Asprin
What is Asprin (Dipyridamole)?
Approved To Treat
Related Clinical Trials
Summary: This prospective study aims to compare functional abnormalities detected using myocardial perfusion SPECT imaging (MPI SPECT) with the extent and severity of anatomical findings on coronary computed tomography angiography (coronary CTA). Additionally, the investigators aim to enhance the diagnostic value of MPI SPECT by quantifying myocardial blood flow and utilizing myocardial flow reserve calcul...
Summary: This study aimed to investigate the effect of low-dose (100 mg) asprin on the prevention of gastric cancer in the early gastric cancer patients with negative H. pylori status who underwent endoscopic submucosal dissection.
Summary: The aim of this study is to document an optimized pharmacologic treatment for patients with Takotsubo Syndrome. There is currently no published documentation in a large number of patients. The study is a Randomized Registry Clinical Trial and in total 1000 patients registered in SWEDEHEART will be included.
Related Latest Advances
Brand Information
- Hypersensitivity [
- Allergy [
- Risk of Bleeding [
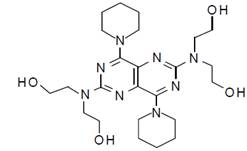
- Molecular formula: C
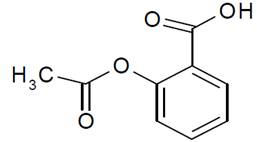
- Molecular formula: C
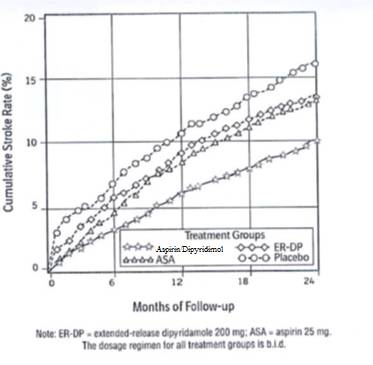
- Figure 1 ESPS2: Cumulative Stroke Rate (Fatal or Nonfatal)
- Risk of Bleeding
- Pregnancy
- Headaches
- Stress Test
- Dosage and Administration
- Storage

- are allergic to any of the ingredients in aspirin and extended-release dipyridamole capsules. See the end of this leaflet for a list of ingredients in aspirin and extended-release dipyridamole capsules.
- are allergic to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- have asthma in combination with runny nose and nasal polyps
- have stomach ulcers
- have a history of bleeding problems
- have heart problems
- have kidney or liver problems
- have low blood pressure
- have myasthenia gravis
- have any other medical conditions
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. You should not take aspirin and extended-release dipyridamole capsules during pregnancy without first talking to your healthcare provider. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you become pregnant while taking aspirin and extended-release dipyridamole capsules.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. Aspirin and extended-release dipyridamole capsules can pass into your milk. Talk to your healthcare provider about the best way to feed your baby if you take aspirin and extended-release dipyridamole capsules.
- a medicine for high blood pressure, irregular heart beat, or heart failure
- acetazolamide [Diamox
- any blood thinner medicines
- warfarin sodium [Coumadin
- a heparin medicine
- anagrelide [Agrylin
- a seizure medicine
- a medicine for Alzheimer's disease
- a water pill
- methotrexate sodium [Trexall
- aspirin or a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAIDs). You should not take NSAIDs during treatment with aspirin and extended-release dipyridamole capsules. Using these medicines with aspirin and extended-release dipyridamole capsules can increase your risk of bleeding.
- a medicine for diabetes
- probenecid [Probalan
- Take aspirin and extended-release dipyridamole capsules exactly as prescribed. Your healthcare provider will tell you how many aspirin and extended-release dipyridamole capsules to take and when to take them.
- Headaches are not uncommon when you first start taking aspirin and extended-release dipyridamole capsules, but often lessen as treatment continues. Tell your healthcare provider if you have a severe headache. Your healthcare provider may change the instructions for taking aspirin and extended-release dipyridamole capsules.
- Swallow aspirin and extended-release dipyridamole capsules whole. Do not crush or chew the capsules.
- You can take aspirin and extended-release dipyridamole capsules with or without food.
- If you miss a dose, take your next dose at the usual time. Do not take two doses at one time.
- If you take more aspirin and extended-release dipyridamole capsules (overdose) than prescribed, call your healthcare provider or Poison Control Center, or get emergency help right away.
- a warm feeling or flushing
- sweating
- restlessness
- weakness or dizziness
- a fast heart rate
- ringing in the ears
- heavy alcohol use. People who drink three or more alcoholic drinks every day have a higher risk of bleeding during treatment with aspirin and extended-release dipyridamole capsules, because it contains aspirin.
- increased risk of bleeding. You may bleed more easily during aspirin and extended-release dipyridamole capsules treatment, and it may take longer than usual for bleeding to stop. This can include:
- bleeding into your brain (intracranial hemorrhage). This can be a medical emergency. Get medical help right away if you have any of these symptoms while taking aspirin and extended-release dipyridamole capsules:
- severe headache with drowsiness
- confusion or memory change
- pass out (become unconscious)
- bleeding in your stomach or intestine.
- stomach pain
- heartburn or nausea
- vomiting blood or vomit looks like "coffee grounds"
- red or bloody stools
- black stools that look like tar
- bleeding into your brain (intracranial hemorrhage). This can be a medical emergency. Get medical help right away if you have any of these symptoms while taking aspirin and extended-release dipyridamole capsules:
- new or worsening chest pain in some people with heart disease. Tell your healthcare provider if you have new chest pain or have any change in your chest pain during treatment with aspirin and extended-release dipyridamole capsules.
- liver problems, including increased liver function tests and liver failure. Tell your healthcare provider if you have any of these symptoms of a liver problem while taking aspirin and extended-release dipyridamole capsules:
- loss of appetite
- pale colored stool
- stomach area (abdomen) pain
- yellowing of your skin or whites of your eyes
- dark urine
- itching
- headache
- upset stomach
- diarrhea
- Store aspirin and extended-release dipyridamole capsules at room temperature 59ºF to 86ºF (15ºC to 30ºC).
- Keep aspirin and extended-release dipyridamole capsules dry.





