Primaxin
What is Primaxin (Imipenem)?
Approved To Treat
Top Global Experts
Related Clinical Trials
Summary: The goal of this clinical trial is to learn if oral treatment with pivmecillinam is effective to treat febrile urinary tract infections in adult patients. Hospitalized patients who have received 2-4 days of intravenous antibiotic therapy for febrile urinary tract infections, and have responded to treatment, will be randomized to either pivmecillinam or standard treatment (other oral or intravenous...
Summary: The goal of this clinical trial is to repurpose cilastatin for preventing acute kidney injury (AKI) in hospitalized patients receiving nephrotoxic medications. The trial will evaluate the efficacy of the re-purposed drug. The main questions it aims to answer are: \- whether cilastatin will prevent nephrotoxic AKI in hospitalized patients. Researchers will compare the drug cilastatin to a placebo (...
Summary: To compare cilastatin vs thiosulfatein renal protection in patients undergoing debulking surgery with intraoperative hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy with cisplatin
Related Latest Advances
Brand Information
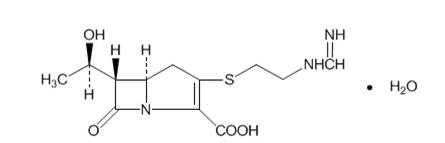
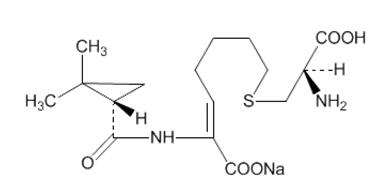
- 500 mg imipenem (anhydrous equivalent) and 500 mg cilastatin (free acid equivalent)
- Hypersensitivity Reactions
- Seizure Potential
- Increased Seizure Potential Due to Interaction with Valproic Acid
- Clostridioides difficile-Associated Diarrhea (CDAD) [see
- Development of Drug-Resistant Bacteria
- Advise patients that allergic reactions, including serious allergic reactions, could occur and that serious reactions require immediate treatment. They should report any previous hypersensitivity reactions to PRIMAXIN, other carbapenems, beta-lactams or other allergens.
- Counsel patients that antibacterial drugs including PRIMAXIN should only be used to treat bacterial infections. They do not treat viral infections (e.g., the common cold). When PRIMAXIN is prescribed to treat a bacterial infection, patients should be told that although it is common to feel better early in the course of therapy, the medication should be taken exactly as directed. Skipping doses or not completing the full course of therapy may (1) decrease the effectiveness of the immediate treatment and (2) increase the likelihood that bacteria will develop resistance and will not be treatable by PRIMAXIN or other antibacterial drugs in the future.
- Counsel patients to inform their physician:
- Advise patients that diarrhea is a common problem caused by antibacterial drugs and usually resolves when the drug is discontinued. Sometimes, frequent watery or bloody diarrhea may occur and may be a sign of a more serious intestinal infection. If severe watery or bloody diarrhea develops, patients should contact their healthcare provider.

NDC 0006-3516-59




