Brand Name
Pegasys
Generic Name
PEGinterferon Alfa-2A
View Brand Information FDA approval date: October 16, 2002
Classification: Interferon alpha
Form: Injection
What is Pegasys (PEGinterferon Alfa-2A)?
PEGASYS is an inducer of the innate immune response indicated for the treatment of Chronic Hepatitis C .
Approved To Treat
Save this treatment for later
Not sure about your diagnosis?
Related Clinical Trials
A Pilot Study of the Combination of VIR-2218 and Peginterferon Alfa-2a for Chronic Hepatitis B
Background: Chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection affects 292 million people worldwide; 887,000 die each year from cirrhosis, liver cancer, and related issues. Treatment options are limited.
Randomized, Open-Label Study of the Bria-IMT Regimen and Check Point Inhibitor vs Physicians' Choice in Advanced Metastatic Breast Cancer.
Summary: This is a multicenter randomized, open label study to evaluate overall survival with the Bria-IMT regimen in combination with Checkpoint Inhibitor \[Retifanlimab\], versus Treatment of Patients'/Physicians' Choice (TPC) in advanced metastatic or locally recurrent breast cancer (aMBC) patients with no approved alternative therapies available.
Related Latest Advances
Brand Information
Pegasys (peginterferon alfa-2a)
1DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
PEGASYS is a colorless to slightly yellowish solution available as:
- Injection: 180 mcg/mL in a single-dose vial
- Injection: 180 mcg/0.5 mL in a single-dose prefilled syringe
2CONTRAINDICATIONS
PEGASYS is contraindicated in patients with:
- Known hypersensitivity reactions such as urticaria, angioedema, bronchoconstriction, anaphylaxis, or Stevens-Johnson syndrome to alpha interferons, including PEGASYS, or any of its components.
- Autoimmune hepatitis
- Hepatic decompensation (Child-Pugh score greater than 6 [class B and C]) in cirrhotic patients before treatment
- Hepatic decompensation with Child-Pugh score greater than or equal to 6 in cirrhotic CHC patients coinfected with HIV before treatment
PEGASYS is contraindicated in neonates and infants because it contains benzyl alcohol. Benzyl alcohol is associated with an increased incidence of neurologic and other complications which are sometimes fatal in neonates and infants.
When PEGASYS is used in combination with other HCV antiviral drugs, the contraindications applicable to those agents are applicable to combination therapies. PEGASYS combination treatment with ribavirin is contraindicated in women who are pregnant and men whose female partners are pregnant
Refer to the prescribing information of the other HCV antiviral drugs, including ribavirin, for a list of their contraindications.
3WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Refer to the prescribing information of the other HCV antiviral drugs, including ribavirin, for their Warnings and Precautions.
3.1Pregnancy: Use with ribavirin
Ribavirin may cause birth defects and/or death of the exposed fetus.Patients must avoid pregnancy (female patients or female partners of male patients) while taking PEGASYS and ribavirin combination therapy. Ribavirin therapy should not be started unless a confirmed negative pregnancy test has been obtained immediately prior to initiation of therapy. Women of childbearing potential and men must use two forms of effective contraception during treatment and for at least 6 months after treatment has concluded. Routine monthly pregnancy tests must be performed during this time [see .
3.2Neuropsychiatric Reactions
Life-threatening or fatal neuropsychiatric reactions may manifest in all patients receiving therapy with PEGASYS and include suicide, suicidal ideation, homicidal ideation, depression, relapse of drug addiction, and drug overdose. These reactions may occur in patients with and without previous psychiatric illness.
PEGASYS should be used with extreme caution in all patients who report a history of depression. Neuropsychiatric adverse events observed with alpha interferon treatment include aggressive behavior, psychoses, hallucinations, bipolar disorders, and mania. Physicians should monitor all patients for evidence of depression and other psychiatric symptoms. Patients should be advised to report any sign or symptom of depression or suicidal ideation to their prescribing physicians. In severe cases, therapy should be stopped immediately and psychiatric intervention instituted
3.3Cardiovascular Disorders
Hypertension, supraventricular arrhythmias, chest pain, and myocardial infarction have been observed in patients treated with PEGASYS. PEGASYS should be administered with caution to patients with pre-existing cardiac disease. Because cardiac disease may be worsened by ribavirin-induced anemia, patients with a history of significant or unstable cardiac disease should not receive PEGASYS/ribavirin
3.4Bone Marrow Suppression
PEGASYS suppresses bone marrow function and may result in severe cytopenias. Ribavirin may potentiate the neutropenia and lymphopenia induced by alpha interferons including PEGASYS. Very rarely, alpha interferons may be associated with aplastic anemia. It is advised that complete blood counts (CBC) be obtained pre-treatment and monitored routinely during therapy
PEGASYS/ribavirin should be used with caution in patients with baseline neutrophil counts less than 1,500 cells/mm
Severe neutropenia and thrombocytopenia occur with a greater incidence in HIV coinfected patients than monoinfected patients and may result in serious infections or bleeding
Pancytopenia (marked decreases in RBCs, neutrophils and platelets) and bone marrow suppression have been reported in the literature to occur within 3 to 7 weeks after the concomitant administration of pegylated interferon/ribavirin and azathioprine. In this limited number of patients (n=8), myelotoxicity was reversible within 4 to 6 weeks upon withdrawal of both HCV antiviral therapy and concomitant azathioprine and did not recur upon reintroduction of either treatment alone. PEGASYS, ribavirin, and azathioprine should be discontinued for pancytopenia, and pegylated interferon/ribavirin should not be re-introduced with concomitant azathioprine.
3.5Autoimmune Disorders
Development or exacerbation of autoimmune disorders including myositis, hepatitis, thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura, idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis, interstitial nephritis, thyroiditis, and systemic lupus erythematosus have been reported in patients receiving alpha interferon. PEGASYS should be used with caution in patients with autoimmune disorders
3.6Endocrine Disorders
PEGASYS causes or aggravates hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism. Hyperglycemia, hypoglycemia, and diabetes mellitus have been observed to develop in patients treated with PEGASYS. Patients with these conditions at baseline who cannot be effectively treated by medication should not begin PEGASYS therapy. Patients who develop these conditions during treatment and cannot be controlled with medication may require discontinuation of PEGASYS therapy.
3.7Ophthalmologic Disorders
Decrease or loss of vision, retinopathy including macular edema, retinal artery or vein thrombosis, retinal hemorrhages and cotton wool spots, optic neuritis, papilledema and serous retinal detachment are induced or aggravated by treatment with PEGASYS or other alpha interferons. All patients should receive an eye examination at baseline. Patients with pre-existing ophthalmologic disorders (e.g., diabetic or hypertensive retinopathy) should receive periodic ophthalmologic exams during interferon alpha treatment. Any patient who develops ocular symptoms should receive a prompt and complete eye examination. PEGASYS treatment should be discontinued in patients who develop new or worsening ophthalmologic disorders.
3.8Cerebrovascular Disorders
Ischemic and hemorrhagic cerebrovascular events have been observed in patients treated with interferon alfa-based therapies, including PEGASYS. Events occurred in patients with few or no reported risk factors for stroke, including patients less than 45 years of age. Because these are spontaneous reports, estimates of frequency cannot be made and a causal relationship between interferon alfa-based therapies and these events is difficult to establish
3.9Hepatic Failure and Hepatitis Exacerbations
Chronic hepatitis C (CHC) patients with cirrhosis may be at risk of hepatic decompensation and death when treated with alpha interferons, including PEGASYS. Cirrhotic CHC patients coinfected with HIV receiving highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) and interferon alfa-2a with or without ribavirin appear to be at increased risk for the development of hepatic decompensation compared to patients not receiving HAART. In Study 7
Exacerbations of hepatitis during hepatitis B therapy are not uncommon and are characterized by transient and potentially severe increases in serum ALT. Chronic hepatitis B subjects experienced transient acute exacerbations (flares) of hepatitis B (ALT elevation greater than 10-fold higher than the upper limit of normal) during PEGASYS treatment (12% and 18%) and post-treatment (7% and 12%) in HBeAg-negative and HBeAg-positive subjects, respectively. Marked transaminase flares while on PEGASYS therapy have been accompanied by other liver test abnormalities. Patients experiencing ALT flares should receive more frequent monitoring of liver function. PEGASYS dose reduction should be considered in patients experiencing transaminase flares. If ALT increases are progressive despite reduction of PEGASYS dose or are accompanied by increased bilirubin or evidence of hepatic decompensation, PEGASYS should be immediately discontinued
3.10Pulmonary Disorders
Dyspnea, pulmonary infiltrates, pneumonia, bronchiolitis obliterans, interstitial pneumonitis, pulmonary hypertension and sarcoidosis, some resulting in respiratory failure and/or patient deaths, may be induced or aggravated by PEGASYS or alpha interferon therapy. Recurrence of respiratory failure has been observed with interferon rechallenge. PEGASYS combination treatment should be suspended in patients who develop pulmonary infiltrates or pulmonary function impairment. Patients who resume interferon treatment should be closely monitored.
3.11Infections
While fever may be associated with the flu-like syndrome reported commonly during interferon therapy, other causes of high or persistent fever must be ruled out, particularly in patients with neutropenia. Serious and severe infections (bacterial, viral, or fungal), some fatal, have been reported during treatment with alpha interferons including PEGASYS. Appropriate anti-infective therapy should be started immediately and discontinuation of therapy should be considered
3.12Colitis
Ulcerative and hemorrhagic/ischemic colitis, sometimes fatal, have been observed within 12 weeks of starting alpha interferon treatment. Abdominal pain, bloody diarrhea, and fever are the typical manifestations of colitis. PEGASYS should be discontinued immediately if these symptoms develop. The colitis usually resolves within 1 to 3 weeks of discontinuation of alpha interferon.
3.13Pancreatitis
Pancreatitis, sometimes fatal, has occurred during alpha interferon and ribavirin treatment. PEGASYS/ribavirin should be suspended if symptoms or signs suggestive of pancreatitis are observed. PEGASYS/ribavirin should be discontinued in patients diagnosed with pancreatitis.
3.14Hypersensitivity
Severe acute hypersensitivity reactions (e.g., urticaria, angioedema, bronchoconstriction, and anaphylaxis) have been observed during alpha interferon and ribavirin therapy. If such reaction occurs, therapy with PEGASYS/ribavirin should be discontinued and appropriate medical therapy immediately instituted. Serious skin reactions including vesiculobullous eruptions, reactions in the spectrum of Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (erythema multiforme major) with varying degrees of skin and mucosal involvement and exfoliative dermatitis (erythroderma) have been reported in patients receiving PEGASYS with and without ribavirin. Patients developing signs or symptoms of severe skin reactions must discontinue therapy
3.15Impact on Growth in Pediatric Patients
Growth inhibition was observed in CHC pediatric subjects 5 to 17 years of age during combination therapy for up to 48 weeks with PEGASYS plus ribavirin. At the end of treatment, 43% of subjects were more than 15 percentiles below their baseline weight curve, and 25% of subjects were more than 15 percentiles below their baseline height curve. At the end of 2 years follow-up after treatment, most subjects had returned to baseline normative curve percentiles for weight and height; 16% of subjects were more than 15 percentiles below their baseline weight curve and 11% were more than 15 percentiles below their baseline height curve.
The available longer-term data on subjects who were followed up to 6 years post-treatment are too limited to determine the risk of reduced adult height in some patients
Growth inhibition was also observed in CHB pediatric subjects 3 to 17 years of age during therapy with PEGASYS lasting up to 48 weeks. At Week 48 of treatment 13% of subjects were more than 15 percentiles below their baseline weight curve and 6% were more than 15 percentiles below their baseline height curve. At 24 weeks after the end of treatment, 11% of subjects were more than 15 percentiles below their baseline weight curve and 12% were more than 15 percentiles below their baseline height curve. At 5 years post-treatment the percentage of subjects with decrease of more than 15 percentiles from baseline was 29% for weight and 18% for height.
3.16Peripheral Neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy has been reported when alpha interferons were given in combination with telbivudine. In one clinical trial, an increased risk and severity of peripheral neuropathy was observed with the combination use of telbivudine and PEGASYS as compared to telbivudine alone. The safety and efficacy of telbivudine in combination with interferons for the treatment of CHB have not been demonstrated.
3.17Laboratory Tests
Before beginning PEGASYS or PEGASYS combination therapy, standard hematological and biochemical laboratory tests are recommended for all patients. Pregnancy screening for women of childbearing potential must be performed. Patients who have pre-existing cardiac abnormalities should have electrocardiograms administered before treatment with PEGASYS/ribavirin.
After initiation of therapy, hematological tests should be performed at 2 weeks and 4 weeks and biochemical tests should be performed at 4 weeks. Additional testing should be performed periodically during therapy. In adult clinical studies, the CBC (including hemoglobin level and white blood cell and platelet counts) and chemistries (including liver function tests and uric acid) were measured at 1, 2, 4, 6, and 8 weeks, and then every 4 to 6 weeks or more frequently if abnormalities were found. In a pediatric clinical trial, hematological and chemistry assessments were at 1, 3, 5, and 8 weeks, then every 4 weeks. Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) was measured every 12 weeks. Monthly pregnancy testing should be performed during combination therapy and for 6 months after discontinuing therapy.
The entrance criteria used for the clinical studies of PEGASYS may be considered as a guideline to acceptable baseline values for initiation of treatment:
- Platelet count greater than or equal to 90,000 cells/mm
- Absolute neutrophil count (ANC) greater than or equal to 1,500 cells/mm
- Serum creatinine concentration less than 1.5 × upper limit of normal
- TSH and T
- CD4+ cell count greater than or equal to 200 cells/mm
- Hemoglobin greater than or equal to 12 g/dL for women and greater than or equal to 13 g/dL for men in CHC monoinfected subjects
- Hemoglobin greater than or equal to 11 g/dL for women and greater than or equal to 12 g/dL for men in subjects with CHC and HIV
4ADVERSE REACTIONS
In clinical trials, a broad variety of serious adverse reactions were observed in 1,010 subjects who received PEGASYS at doses of 180 mcg for 48 weeks, alone or in combination with ribavirin
4.1Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying and controlled conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug, and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
4.2Immunogenicity
As with all therapeutic proteins, there is potential for immunogenicity. The detection of antibody formation is highly dependent on the sensitivity and specificity of the assay. Additionally, the observed incidence of antibody (including neutralizing antibody) positivity in an assay may be influenced by several factors including assay methodology, sample handling, timing of sample collection, concomitant medications, and underlying disease. For these reasons, comparison of the incidence of antibodies to peginterferon alfa-2a in the studies described below with the incidence of antibodies in other studies or to other products may be misleading.
4.3Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified and reported during post-approval use of PEGASYS therapy. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Blood and lymphatic system disorders:pure red cell aplasia
Ear and labyrinth disorders:hearing impairment, hearing loss
Gastrointestinal disorders:tongue pigmentation
Immune system disorders:liver graft rejection and renal graft rejection [see
Infections and infestations:limb abscess
Metabolism and nutrition disorders:dehydration
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders:serious skin reactions
Neurological:seizures
5OVERDOSAGE
There is limited experience with overdosage. The maximum dose received by any patient was 7 times the intended dose of PEGASYS (180 mcg/day for 7 days). There were no serious reactions attributed to overdosages. Weekly doses of up to 630 mcg have been administered to patients with cancer. Dose-limiting toxicities were fatigue, elevated liver enzymes, neutropenia, and thrombocytopenia. There is no specific antidote for PEGASYS. Hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis are not effective.
6DESCRIPTION
Peginterferon alfa-2a, is a covalent conjugate of recombinant alfa-2a interferon (approximate molecular weight [MW] 20,000 daltons) with a single branched bis-monomethoxy polyethylene glycol (PEG) chain (approximate MW 40,000 daltons). The PEG moiety is linked at a single site to the interferon alfa moiety via a stable amide bond to lysine. Peginterferon alfa-2a has an approximate molecular weight of 60,000 daltons. Interferon alfa-2a is produced using recombinant DNA technology in which a cloned human leukocyte interferon gene is inserted into and expressed in
PEGASYS is a sterile, preservative-free, colorless to slightly yellowish solution available as an injection and is administered subcutaneously.
Each vial of 180 mcg/mL peginterferon alfa-2a (expressed as the amount of interferon alfa-2a) also contains acetic acid (0.05 mg), benzyl alcohol (10 mg), polysorbate 80 (0.05 mg), sodium acetate trihydrate (2.62 mg), and sodium chloride (8 mg) at pH 6 ± 0.5.
Each prefilled syringe of 180 mcg/0.5 mL peginterferon alfa-2a (expressed as the amount of interferon alfa-2a) also contains acetic acid (0.0231 mg), benzyl alcohol (5 mg), polysorbate 80 (0.025 mg), sodium acetate trihydrate (1.3085 mg), and sodium chloride (4 mg) at pH 6 ± 0.5.
7HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
PEGASYS (peginterferon alfa-2a) injection is a sterile, preservative-free, colorless to slightly yellowish solution administered subcutaneously.
8PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (
Patients receiving PEGASYS alone or in combination with an approved HCV antiviral drug should be directed in its appropriate use, informed of the benefits and risks associated with treatment, and referred to FDA-approved patient labeling (
9Instructions for Use PEGASYS ®(PEG-ah-sis) (peginterferon alfa-2a) Injection For Subcutaneous Use Prefilled Syringe
First read the
PEGASYS prefilled syringes come in a Monthly Convenience Pack that contains 4 prefilled syringes of PEGASYS in a box with 4 needles. Each needle has a needle-stick protection device.
Before starting, collect all of the supplies that you will need to use for preparing and injecting PEGASYS. You will need the following supplies:
- 1 single-dose disposable prefilled syringe of PEGASYS
- 1 needle with needle-stick protection device
- several alcohol pads
- You will also need a puncture-resistant disposable container to throw away used prefilled syringes and needles as soon as you finish your injection. See "
Important:
- Never reuse disposable prefilled syringes and needles.
- Throw away the prefilled syringe of PEGASYS after you use it 1 time, even if there is any medicine left in it.
- Do notshake PEGASYS. If shaken, PEGASYS may not work properly.
How should I prepare a dose of PEGASYS?
- Find a well-lit, clean, flat surface such as a table.
- Take a carton containing PEGASYS out of the refrigerator. Check the date on the carton the PEGASYS comes in. Make sure the expiration date has not passed. Do not use if the expiration date has passed (see
- Figure A:
- Remove the prefilled syringe of PEGASYS from the carton. Look at the prefilled syringe of PEGASYS. The solution should be clear and colorless to slightly yellowish, without particles (see
- Figure B:
- Do notuse the prefilled syringe of PEGASYS if:
- the medicine remains cloudy after a few minutes at room temperature
- has particles
- the medicine is not colorless to slightly yellowish
- the expiration date has passed (see
- Figure C:
- Wash your hands well with soap and warm water. Keep your work area, your hands, and injection site clean to decrease the risk of infection.
- Lay the syringe on a flat clean surface and wait a few minutes until it reaches room temperature. If you notice condensation water on the outside of the syringe, wait another few minutes until it disappears.
How do I attach the needle to the PEGASYS prefilled syringe?
- Remove the needle from its package.
- Figure D:
- Remove and throw away the rubber cap from the tip of the syringe barrel (see
- Figure E:
- With one hand, hold the syringe by the barrel. With your other hand, hold the needle close to the hub where the green needle cover connects to the syringe (see
- Figure F:
- Push the needle onto the syringe and tighten by using an easy twisting motion in the direction of the arrow (see
- Figure G:
- Here is a picture of what the syringe will look like after you finish attaching the needle (see
- Figure H:
- Lay the syringe and needle down on your clean work surface. Be sure that the plastic needle shield covers the needle. Never let the needle touch any surface.
How should I choose a site for injection?
- You can inject PEGASYS under the skin on your stomach or thigh (see
- Figure I:
- Clean the area using an alcohol pad. Let the skin air dry.
How do I prepare the PEGASYS prefilled syringe for injection?
- Pull the green needle cover back from the needle toward the syringe barrel. The green needle cover will stay in the position you set. Do not remove it. This is the needle-stick protection device (see
- Figure J:
- Hold the syringe and needle tightly at the hub. Gently rock the plastic needle shield back and forth to prepare for removal. Remove the plastic needle shield by pulling it straight off (see
- Figure K:
- Remove air bubbles from the syringe.
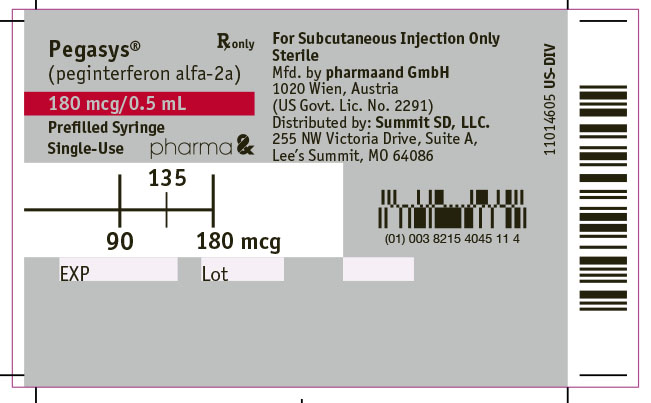
- Depending on the dose of PEGASYS that your healthcare provider prescribes, you may have to get rid of (discard) some of the medicine from the prefilled syringe before you inject the medicine. The syringe has markings for 180 mcg, 135 mcg, and 90 mcg. Your healthcare provider will tell you which mark to use (see
- Do notdecrease or increase your dose of PEGASYS unless your healthcare provider tells you to.
How do I give the injection of PEGASYS?
- Position the point of the needle (the bevel) so it is facing up (see
- Figure O:
- Pinch a fold of skin on your stomach or thigh firmly with your thumb and forefinger (see
- Figure P:
- Hold the syringe like a pencil at a 45° to 90° angle to your skin. With a quick "dart-like" motion, push the needle into the skin as far as it will go (see
- Figure Q:
- After the needle is inserted, remove the hand used to pinch the skin and use it to hold the syringe barrel.
- When the syringe is empty, pull the needle out of the skin. Wipe the area with an alcohol pad.
- To prevent needle-stick injuries, before you dispose of the syringe and needle, push the green needle cover toward the needle (see
- Throw away the used syringe and needle right away as described below. See “
How should I dispose of used syringes and needles?
- Put your used needles and syringes in a FDA-cleared sharps disposal container right away after use.
- If you do not have a FDA-cleared sharps disposal container, you may use a household container that is:
- When your sharps disposal container is almost full, you will need to follow your community guidelines for the right way to dispose of your sharps disposal container. There may be state or local laws about how you should throw away used needles and syringes. For more information about safe sharps disposal, and for specific information about sharps disposal in the state that you live in, go to the FDA's website at:
- Do not dispose of your used sharps disposal container in your household trash unless your community guidelines permit this. Do not recycle your used sharps disposal container.
Always keep the puncture-resistant container out of the reach of children.
How should I store PEGASYS?
- Store PEGASYS prefilled syringes in a refrigerator at 36°F to 46°F (2°C to 8°C).
- Do not leave PEGASYS out of the refrigerator for more than 24 hours.
- Do not freeze or shake PEGASYS.
- Protect PEGASYS from light.
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Revised: Februaury 2024
PEGASYS
Manufactured by:
pharmaand GmbH
Taborstrasse 1,
U.S. License No. 2291
Distributed by:
Summit SD, LLC.
255 Northwest Victoria Drive, Suite A
© 2023 pharmaand GmbH, All rights reserved.
10Instructions for Use PEGASYS ®(PEG-ah-sis) (peginterferon alfa-2a) Injection For Subcutaneous Use Vial
First read the
Before starting, collect all of the supplies that you will need to use for preparing and injecting PEGASYS. You will need the following supplies:
- 1 vial of PEGASYS
- 1 single-use disposable syringe and needle
- several alcohol pads
- You will also need a puncture-resistant disposable container to throw away used syringes, needles, and vials as soon as you finish your injection. See “
Follow your healthcare provider's instructions for the type of syringe and needle to use to prepare and inject your dose. If you will be injecting a child with PEGASYS, you will need a special syringe called a tuberculin syringe, which can measure doses of PEGASYS that are 1 milliliter (1mL) or less. When you get your prescription from the pharmacy, ask your pharmacist for the syringe and needle that you need to prepare and inject a dose of PEGASYS from the single-dose vial.
Important:
- Never reuse disposable syringes and needles.
- Throw away the vial of PEGASYS after you use it 1 time even if there is medicine left in the vial.
- Do not shake PEGASYS. If shaken, PEGASYS may not work properly.
How should I prepare a dose of PEGASYS?
- Find a well-lit, clean, flat working surface such as a table.
- Take a carton containing PEGASYS out of the refrigerator. Check the date on the carton the PEGASYS comes in. Make sure the expiration date has not passed. Do not use if the expiration date has passed (see
- Figure A:
- Wash your hands well with soap and warm water. Keep your work area, your hands, and injection site clean to decrease the risk of infection.
- Remove the vial of PEGASYS from the carton. Look at the vial of PEGASYS. The solution should be clear and colorless to slightly yellowish, without particles (see
- Figure B:
- Do not use the vial of PEGASYS if:
- Warm the refrigerated medicine by gently rolling it in the palms of your hands for about one minute. Do not shake PEGASYS.
- Remove (flip off) the plastic cap from the top of the PEGASYS vial (see
- If you are not sure how much medicine to use or which mark on the syringe to use, stop and call your healthcare provider right away.
- Open the package for the syringe you are using and if it does not have a needle attached, then attach a new needle to the syringe.
- Remove the protective cap from the needle on the syringe. Never let the needle touch any surface. Fill the syringe with air by pulling back on the plunger to the mark on the syringe barrel that matches the dose prescribed by your healthcare provider (see
- Figure E:
- Hold the vial of PEGASYS on your flat surface. Do not touch the cleaned rubber stopper.
- Push the needle straight down through the middle of the rubber stopper on the vial. Slowly inject all the air from the syringe into the air space above the solution. Do not inject air into the fluid (see
- Figure F:
- Keep the needle in the vial. Turn the vial upside down.
Make sure the tip of the needle is in the PEGASYS solution.- Slowly pull the plunger back to fill the syringe with PEGASYS solution to the dose (mL or cc markings on the syringe) that matches the dose prescribed by your healthcare provider (see
- Figure G:
- Do not remove the needle from the vial. Lay the vial and syringe on its side on your flat work surface until you are ready to inject the PEGASYS solution (see
- Figure H:
How should I choose a site for injection?
- You can inject PEGASYS under the skin on your stomach or thigh (see
- Figure I:
- Clean the area using an alcohol pad and let the skin air dry.
How should I give an injection?
- Pick up the vial and syringe from your flat work surface. Remove the syringe and needle from the vial.
- Remove air bubbles from the syringe.
- Position the point of the needle (the bevel) so it is facing up (see
- Figure K:
- Pinch a fold of skin on your stomach or thigh firmly between your thumb and forefinger (see
- Figure L:
- Hold the syringe like a pencil at a 45° to 90° angle to your skin. With a quick "dart-like" motion, push the needle into the skin as far as it will go (see
- Figure M:
- After the needle is inserted, remove the hand used to pinch the skin and use it to hold the syringe barrel.
- When the syringe is empty, pull the needle out of the skin. Wipe the area with an alcohol pad.
- Throw away the used syringe, needle, and vial. See “
How should I dispose of used syringes, needles, and vials?
- Put your used needles and syringes in a FDA-cleared sharps disposal container right away after use.
- If you do not have a FDA-cleared sharps disposal container, you may use a household container that is:
- When your sharps disposal container is almost full, you will need to follow your community guidelines for the right way to dispose of your sharps disposal container. There may be state or local laws about how you should throw away used needles and syringes. For more information about safe sharps disposal, and for specific information about sharps disposal in the state that you live in, go to the FDA's website at:
- Do not dispose of your used sharps disposal container in your household trash unless your community guidelines permit this. Do not recycle your used sharps disposal container.
How should I store PEGASYS?
- Store PEGASYS single-dose vials in a refrigerator at 36°F to 46°F (2°C to 8°C).
- Do not leave PEGASYS out of the refrigerator for more than 24 hours.
- Do not freeze or shake PEGASYS.
- Protect PEGASYS from light.
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Revised: February 2024
PEGASYS
Manufactured by:
Distributed by:
© 2023 pharmaand GmbH, All rights reserved.
11PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 180 mcg/1 mL Vial Box
NDC 82154-0449-1
Pegasys
(peginterferon alfa-2a)
(peginterferon alfa-2a)
180 mcg/1 mL
For Subcutaneous Use
For Single Use
Sterile
For Single Use
Sterile
ATTENTION PHARMACIST:
Each patient is required to
receive the enclosed
Medication Guide.
Each patient is required to
receive the enclosed
Medication Guide.
Refrigerate Immediately
Vial contains: 180 mcg/1 mL
Rx only


12PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 180 mcg/0.5 mL Syringe Box
NDC 82154-0451-4
ATTENTION PHARMACIST:
Refrigerate Immediately
Pegasys
(peginterferon alfa-2a)
(peginterferon alfa-2a)
Rx only
180 mcg/0.5 mL
For Subcutaneous Injection Only
Sterile
Prefilled Syringes Monthly Convenience Pack Package Contains:
4 Single-Use Prefilled Syringes Pegasys ®180 mcg/0.5 mL, NDC 82154-0451-1
4 Needles (27-gauge, 1/2-inch)
Sterile
Prefilled Syringes Monthly Convenience Pack Package Contains:
4 Single-Use Prefilled Syringes Pegasys ®180 mcg/0.5 mL, NDC 82154-0451-1
4 Needles (27-gauge, 1/2-inch)
Each Prefilled Syringe Contains: