Generic Name
Tadalafil
Brand Names
Cialis, Adcirca, Opsynvi, Tadliq, ALYQ
FDA approval date: November 26, 2003
Classification: Phosphodiesterase 5 Inhibitor
Form: Tablet, Suspension
What is Cialis (Tadalafil)?
CIALIS ® is a phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitor indicated for the treatment of: erectile dysfunction .
Approved To Treat
Top Global Experts
There are no experts for this drug
Save this treatment for later
Not sure about your diagnosis?
Related Clinical Trials
There is no clinical trials being done for this treatment
Related Latest Advances
There is no latest advances for this treatment
Brand Information
Cialis (Tadalafil)
1DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Do not split CIALIS tablets; entire dose should be taken.
1.1CIALIS for Use as Needed for Erectile Dysfunction
- The recommended starting dose of CIALIS for use as needed in most patients is 10 mg, taken prior to anticipated sexual activity.
- The dose may be increased to 20 mg or decreased to 5 mg, based on individual efficacy and tolerability. The maximum recommended dosing frequency is once per day in most patients.
- CIALIS for use as needed was shown to improve erectile function compared to placebo up to 36 hours following dosing. Therefore, when advising patients on optimal use of CIALIS, this should be taken into consideration.
1.2CIALIS for Once Daily Use for Erectile Dysfunction
- The recommended starting dose of CIALIS for once daily use is 2.5 mg, taken at approximately the same time every day, without regard to timing of sexual activity.
- The CIALIS dose for once daily use may be increased to 5 mg, based on individual efficacy and tolerability.
1.3CIALIS for Once Daily Use for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
- The recommended dose of CIALIS for once daily use is 5 mg, taken at approximately the same time every day.
- When therapy for BPH is initiated with CIALIS and finasteride, the recommended dose of CIALIS for once daily use is 5 mg, taken at approximately the same time every day for up to 26 weeks.
1.4CIALIS for Once Daily Use for Erectile Dysfunction and Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
The recommended dose of CIALIS for once daily use is 5 mg, taken at approximately the same time every day, without regard to timing of sexual activity.
1.5Use with Food
CIALIS may be taken without regard to food.
2DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Four strengths of almond-shaped tablets are available in different sizes and different shades of yellow:
- 2.5 mg tablets debossed with “C 2 1/2”
- 5 mg tablets debossed with “C 5”
- 10 mg tablets debossed with “C 10”
- 20 mg tablets debossed with “C 20”
3WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Evaluation of erectile dysfunction and BPH should include an appropriate medical assessment to identify potential underlying causes, as well as treatment options.
Before prescribing CIALIS, it is important to note the following:
3.1Cardiovascular
Physicians should consider the cardiovascular status of their patients, since there is a degree of cardiac risk associated with sexual activity. Therefore, treatments for erectile dysfunction, including CIALIS, should not be used in men for whom sexual activity is inadvisable as a result of their underlying cardiovascular status. Patients who experience symptoms upon initiation of sexual activity should be advised to refrain from further sexual activity and seek immediate medical attention.
Physicians should discuss with patients the appropriate action in the event that they experience anginal chest pain requiring nitroglycerin following intake of CIALIS. In such a patient, who has taken CIALIS, where nitrate administration is deemed medically necessary for a life-threatening situation, at least 48 hours should have elapsed after the last dose of CIALIS before nitrate administration is considered. In such circumstances, nitrates should still only be administered under close medical supervision with appropriate hemodynamic monitoring. Therefore, patients who experience anginal chest pain after taking CIALIS should seek immediate medical attention.
Patients with left ventricular outflow obstruction, (e.g., aortic stenosis and idiopathic hypertrophic subaortic stenosis) can be sensitive to the action of vasodilators, including PDE5 inhibitors.
The following groups of patients with cardiovascular disease were not included in clinical safety and efficacy trials for CIALIS, and therefore until further information is available, CIALIS is not recommended for the following groups of patients:
- myocardial infarction within the last 90 days
- unstable angina or angina occurring during sexual intercourse
- New York Heart Association Class 2 or greater heart failure in the last 6 months
- uncontrolled arrhythmias, hypotension (<90/50 mm Hg), or uncontrolled hypertension
- stroke within the last 6 months.
As with other PDE5 inhibitors, tadalafil has mild systemic vasodilatory properties that may result in transient decreases in blood pressure. In a clinical pharmacology study, tadalafil 20 mg resulted in a mean maximal decrease in supine blood pressure, relative to placebo, of 1.6/0.8 mm Hg in healthy subjects
3.2Potential for Drug Interactions When Taking CIALIS for Once Daily Use
Physicians should be aware that CIALIS for once daily use provides continuous plasma tadalafil levels and should consider this when evaluating the potential for interactions with medications (e.g., nitrates, alpha-blockers, anti-hypertensives and potent inhibitors of CYP3A4) and with substantial consumption of alcohol
3.3Prolonged Erection
There have been rare reports of prolonged erections greater than 4 hours and priapism (painful erections greater than 6 hours in duration) for this class of compounds. Priapism, if not treated promptly, can result in irreversible damage to the erectile tissue. Patients who have an erection lasting greater than 4 hours, whether painful or not, should seek emergency medical attention.
CIALIS should be used with caution in patients who have conditions that might predispose them to priapism (such as sickle cell anemia, multiple myeloma, or leukemia), or in patients with anatomical deformation of the penis (such as angulation, cavernosal fibrosis, or Peyronie's disease).
3.4Effects on the Eye
Physicians should advise patients to stop use of all phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5) inhibitors, including CIALIS, and seek medical attention in the event of a sudden loss of vision in one or both eyes. Such an event may be a sign of non-arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy (NAION), a rare condition and a cause of decreased vision, including permanent loss of vision, that has been reported rarely postmarketing in temporal association with the use of all PDE5 inhibitors. Based on published literature, the annual incidence of NAION is 2.5-11.8 cases per 100,000 in males aged ≥50.
An observational case-crossover study evaluated the risk of NAION when PDE5 inhibitor use, as a class, occurred immediately before NAION onset (within 5 half-lives), compared to PDE5 inhibitor use in a prior time period. The results suggest an approximate 2-fold increase in the risk of NAION, with a risk estimate of 2.15 (95% CI 1.06, 4.34). A similar study reported a consistent result, with a risk estimate of 2.27 (95% CI 0.99, 5.20). Other risk factors for NAION, such as the presence of "crowded" optic disc, may have contributed to the occurrence of NAION in these studies.
Neither the rare postmarketing reports, nor the association of PDE5 inhibitor use and NAION in the observational studies, substantiate a causal relationship between PDE5 inhibitor use and NAION
Physicians should consider whether their patients with underlying NAION risk factors could be adversely affected by use of PDE5 inhibitors. Individuals who have already experienced NAION are at increased risk of NAION recurrence. Therefore, PDE5 inhibitors, including CIALIS, should be used with caution in these patients and only when the anticipated benefits outweigh the risks. Individuals with "crowded" optic disc are also considered at greater risk for NAION compared to the general population; however, evidence is insufficient to support screening of prospective users of PDE5 inhibitors, including CIALIS, for this uncommon condition.
Patients with known hereditary degenerative retinal disorders, including retinitis pigmentosa, were not included in the clinical trials, and use in these patients is not recommended.
3.5Sudden Hearing Loss
Physicians should advise patients to stop taking PDE5 inhibitors, including CIALIS, and seek prompt medical attention in the event of sudden decrease or loss of hearing. These events, which may be accompanied by tinnitus and dizziness, have been reported in temporal association to the intake of PDE5 inhibitors, including CIALIS. It is not possible to determine whether these events are related directly to the use of PDE5 inhibitors or to other factors
3.6Alpha-blockers and Antihypertensives
Physicians should discuss with patients the potential for CIALIS to augment the blood-pressure-lowering effect of alpha-blockers and antihypertensive medications
Caution is advised when PDE5 inhibitors are coadministered with alpha-blockers. PDE5 inhibitors, including CIALIS, and alpha-adrenergic blocking agents are both vasodilators with blood-pressure-lowering effects. When vasodilators are used in combination, an additive effect on blood pressure may be anticipated. In some patients, concomitant use of these two drug classes can lower blood pressure significantly
3.7Alcohol
Patients should be made aware that both alcohol and CIALIS, a PDE5 inhibitor, act as mild vasodilators. When mild vasodilators are taken in combination, blood-pressure-lowering effects of each individual compound may be increased. Therefore, physicians should inform patients that substantial consumption of alcohol (e.g., 5 units or greater) in combination with CIALIS can increase the potential for orthostatic signs and symptoms, including increase in heart rate, decrease in standing blood pressure, dizziness, and headache
3.8Concomitant Use of Potent Inhibitors of Cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4)
CIALIS is metabolized predominantly by CYP3A4 in the liver. The dose of CIALIS for use as needed should be limited to 10 mg no more than once every 72 hours in patients taking potent inhibitors of CYP3A4 such as ritonavir, ketoconazole, and itraconazole
3.9Combination With Other PDE5 Inhibitors or Erectile Dysfunction Therapies
The safety and efficacy of combinations of CIALIS and other PDE5 inhibitors or treatments for erectile dysfunction have not been studied. Inform patients not to take CIALIS with other PDE5 inhibitors, including ADCIRCA.
3.10Effects on Bleeding
Studies
3.11Counseling Patients About Sexually Transmitted Diseases
The use of CIALIS offers no protection against sexually transmitted diseases. Counseling patients about the protective measures necessary to guard against sexually transmitted diseases, including Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) should be considered.
3.12Consideration of Other Urological Conditions Prior to Initiating Treatment for BPH
Prior to initiating treatment with CIALIS for BPH, consideration should be given to other urological conditions that may cause similar symptoms. In addition, prostate cancer and BPH may coexist.
4OVERDOSAGE
Single doses up to 500 mg have been given to healthy subjects, and multiple daily doses up to 100 mg have been given to patients. Adverse events were similar to those seen at lower doses. In cases of overdose, standard supportive measures should be adopted as required. Hemodialysis contributes negligibly to tadalafil elimination.
5DESCRIPTION
CIALIS (tadalafil) is a selective inhibitor of cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP)-specific phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5). Tadalafil has the empirical formula C
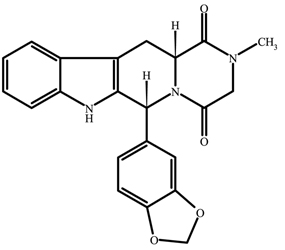
The chemical designation is pyrazino[1´,2´:1,6]pyrido[3,4-b]indole-1,4-dione, 6-(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-2,3,6,7,12,12a-hexahydro-2-methyl-, (6R,12aR)-. It is a crystalline solid that is practically insoluble in water and very slightly soluble in ethanol.
CIALIS is available as almond-shaped tablets for oral administration. Each tablet contains 2.5, 5, 10, or 20 mg of tadalafil and the following inactive ingredients: croscarmellose sodium, hydroxypropyl cellulose, hypromellose, iron oxide, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, sodium lauryl sulfate, talc, titanium dioxide, and triacetin.
6PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
“See FDA-approved patient labeling (
6.1Nitrates
Physicians should discuss with patients the contraindication of CIALIS with regular and/or intermittent use of organic nitrates. Patients should be counseled that concomitant use of CIALIS with nitrates could cause blood pressure to suddenly drop to an unsafe level, resulting in dizziness, syncope, or even heart attack or stroke.
Physicians should discuss with patients the appropriate action in the event that they experience anginal chest pain requiring nitroglycerin following intake of CIALIS. In such a patient, who has taken CIALIS, where nitrate administration is deemed medically necessary for a life-threatening situation, at least 48 hours should have elapsed after the last dose of CIALIS before nitrate administration is considered. In such circumstances, nitrates should still only be administered under close medical supervision with appropriate hemodynamic monitoring. Therefore, patients who experience anginal chest pain after taking CIALIS should seek immediate medical attention
6.2Guanylate Cyclase (GC) Stimulators
Physicians should discuss with patients the contraindication of CIALIS with any use of a GC stimulator, such as riociguat, for pulmonary arterial hypertension. Patients should be counseled that the concomitant use of CIALIS with GC stimulators may cause blood pressure to drop to an unsafe level.
6.3Cardiovascular Considerations
Physicians should consider the potential cardiac risk of sexual activity in patients with preexisting cardiovascular disease. Physicians should advise patients who experience symptoms upon initiation of sexual activity to refrain from further sexual activity and seek immediate medical attention
6.4Concomitant Use with Drugs Which Lower Blood Pressure
Physicians should discuss with patients the potential for CIALIS to augment the blood-pressure-lowering effect of alpha-blockers, and antihypertensive medications
6.5Potential for Drug Interactions When Taking CIALIS for Once Daily Use
Physicians should discuss with patients the clinical implications of continuous exposure to tadalafil when prescribing CIALIS for once daily use, especially the potential for interactions with medications (e.g., nitrates, alpha-blockers, antihypertensives and potent inhibitors of cytochrome P450 3A4) and with substantial consumption of alcohol.
6.6Priapism
There have been rare reports of prolonged erections greater than 4 hours and priapism (painful erections greater than 6 hours in duration) for this class of compounds. Priapism, if not treated promptly, can result in irreversible damage to the erectile tissue. Physicians should advise patients who have an erection lasting greater than 4 hours, whether painful or not, to seek emergency medical attention.
6.7Sudden Loss of Vision
Physicians should advise patients to stop use of all PDE5 inhibitors, including CIALIS, and seek medical attention in the event of a sudden loss of vision in one or both eyes. Such an event may be a sign of non-arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy (NAION), a cause of decreased vision, including possible permanent loss of vision, that has been reported rarely postmarketing in temporal association with the use of all PDE5 inhibitors. Physicians should discuss with patients the increased risk of NAION in individuals who have already experienced NAION in one eye. Physicians should also discuss with patients the increased risk of NAION among the general population in patients with a "crowded" optic disc, although evidence is insufficient to support screening of prospective users of PDE5 inhibitors, including CIALIS, for this uncommon condition
6.8Sudden Hearing Loss
Physicians should advise patients to stop taking PDE5 inhibitors, including CIALIS, and seek prompt medical attention in the event of sudden decrease or loss of hearing. These events, which may be accompanied by tinnitus and dizziness, have been reported in temporal association to the intake of PDE5 inhibitors, including CIALIS. It is not possible to determine whether these events are related directly to the use of PDE5 inhibitors or to other factors
6.9Alcohol
Patients should be made aware that both alcohol and CIALIS, a PDE5 inhibitor, act as mild vasodilators. When mild vasodilators are taken in combination, blood-pressure-lowering effects of each individual compound may be increased. Therefore, physicians should inform patients that substantial consumption of alcohol (e.g., 5 units or greater) in combination with CIALIS can increase the potential for orthostatic signs and symptoms, including increase in heart rate, decrease in standing blood pressure, dizziness, and headache
6.10Sexually Transmitted Disease
The use of CIALIS offers no protection against sexually transmitted diseases. Counseling of patients about the protective measures necessary to guard against sexually transmitted diseases, including Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) should be considered.
6.11Recommended Administration
Physicians should instruct patients on the appropriate administration of CIALIS to allow optimal use.
For CIALIS for use as needed in men with ED, patients should be instructed to take one tablet at least 30 minutes before anticipated sexual activity. In most patients, the ability to have sexual intercourse is improved for up to 36 hours.
For CIALIS for once daily use in men with ED or ED/BPH, patients should be instructed to take one tablet at approximately the same time every day without regard for the timing of sexual activity. Cialis is effective at improving erectile function over the course of therapy.
For CIALIS for once daily use in men with BPH, patients should be instructed to take one tablet at approximately the same time every day.