast cancer in women following total mastectomy or segmental mastectomy, axillary dissection, and breast irradiation. The estrogen and progesterone receptor values may help to predict whether adjuvant tamoxifen citrate tablets therapy are likely to be beneficial. Tamoxifen citrate tablets reduces the occurrence of contralateral breast cancer in patients receiving adjuvant tamoxifen citrate tablets therapy for breast cancer. Ductal Carcinoma in Situ : In women with DCIS, following breast surgery and radiation, tamoxifen citrate tablets are indicated to reduce the risk of invasive breast cancer. The decision regarding therapy with tamoxifen citrate tablets for the reduction in breast cancer incidence should be based upon an individual assessment of the benefits and risks of tamoxifen citrate tablets therapy. Current data from clinical trials support five years of adjuvant tamoxifen citrate tablets therapy for patients with breast cancer. Reduction in Breast Cancer Incidence in High Risk Women: Tamoxifen citrate tablets are indicated to reduce the incidence of breast cancer in women at high risk for breast cancer. This effect was shown in a study of 5 years planned duration with a median follow-up of.
Approved To Treat
Top Global Experts
There are no experts for this drug
Save this treatment for later
Not sure about your diagnosis?
Related Clinical Trials
There is no clinical trials being done for this treatment
Related Latest Advances
There is no latest advances for this treatment
Brand Information
SOLTAMOX (TAMOXIFEN CITRATE)
WARNING: UTERINE MALIGNANCIES and THROMBOEMBOLIC EVENTS
Serious and life-threatening events from the use of SOLTAMOX include uterine malignancies, stroke, and pulmonary embolism
Incidence rates per 1000 women-years for these events were estimated from the National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project (NSABP) P-1 trial in women at high risk for breast cancer
- Endometrial adenocarcinoma: 2.20 for tamoxifen vs. 0.71 for placebo
- Uterine sarcoma: 0.17 for tamoxifen vs. 0.04 for placebo
- Stroke: 1.43 for tamoxifen vs. 1.00 for placebo.
- Pulmonary embolism: 0.75 for tamoxifen versus 0.25 for placebo.
Discuss the potential benefits of tamoxifen versus the potential risks of these serious events with women at high risk for breast cancer and women with ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) considering tamoxifen to reduce the risk of developing breast cancer
1DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
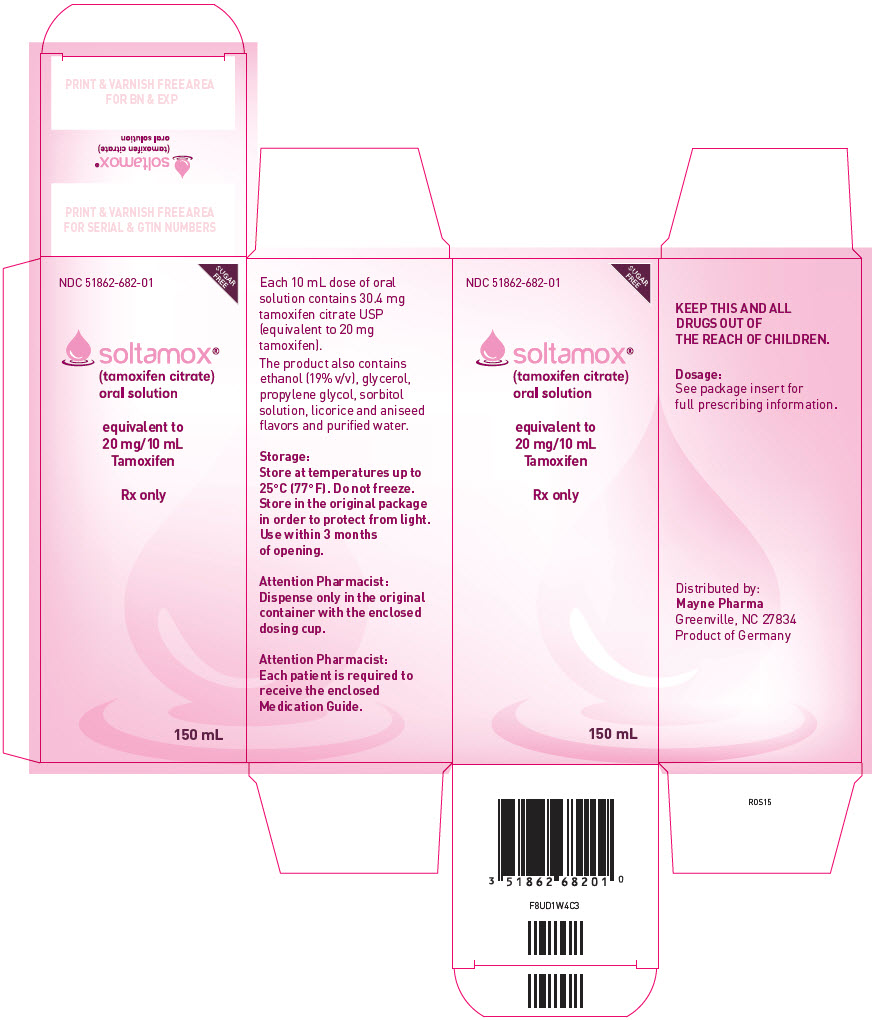
SOLTAMOX oral solution: Each 10 mL of solution contains 20 mg tamoxifen, equivalent to 30.4 mg tamoxifen citrate.
2CONTRAINDICATIONS
- SOLTAMOX is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity (e.g., angioedema, serious skin reactions) to tamoxifen or any other SOLTAMOX ingredient
- SOLTAMOX is contraindicated in patients who require concomitant warfarin therapy or have a history of deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolus if the indication for treatment is either reduction of breast cancer incidence in high-risk patients or risk reduction of invasive breast cancer after treatment of DCIS
3ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious adverse reactions are discussed below and elsewhere in the labeling:
- Uterine malignancies
- Thromboembolic events
- Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
- Liver cancer
3.1Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
3.2Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during postapproval use of tamoxifen. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Skin and Subcutaneous Disorders: Erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, bullous pemphigoid
Respiratory, Thoracic, Mediastinal Disorders: Interstitial pneumonitis
Immune System Disorders: Hypersensitivity reactions including angioedema; in some of these cases, the time to onset was more than one year.
Gastrointestinal Disorders: Elevation of serum triglyceride levels, in some cases with pancreatitis
4OVERDOSAGE
No specific treatment for SOLTAMOX overdosage is recommended, other than symptomatic treatment.
In a study of advanced metastatic cancer patients to determine the maximum tolerated dose of tamoxifen that could reverse multidrug resistance, the following adverse events were observed: acute neurotoxicity manifested by tremor, hyperreflexia, unsteady gait, and dizziness. These symptoms occurred within 3 to 5 days of beginning tamoxifen and cleared within 2 to 5 days after stopping therapy. No permanent neurologic toxicity was noted. One patient experienced a seizure several days after tamoxifen was discontinued and neurotoxic symptoms had resolved. The causal relationship of the seizure to tamoxifen therapy is unknown. Doses given in these patients were all greater than 400 mg/m
In the same study, prolongation of the QT interval on the electrocardiogram was noted when patients were given doses higher than 250 mg/m
Signs observed at the highest doses following studies to determine LD
5DESCRIPTION
SOLTAMOX (tamoxifen citrate) oral solution is for oral administration. Tamoxifen citrate is an estrogen agonist/antagonist.
Chemically, tamoxifen is the trans-isomer of a triphenylethylene derivative. The chemical name is (Z)2-[4-(1,2- diphenyl-1-butenyl)phenoxy]-
Tamoxifen citrate has a pKa′ of 8.85. The equilibrium solubility in water at 37°C is 0.5 mg/mL, and is 0.2 mg/mL in 0.02 N HCl at 37°C.
Each 10 mL of SOLTAMOX oral solution contains 20 mg tamoxifen, equivalent to 30.4 mg tamoxifen citrate. The oral solution is a sugar-free, clear colorless liquid, with licorice and aniseed odor and taste supplied in a 150 mL bottle with a dosing cup. SOLTAMOX oral solution contains the following inactive ingredients: ethanol, glycerol, propylene glycol, sorbitol solution, licorice flavor, aniseed flavor, purified water.
6REFERENCES
1Cancer.gov [Internet]. Bethesda (MD):National Cancer Institute [updated 2011 May 16]. Available from: http://www.cancer.gov/bcrisktool/.
7HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
SOLTAMOX oral solution is a sugar-free, clear colorless liquid, with licorice and aniseed odor and taste. It is supplied in a 150 mL bottle with a dosing cup intended for the measurement of SOLTAMOX oral solution only. Each 10 mL of solution contains 20 mg tamoxifen, equivalent to 30.4 mg tamoxifen citrate.
NDC# 51862-
8PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide).
9MEDICATION GUIDE SOLTAMOX®(SOL-ta-mox) (tamoxifen citrate) oral solution
Before taking SOLTAMOX, you and your healthcare provider should talk about the possible benefits and risks.
- The benefits and risks are different for women at high risk for breast cancer and women with breast cancer that is only inside the milk ducts (ductal carcinoma in-situ or DCIS) than for women who have been diagnosed with invasive breast cancer.
- For most people who already have invasive breast cancer, the benefits of SOLTAMOX are greater than the risks.
- Talk to your healthcare provider about which risks may affect you.
What is the most important information I should know about SOLTAMOX?
SOLTAMOX can cause serious side effects, including:
- Uterine cancer. Cancer of the lining of the uterus (endometrial adenocarcinoma) or cancer of the body of the uterus (uterine sarcoma) may happen more often in women who take SOLTAMOX and can lead to death. People who take or have taken SOLTAMOX should have a gynecologic exam every year.
SOLTAMOX can also cause other non-cancer effects on the uterus, including:- overgrowth of the lining of the uterus (hyperplasia) and uterine polyps
- endometriosis
- fibroids
- irregular menstrual periods or no menstrual periods (amenorrhea)
- irregular menstrual periods
- abnormal vaginal bleeding
- a change in your vaginal discharge
- pelvic pain or pressure
- Blood clots in your veins or lungs. Blood clots in your veins or lungs may happen more often in people who take SOLTAMOX and can lead to death, especially in people who take SOLTAMOX during their treatment with chemotherapy.
Tell your healthcare provider right away if you get any of the following symptoms of a blood clot during treatment with SOLTAMOX:- sudden chest pain, shortness of breath, or coughing up blood
- pain, tenderness, or swelling in one or both of your legs
- Stroke. Stroke can cause serious problems and can lead to death. Get medical help right away if you get any of these symptoms of a stroke:
- sudden weakness, tingling, or numbness of your face, arm or leg, especially on one side of your body
- sudden confusion, trouble speaking or understanding
- sudden trouble seeing in one or both eyes
- sudden trouble walking, dizziness, loss of balance or coordination
- sudden severe headache with no known cause
What is SOLTAMOX?
SOLTAMOX is a prescription medicine used:
- to treat adults with estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer that has spread to other parts of the body (metastatic)
- to treat adults with early stage estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer after surgery and radiation for breast cancer
- to reduce the chance of developing breast cancer in the other breast in adults after surgery and radiation for breast cancer
- to reduce the risk of invasive breast cancer in adult women with DCIS, after breast surgery and radiation treatment
- to reduce the risk of getting breast cancer in women with a high risk of getting breast cancer
It is not known if SOLTAMOX is safe and effective in children.
Do not take SOLTAMOX if you:
- have had a serious allergic reaction to tamoxifen or any other ingredient in SOLTAMOX. Ask your healthcare provider if you are not sure.
- have DCIS or a high-risk of breast cancer, and you
Before taking SOLTAMOX, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
- have uterine cancer or other problems with your uterus.
- have irregular menstrual periods, no menstrual periods, or abnormal vaginal bleeding
- have or had a blood clot in your veins or lungs
- have had a stroke
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. SOLTAMOX can harm your unborn baby.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if SOLTAMOX passes into your breast milk. You should not breastfeed during treatment with SOLTAMOX and for 3 months after the last dose.
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them to show to your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get a new medicine.
How should I take SOLTAMOX?
- Take SOLTAMOX exactly as your healthcare provider tells you to take it.
- Your healthcare provider will tell you how much SOLTAMOX to take and when to take it.
- Your healthcare provider will decide how long you should continue to take SOLTAMOX, depending on your medical condition.
- Do not stop taking SOLTAMOX without first talking with your healthcare provider.
- Use the dosing cup that comes with SOLTAMOX to measure the correct amount for each dose. Ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist if you are not sure how to measure your dose.
- If you forget a dose of SOLTAMOX, take it when you remember, then take the next dose at your usual time. If it is almost time for your next dose, skip the missed dose. Just take the next dose at your regular time. Do not take 2 doses at the same time. If you are not sure about your dosing, call your healthcare provider.
- If you take too much SOLTAMOX, call your healthcare provider right away.
What are the possible side effects of SOLTAMOX?
SOLTAMOX can cause serious side effects, including:
- See "
- Liver problems, including liver cancer. SOLTAMOX can cause changes in liver function blood tests, and sometimes can cause liver cancer and other serious liver problems that can lead to death. Your healthcare provider should do blood tests to check you for these problems during treatment with SOLTAMOX.
- Other cancers.
- High levels of calcium in the blood (hypercalcemia). People with breast cancer that has spread to their bones may develop hypercalcemia. Hypercalcemia can happen within a few weeks after you start taking SOLTAMOX. Your healthcare provider should check you for this problem. If it is severe, your healthcare provider may tell you to stop taking SOLTAMOX.
- Decreased blood cell counts. SOLTAMOX can cause a decrease in platelet counts, red blood cell counts, and white blood cell counts that can be severe. Your healthcare provider should check your blood counts during treatment with SOLTAMOX.
- Eye problems. SOLTAMOX can increase your chance of developing cataracts and other eye problems. Tell your healthcare provider about any changes in your vision or other eye symptoms during treatment with SOLTAMOX.
The most common side effects of SOLTAMOX include:
- hot flashes
- mood changes
- vaginal discharge
- vaginal bleeding. See "
- nausea
- swelling (fluid retention)
Tell your healthcare provider if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away.
These are not all the possible side effects of SOLTAMOX.
Call your healthcare provider for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store SOLTAMOX?
- Store SOLTAMOX at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
- Keep SOLTAMOX in the original bottle to protect it from light.
- Keep the bottle tightly closed.
- Use within 3 months of opening. Throw away any SOLTAMOX remaining in the bottle after 3 months.
Keep SOLTAMOX and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about the safe and effective use of SOLTAMOX.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use SOLTAMOX for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give SOLTAMOX to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. If you would like more information, talk with your healthcare provider. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about SOLTAMOX that is written for health professionals.
What are the ingredients in SOLTAMOX?
Active ingredient: tamoxifen citrate
Inactive ingredients: ethanol, glycerol, propylene glycol, sorbitol solution, licorice flavor, aniseed flavor, purified water.
Distributed by:
The brands listed (other than SOLTAMOX
For more information, call 1-844-825-8500.
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Revised: 11/2020
F8UD1W4JB2
10PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 150 mL Container Carton
NDC 51862-682-01
SUGAR
soltamox
equivalent to
Rx only
150 mL