Generic Name
Atazanavir
Brand Names
Reyataz, Evotaz
FDA approval date: June 24, 2003
Classification: Protease Inhibitor
Form: Tablet, Powder, Capsule
What is Reyataz (Atazanavir)?
Atazanavir capsules are indicated in combination with other antiretroviral agents for the treatment of HIV-1 infection in adults and in pediatric patients 6 years and older weighing at least 15 kg. Limitations of Use: Atazanavir is not recommended for use in pediatric patients below the age of 3 months due to the risk of kernicterus [see Use in Specific Populations.
Approved To Treat
Top Global Experts
There are no experts for this drug
Save this treatment for later
Not sure about your diagnosis?
Related Clinical Trials
There is no clinical trials being done for this treatment
Related Latest Advances
There is no latest advances for this treatment
Brand Information
REYATAZ (ATAZANAVIR)
1INDICATIONS AND USAGE
REYATAZ
Limitations of Use:
- REYATAZ is not recommended for use in pediatric patients below the age of 3 months due to the risk of kernicterus
- Use of REYATAZ with ritonavir in treatment-experienced patients should be guided by the number of baseline primary protease inhibitor resistance substitutions
2DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
REYATAZ Capsules:
- 200 mg capsule with blue cap and blue body, printed with white ink “BMS 200 mg” on the cap and with white ink “3631” on the body.
- 300 mg capsule with red cap and blue body, printed with white ink “BMS 300 mg” on the cap and with white ink “3622” on the body.
REYATAZ Oral Powder:
- 50 mg of atazanavir as an oral powder in a packet.
3CONTRAINDICATIONS
REYATAZ is contraindicated:
- in patients with previously demonstrated clinically significant hypersensitivity (eg, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, erythema multiforme, or toxic skin eruptions) to any of the components of REYATAZ capsules or REYATAZ oral powder
- when coadministered with drugs that are highly dependent on CYP3A or UGT1A1 for clearance, and for which elevated plasma concentrations of the interacting drugs are associated with serious and/or life-threatening events (see Table 6).
- when coadministered with drugs that are strong inducers of CYP3A due to the potential for loss of therapeutic effect and development of resistance.
Coadministration is contraindicated with, but not limited to, the following drugs listed in Table 6:
4ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the labeling:
- cardiac conduction abnormalities
- rash
- hyperbilirubinemia
- chronic kidney disease
- nephrolithiasis and cholelithiasis
4.1Clinical Trial Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
4.1.1Adverse Reactions in Treatment-Naive Adult Participants
The safety profile of REYATAZ in treatment-naive adults is based on 1625 participants with HIV-1 in clinical trials. 536 participants received REYATAZ 300 mg with ritonavir 100 mg and 1089 participants received REYATAZ 400 mg or higher (without ritonavir).
The most common adverse reactions were nausea, jaundice/scleral icterus, and rash.
Selected clinical adverse reactions of moderate or severe intensity reported in ≥ 2% of treatment-naive participants receiving combination therapy including REYATAZ 300 mg with ritonavir 100 mg and REYATAZ 400 mg (without ritonavir) are presented in Tables 7 and 8, respectively.
4.1.2Adverse Reactions in Treatment-Experienced Adult Participants
The safety profile of REYATAZ in treatment-experienced adults with HIV-1 is based on 119 participants with HIV-1 in clinical trials.
The most common adverse reactions are jaundice/scleral icterus and myalgia.
Selected clinical adverse reactions of moderate or severe intensity reported in ≥2% of treatment-experienced participants receiving REYATAZ with ritonavir are presented in Table 9.
4.1.3Laboratory Abnormalities in Treatment-Naive Participants
The percentages of adult treatment-naive participants with HIV-1 treated with combination therapy, including REYATAZ 300 mg with ritonavir 100 mg or REYATAZ 400 mg (without ritonavir) with Grade 3–4 laboratory abnormalities, are presented in Tables 10 and 11, respectively.
4.1.3.1Change in Lipids from Baseline in Treatment-Naive Participants with HIV-1
For Study AI424-138 and Study AI424-034, changes from baseline in LDL-cholesterol, HDL-cholesterol, total cholesterol, and triglycerides are shown in Tables 12 and 13, respectively.
4.1.4Laboratory Abnormalities in Treatment-Experienced Participants with HIV-1
The percentages of adult treatment-experienced participants with HIV-1 treated with combination therapy, including REYATAZ with ritonavir having Grade 3–4 laboratory abnormalities, are presented in Table 14.
4.1.4.1Change in Lipids from Baseline in Treatment-Experienced Participants with HIV-1
For Study AI424-045, changes from baseline in LDL-cholesterol, HDL-cholesterol, total cholesterol, and triglycerides are shown in Table 15. The observed magnitude of dyslipidemia was less with REYATAZ with ritonavir than with lopinavir/ritonavir. However, the clinical impact of such findings has not been demonstrated.
4.1.5Adverse Reactions in Pediatric Participants with HIV-1: REYATAZ Capsules
The safety and tolerability of REYATAZ Capsules with and without ritonavir have been established in pediatric participants with HIV-1, at least 6 years of age from the open-label, multicenter clinical trial PACTG 1020A.
The safety profile of REYATAZ in pediatric participants with HIV-1 (6 to less than 18 years of age) taking the capsule formulation was generally similar to that observed in clinical studies of REYATAZ in adults. The most common Grade 2–4 adverse events (≥5%, regardless of causality) reported in pediatric participants were cough (21%), fever (18%), jaundice/scleral icterus (15%), rash (14%), vomiting (12%), diarrhea (9%), headache (8%), peripheral edema (7%), extremity pain (6%), nasal congestion (6%), oropharyngeal pain (6%), wheezing (6%), and rhinorrhea (6%). Asymptomatic second-degree atrioventricular block was reported in <2% of participants. The most common Grade 3–4 laboratory abnormalities occurring in pediatric participants taking the capsule formulation were elevation of total bilirubin (≥3.2 mg/dL, 58%), neutropenia (9%), and hypoglycemia (4%). All other Grade 3–4 laboratory abnormalities occurred with a frequency of less than 3%.
4.1.6Adverse Reactions in Pediatric Participants with HIV-1: REYATAZ Oral Powder
The data described below reflect exposure to REYATAZ oral powder in 155 participants weighing at least 5 kg to less than 35 kg, including 134 participants exposed for 48 weeks. These data are from two pooled, open-label, multi-center clinical trials in treatment-naive and treatment-experienced pediatric participants with HIV-1 (AI424-397 [PRINCE I] and AI424-451 [PRINCE II]). Age ranged from 3 months to 10 years of age. In these studies, 51% were female and 49% were male. All participants received ritonavir and 2 nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs).
The safety profile of REYATAZ in pediatric participants taking REYATAZ oral powder was generally similar to that observed in clinical studies of REYATAZ in pediatric participants taking REYATAZ capsules. The most common Grade 3–4 laboratory abnormalities occurring in pediatric participants weighing 5 kg to less than 35 kg taking REYATAZ oral powder were increased amylase (33%), neutropenia (9%), increased SGPT/ALT (9%), elevation of total bilirubin (≥2.6 times ULN, 16%), and increased lipase (8%). All other Grade 3–4 laboratory abnormalities occurred with a frequency of less than 3%.
4.1.7Adverse Reactions in Participants with HIV-1 and Hepatitis B and/or Hepatitis C Virus
In Study AI424-138, 60 participants administered REYATAZ 300 mg with ritonavir 100 mg once daily, and 51 participants treated with lopinavir/ritonavir 400 mg/100 mg (as fixed-dose product) twice daily, each with fixed-dose tenofovir DF/emtricitabine, were seropositive for hepatitis B and/or C at study entry. ALT levels >5 times ULN developed in 10% (6/60) of the participants administered REYATAZ with ritonavir and 8% (4/50) of the participants treated with lopinavir/ritonavir. AST levels >5 times ULN developed in 10% (6/60) of the participants administered REYATAZ with ritonavir and none (0/50) of the participants treated with lopinavir/ritonavir.
In Study AI424-045, 20 participants administered REYATAZ 300 mg with ritonavir 100 mg once daily, and 18 participants treated with lopinavir/ritonavir 400 mg/100 mg twice daily (as fixed-dose product), were seropositive for hepatitis B and/or C at study entry. ALT levels >5 times ULN developed in 25% (5/20) of the participants administered REYATAZ with ritonavir and 6% (1/18) of the participants treated with lopinavir/ritonavir treated. AST levels >5 times ULN developed in 10% (2/20) of the participants administered REYATAZ with ritonavir and 6% (1/18) of the participants treated with lopinavir/ritonavir.
In Studies AI424-008 and AI424-034, 74 participants treated with REYATAZ 400 mg once daily, 58 who received efavirenz, and 12 who received nelfinavir were seropositive for hepatitis B and/or C at study entry. ALT levels >5 times ULN developed in 15% of the participants treated with REYATAZ, 14% of the participants treated with efavirenz, and 17% of the participants treated with nelfinavir. AST levels >5 times ULN developed in 9% of the participants treated with REYATAZ, 5% of the participants treated with efavirenz, and 17% of the participants treated with nelfinavir. Within REYATAZ and control regimens, no difference in frequency of bilirubin elevations was noted between seropositive and seronegative participants
4.2Postmarketing Experience
The following events have been identified during postmarketing use of REYATAZ. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of unknown size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Body as a Whole: edema
Cardiovascular System: second-degree AV block, third-degree AV block, left bundle branch block, QTc prolongation [see
Gastrointestinal System: pancreatitis
Hepatic System: hepatic function abnormalities
Hepatobiliary Disorders: cholelithiasis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)], cholecystitis, cholestasis
Metabolic System and Nutrition Disorders: diabetes mellitus, hyperglycemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]
Musculoskeletal System: arthralgia
Renal System: nephrolithiasis [see , interstitial nephritis, granulomatous interstitial nephritis, chronic kidney disease [see
Skin and Appendages: alopecia, maculopapular rash [see , pruritus, angioedema
5OVERDOSAGE
Human experience of acute overdose with REYATAZ is limited. Single doses up to 1200 mg (three times the 400 mg maximum recommended dose) have been taken by healthy participants without symptomatic untoward effects. A single self-administered overdose of 29.2 g of REYATAZ in a patient with HIV-1 (73 times the 400-mg recommended dose) was associated with asymptomatic bifascicular block and PR interval prolongation. These events resolved spontaneously. At REYATAZ doses resulting in high atazanavir exposures, jaundice due to indirect (unconjugated) hyperbilirubinemia (without associated liver function test changes) or PR interval prolongation may be observed
Treatment of overdosage with REYATAZ should consist of general supportive measures, including monitoring of vital signs and ECG, and observations of the patient’s clinical status. If indicated, elimination of unabsorbed atazanavir should be achieved by emesis or gastric lavage. Administration of activated charcoal may also be used to aid removal of unabsorbed drug. There is no specific antidote for overdose with REYATAZ. Since atazanavir is extensively metabolized by the liver and is highly protein bound, dialysis is unlikely to be beneficial in significant removal of this medicine.
6DESCRIPTION
The active ingredient in REYATAZ capsules and oral powder is atazanavir sulfate, which is an HIV-1 protease inhibitor.
The chemical name for atazanavir sulfate is (3
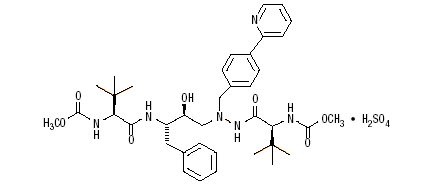
Atazanavir sulfate is a white to pale-yellow crystalline powder. It is slightly soluble in water (4-5 mg/mL, free base equivalent) with the pH of a saturated solution in water being about 1.9 at 24 ± 3°C.
REYATAZ Capsules are available for oral administration in strengths of 200 mg or 300 mg of atazanavir, which are equivalent to 227.8 mg or 341.69 mg of atazanavir sulfate, respectively. The capsules also contain the following inactive ingredients: crospovidone, lactose monohydrate, and magnesium stearate. The capsule shells contain the following inactive ingredients: gelatin, FD&C Blue No. 2, titanium dioxide, black iron oxide, red iron oxide, and yellow iron oxide. The capsules are printed with ink containing shellac, titanium dioxide, FD&C Blue No. 2, isopropyl alcohol, ammonium hydroxide, propylene glycol, n-butyl alcohol, simethicone, and dehydrated alcohol.
REYATAZ oral powder comes in a packet containing 50 mg of atazanavir equivalent to 56.9 mg of atazanavir sulfate in 1.5 g of powder. The powder is off-white to pale yellow and contains the following inactive ingredients: aspartame, sucrose, and orange-vanilla flavor.
7PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling
REYATAZ is not a cure for HIV-1 infection. Advise patients to remain under the care of a healthcare provider while using REYATAZ.
8Patient Package Insert
This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Revised: December 2024
[print code]
9Instructions for Use
Instructions for Use
REYATAZ
(atazanavir)
oral powder
REYATAZ
(atazanavir)
oral powder
Read this Instructions for Use before you prepare your child’s first dose of REYATAZ oral powder, each time you get a refill, and as needed. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking to your child’s healthcare provider about their medical condition or treatment. Ask your child’s healthcare provider or pharmacist if you have questions about how to mix or give a dose of REYATAZ oral powder.
Important information:
- For more information about REYATAZ oral powder, see the Patient Information leaflet.
- REYATAZ oral powder must be mixed with food or liquid. If REYATAZ oral powder is mixed with water, your child must eat food right after taking REYATAZ oral powder.
- REYATAZ oral powder must be taken with ritonavir.
- Talk with your child’s healthcare provider to help decide the best schedule for giving your child REYATAZ oral powder.
Instructions for mixing REYATAZ oral powder:
REYATAZ oral powder should be mixed with food such as applesauce or yogurt, instead of a liquid (milk, infant formula, or water) in young children and infants who can take food.
- Infants less than 6 months old and who cannot eat solid food or drink from a cup should be given REYATAZ oral powder mixed with infant formula using an oral dosing syringe.
- REYATAZ oral powder that is mixed in infant formula or liquid should not be given using a baby bottle.
When preparing REYATAZ oral powder with either food or liquid, choose a clean, flat work surface. Place a clean paper towel on the work surface. Place the supplies you will need on the paper towel.
Wash and dry your hands before and after preparing REYATAZ oral powder.
Preparing a dose of REYATAZ oral powder mixed with food:
Before you prepare a dose of REYATAZ oral powder mixed with food, gather the following supplies:
How should I store REYATAZ oral powder?
- Store REYATAZ oral powder at a temperature of 68°F to 86°F (20°C to 30°C).
- Store REYATAZ oral powder in the original packet. Do not open until ready to use.
- After REYATAZ oral powder is mixed with food or liquid, it may be kept at a temperature of 68°F to 86°F (20°C to 30°C) for up to 1 hour. Take REYATAZ oral powder within 1 hour after mixing with food or liquid.
- Keep REYATAZ oral powder and all medicines out of the reach of children.
- This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Distributed by:
Bristol-Myers Squibb Company
Princeton, NJ 08543 USA
10REYATAZ 150 mg Capsules Representative Packaging
See
NDC 0003-3624-12
Note to pharmacist: Do not cover ALERT box with pharmacy label.
ALERT: Find out about medicines that should NOT be taken with REYATAZ
ALERT: Find out about medicines that should NOT be taken with REYATAZ

11REYATAZ 200 mg Capsules Representative Packaging
NDC 0003-3631-12

12REYATAZ 300 mg Capsules Representative Packaging
NDC 0003-3622-12

13REYATAZ 50 mg Oral Powder Representative Packaging
NDC 0003-3638-10
